|
Fescennia
Fescennia or Fescennium was an ancient city of Etruscan/ Faliscan origin, which is probably to be placed immediately to the north of the modern Corchiano, north west of Civita Castellana, in central Italy. The Via Amerina traverses it. At the Riserva S. Silvestro, walls exist. At Corchiano itself, however, similar walls may be traced, and the site is a strong and characteristic triangle between two deep ravines, with the third (west) side cut off by a ditch. Here, too, remains of two bridges may be seen, and several rich tombs have been excavated. The term ''Fescennine Verses'' refers to a certain kind of drinking song popular at festivals in ancient Rome and elsewhere. According to Festus, these songs were introduced from Fescennia, but others have thought that there is no reason to assume that any particular town was especially devoted to the use of such songs. Fescennia's warriors are also mentioned in Book VII of Virgil's Aeneid as following Messapus, the 'Steed Tamer' in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fescennine Verses
Fescennine Verses (Fescennina carmina), one of the earliest kinds of Italian poetry, subsequently developed into satire and Roman comic drama. History Originally sung at village harvest-home rejoicing, they made their way into the towns, and became the fashion at religious festivals and private gatherings, especially weddings, to which in later times they were practically restricted. They were usually in the Saturnine metre and took the form of a dialogue consisting of an interchange of extemporaneous raillery. Those who took part in them wore masks made of the bark of trees. At first harmless and good-humored, if somewhat coarse, these songs gradually outstripped the bounds of decency; malicious attacks were made upon both gods and men, and the matter became so serious that the law intervened and scurrilous personalities were forbidden by the Twelve Tables (Cicero, ''De re publica'', 4.10; see also Horace ''epist''. 2.1.139). Examples Specimens of the Fescennines used at weddings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falisci
Falisci ( grc, Φαλίσκοι, ''Phaliskoi'') is the ancient Roman exonym for an Italic tribe who lived in what is now northern Lazio, on the Etruscan side of the Tiber River. They spoke an Italic language, Faliscan, closely akin to Latin. Originally a sovereign state, politically and socially they supported the Etruscans, joining the Etruscan League. This conviction and affiliation led to their ultimate near destruction and total subjugation by Rome. Only one instance of their own endonym has been found to date: an inscription from Falerii Novi from the late 2nd century AD refers to the ''falesce quei in Sardinia sunt'', "the Faliscans who are in Sardinia", where ''falesce'' is the nominative plural case. An Etruscan inscription calls them the ''feluskeś''. The Latin cannot be far different from the original name. The -sc- suffix is "distinctive of the Italic ethnonyms". Geography The Falisci resided in a region called by the Romans the ''Ager Faliscus'', "Faliscan Countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
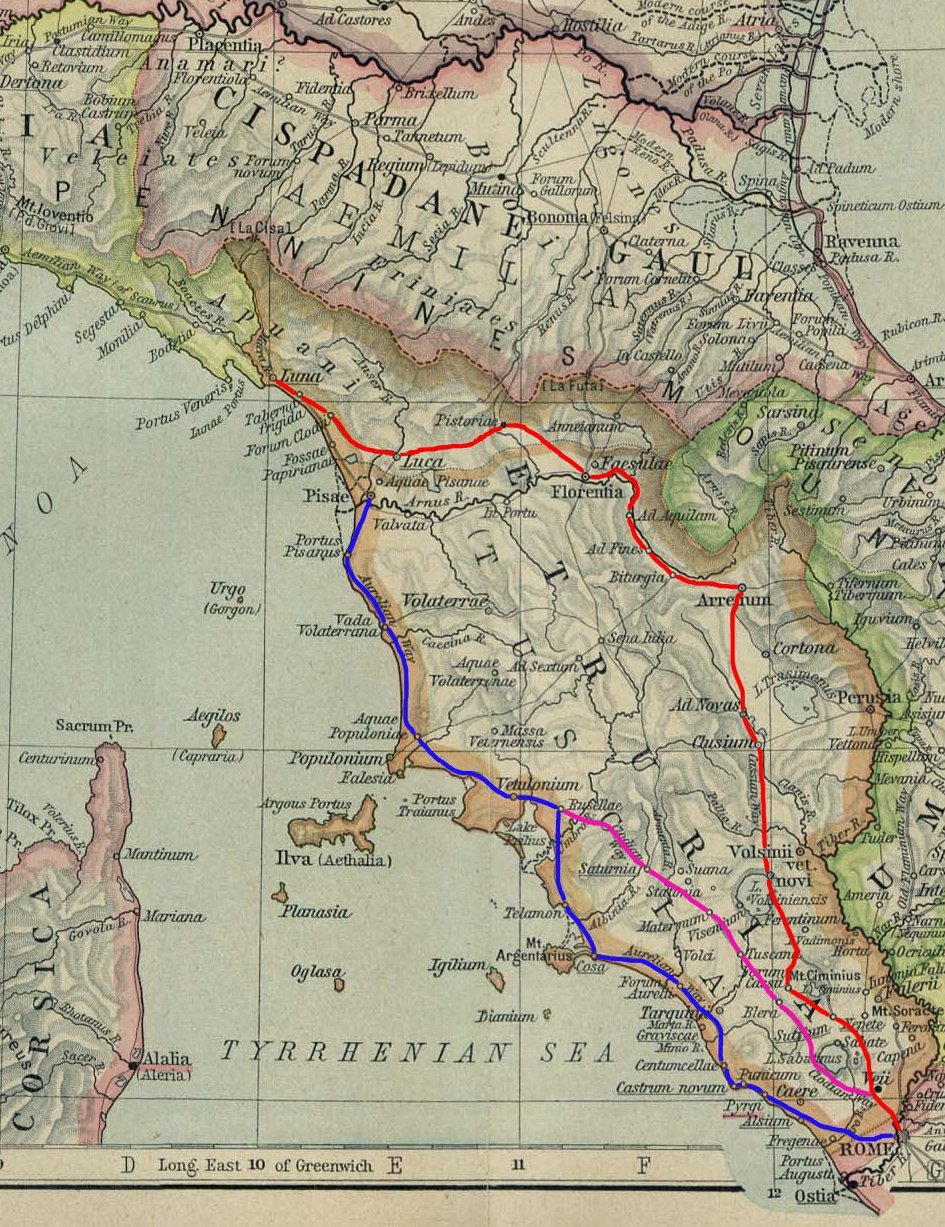
Etruscan Civilization
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region. Etruscan civilization endured until it was assimilated into Roman society. Assimilation began in the late 4thcenturyBC as a result of the Roman–Etruscan Wars; it accelerated with the grant of Roman citizenship in 90 BC, and became complete in 27 BC, when the Etr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corchiano
