|
Flaviemys
The Manning River snapping turtle (''Myuchelys purvisi'') is a species of turtle in the family Chelidae. It is endemic Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ... to Australia. References External links * * The Aussie Manning River Turtle Ark Conservation Project Turtles of Australia Myuchelys Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Reptiles described in 1985 {{Turtle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myuchelys
The ''Myuchelys'' is a genus of turtles, the Australian saw-shelled turtles, in the family Chelidae and subfamily Chelodininae. They inhabit the headwaters and tributaries of rivers within their range and this led to the name ''Myuchelys'', which is formed from the Aboriginal word ''myuna'' meaning clear water and the Greek ''chelys'' meaning turtle. They have a short neck and the intergular scute completely separates the gular scutes. They have no alveolar ridge separating them from the snapping turtles of the genus ''Elseya''. Species The genus currently contains these cryptic small species of freshwater turtles, endemic to eastern and northern Australia: * '' Myuchelys bellii'', Namoi River snapping turtle Gray, 1844Gray, J. E. 1844. ''Catalogue of the Tortoises, Crocodiles and Amphibaenians in the Collection of the British Museum''. London. Edward Newman. 80pp. * '' Myuchelys georgesi'', Bellinger River snapping turtle Cann, 1997Cann, J. 1998a. Georges short-neck turtle. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelidae
Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.Georges, A. & Thomson, S. (2006). "Evolution and Zoogeography of Australian freshwater turtles". In: Merrick, J. R.; Archer, M.; Hickey, G. & Lee, M. (eds.) ''Evolution and Zoogeography of Australasian Vertebrates''. Sydney: Australia. Description Like all pleurodirous turtles, the chelids withdraw their necks sideways into their shells, differing from cryptodires that fold their necks in the vertical plane. They are all highly aquatic species with webbed feet and the capacity to stay submerged for long periods of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wells And Wellington Affair
The Wells and Wellington affair was a dispute about the publication of three papers in the ''Australian Journal of Herpetology'' in 1983 and 1985. The periodical was established in 1981 as a peer-reviewed scientific journal focusing on the study of amphibians and reptiles ( herpetology). Its first two issues were published under the editorship of Richard W. Wells, a first-year biology student at Australia's University of New England. Wells then ceased communicating with the journal's editorial board for two years before suddenly publishing three papers without peer review in the journal in 1983 and 1985. Coauthored by himself and high school teacher Cliff Ross Wellington, the papers reorganized the taxonomy of all of Australia's and New Zealand's amphibians and reptiles and proposed over 700 changes to the binomial nomenclature of the region's herpetofauna. Members of the herpetological community reacted strongly to the pair's actions and eventually brought a case to the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ex Errore
This is a list of terms and symbols used in scientific names for organisms, and in describing the names. For proper parts of the names themselves, see List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. Note that many of the abbreviations are used with or without a stop. Naming standards and taxonomic organizations and their codes and taxonomies * ICTV – International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses * ICSP – International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes ** formerly the ICSB – International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology ** publishes the ICNP – International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes *** formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC) * ICZN – International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature ** publishes ''ICZN'' the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature'' or "ICZN Code" * IBC – International Botanical Congress ** publishes ''ICN'' the ''International Code of Nomenclature f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
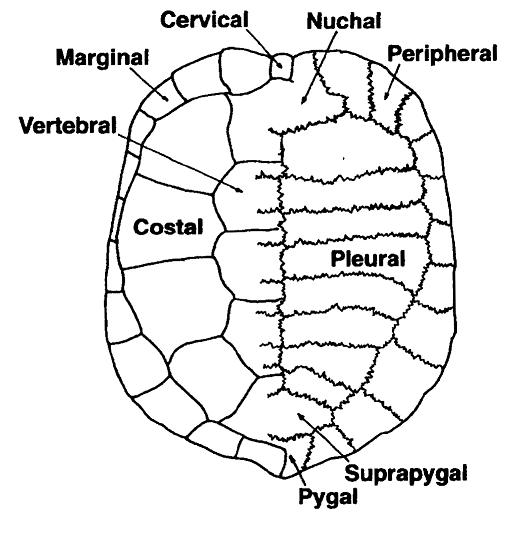
Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones develop from ribs that grow sideways and develop into broad flat plates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtles Of Australia
Turtles are an order (biology), order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other Amniote, amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed Turtle shell#Carapace, carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scale (anatomy), scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy Articles Created By Polbot
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification (general theory), classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. Among other things, a taxonomy can be used to organize and index knowledge (stored as documents, articles, videos, etc.), such as in the form of a library classification system, or a Taxonomy for search engines, search engine taxonomy, so that users can more easily find the information they are searching for. Many taxonomies are hierarchy, hierarchies (and thus, have an intrinsic tree structure), but not all are. Originally, taxonomy referred only to the categorisation of organisms or a particular categorisation of organisms. In a wider, more general sense, it may refer to a categorisation of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such a categorisation. Taxonomy organizes taxonomic uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