Corchiano is a town and ''comune ''in the province of Viterbo, Lazio, central Italy. It was an ancient settlement of the Faliscans and, in the Renaissance and later, a fief of the Farnese family. The local produce is hazelnuts and wine. Annual sagre include a live re-enactment of the birth of Jesus performed during Advent Advent is a Christian season of preparation for the Nativity of Christ at Christmas. It is the beginning of the liturgical year in Western Christianity. The name was adopted from Latin "coming; arrival", translating Greek ''parousia''. In .... In the summer, a park not far from the centre of the village stays open very late, and the town has several restaurants. References Cities and towns in Lazio Falisci Italic archaeological sites {{Lazio-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civita Castellana
Civita Castellana is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Viterbo, north of Rome. Mount Soracte lies about to the south-east. History Civita Castellana was settled during the Iron Age by the Italic people of the Falisci, who called it "Falerii." After the Faliscan defeat against the Romans, a new city was built by the latter, about away, and called "Falerii Novi." The abandoned city was repopulated beginning in the early Middle Ages, with the new name of Civita Castellana (roughly translated as "City of the Castle") mentioned first in 994. In the following centuries the city was a flourishing independent commune, often contended by the Pope and the Holy Roman Empire. Captured by Pope Paschal II at the beginning of the 12th century, the city was given as fief to the Savelli by Gregory XIV. Sixtus IV assigned the city to Cardinal Rodrigo Borgia, the future Pope Alexander VI, who started the construction of the Rocca ("Castle"), which was completed under Julius II. Civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Amerina
The ''Via Cassia'' ("way of Cassius") was an important Roman road striking out of the ''Via Flaminia'' near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii, traversed Etruria. The ''Via Cassia'' passed through Baccanae, Sutrium, Volsinii, Clusium, Arretium, Florentia, Pistoria, and Luca, joining the ''Via Aurelia'' at Luna. The ''Via Cassia'' intersected other important roads. At mile 11 the ''Via Clodia'' diverged north-north-west. At Sette Vene, another road, probably the ''Via Annia'', branched off to Falerii. In Sutrium, the ''Via Ciminia'' split off and later rejoined. The date of its construction is uncertain: it cannot have been earlier than 187 BC, when the consul Gaius Flaminius constructed a road from Bononia to Arretium, which must have coincided with a portion of the later Via Cassia. It is not mentioned by any ancient authorities before the time of Cicero, who in 45 BC speaks of the existence of three roads from Rome to Muti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festus (historian)
Festus (), whose name also appears in the manuscripts of his work as Rufus Festus, Ruffus Festus, Sextus Festus, Sextus Rufus, and Sextus, was a Late Roman historian and proconsul of Asia whose epitome ''Breviarium rerum gestarum populi Romani'' ("Summary of the history of Rome") was commissioned by the emperor Valens in preparation for his war against Persia. It was completed about AD 370. The ''Breviarium'' covers the entire history of the Roman state from the foundation of the City until AD 364. The book consists of 30 chapters treating events in Roman history in terse overview, mainly focused on military and political conflicts. It is estimated as a work of very low quality. Festus of Tridentum, magister memoriae (secretary) to Valens and notoriously severe proconsul of the province of Asia, where he was sent to punish those implicated in the conspiracy of Theodorus. The work itself (Breviarium rerum gestarum populi Romani) is divided into two parts, one geographical, the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the ''Eclogues'' (or ''Bucolics''), the ''Georgics'', and the epic ''Aeneid''. A number of minor poems, collected in the ''Appendix Vergiliana'', were attributed to him in ancient times, but modern scholars consider his authorship of these poems as dubious. Virgil's work has had wide and deep influence on Western literature, most notably Dante's ''Divine Comedy'', in which Virgil appears as the author's guide through Hell and Purgatory. Virgil has been traditionally ranked as one of Rome's greatest poets. His ''Aeneid'' is also considered a national epic of ancient Rome, a title held since composition. Life and works Birth and biographical tradition Virgil's biographical tradition is thought to depend on a lost biography by the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin Epic poetry, epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Troy, Trojan who fled the Trojan_War#Sack_of_Troy, fall of Troy and travelled to Italy, where he became the ancestor of the Ancient Rome, Romans. It comprises 9,896 lines in dactylic hexameter. The first six of the poem's twelve books tell the story of Aeneas' wanderings from Troy to Italy, and the poem's second half tells of the Trojans' ultimately victorious war upon the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins, under whose name Aeneas and his Trojan followers are destined to be subsumed. The hero Aeneas was already known to Greco-Roman legend and myth, having been a character in the ''Iliad''. Virgil took the disconnected tales of Aeneas' wanderings, his vague association with the foundation of Ancient Rome, Rome and his description as a personage of no fixed characteristics other than a scrupulous ''pietas'', and fashioned th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messapus
Messapus, (Greek: Μέσσαπος, ''Messapos'') a character in Virgil's ''Aeneid'', appears in Books VII to XII of the Latin epic poem. He was a son of Neptune, a famous tamer of horses, and king of Etruria, known for being one "whom no one can fell by fire or steel" (Mandelbaum, VII.911-912). Narrative Although accustomed to peace, in Book VII Messapus joins forces with Turnus in his battle against Aeneas and the Trojans. Book VIII lists him as one of Turnus' chief captains, along with Ufens and Mezentius. In Book IX, which recounts the nighttime raid by Nisus and Euryalus on the Rutulian camp, the battle helmet of Messapus is taken by Euryalus. Light reflected off the stolen helmet, betraying Euryalus to his enemies and leading not only to his own death, but also that of Nisus. Messapus fought in battle in Book X, killing Clonius, and Ericetes son of Lycaon. In Book XI, he led a cavalry charge alongside Coras and Camilla. Book XII again lists Messapus as one of the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turnus
Turnus ( grc, Τυρρηνός, Tyrrhênós) was the legendary King of the Rutuli in Roman history, and the chief antagonist of the hero Aeneas in Virgil's ''Aeneid''. According to the ''Aeneid'', Turnus is the son of Daunus and the nymph Venilia and is brother of the nymph Juturna. Historical tradition While there is a limited amount of information in historical sources about Turnus, some key details about Turnus and the Rutuli differ significantly from the account in the Aeneid. The only source predating the Aeneid is Marcus Portius Cato's Origines. Turnus is also mentioned by Livy in his ''Ab Urbe Condita'' and by Dionysius of Halicarnassus in his (''Rômaïkê Archaiologia'', "''Roman Antiquities''"), both of which come later than the ''Aeneid''. Turnus is mentioned in the Book of Jasher, along with Angeas of Africa. In all of these historical sources, Turnus' heritage is unclear. Dionysius calls him ''Tyrrhenus'', which means "Etruscan", while other sources suggest a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |