|
Favites Complanata
''Favites complanata'' is a species of stony coral in the family Merulinidae, sometimes known as the larger star coral. It is native to the Indo-Pacific region and its range extends from the Red Sea and Indian Ocean to the western and central Pacific Ocean. This is an uncommon species of coral and seems to be decreasing in abundance, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being "near threatened". Description A colony of ''Favites complanata'' forms a solid dome or mound. The corallites (stony cups in which the polyps sit) are large and somewhat angular, with thick, rounded walls between them. The calyces are in diameter. The septa (stony ridges inside the corallites) are in two whorls and each has four or five teeth. The paliform lobes are distinct on the first whorl of septa and the columella at the centre of the corallite is large. The stony ridges, now known as costae, continue between the corallites and often form three-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. Ehrenberg was an evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Berlin and became a friend of the famous explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, where he made a special study of the corals. Subsequently, parts of Syria, Arabia and Abyss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa (coral)
In corals, a costa (plural costae) is one of the vertical plates lying outside the corallite wall, a continuation of a septum (plural septa) which lies inside the wall. The costae may continue to the edge of the colony and in solitary species, such as those in the family Fungiidae The Fungiidae () are a family of Cnidaria, commonly known as mushroom corals or plate corals. The family contains thirteen extant genera. They range from solitary corals to colonial species. Some genera such as '' Cycloseris'' and ''Fungia'' ar ..., refers to the ridges on the underside of the coral. References {{reflist Cnidarian anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients. Bleaching occurs when coral polyps expel the zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates that are commonly referred to as algae) that live inside their tissue, causing the coral to turn white. The zooxanthellae are photosynthetic, and as the water temperature rises, they begin to produce reactive oxygen species. This is toxic to the coral, so the coral expels the zooxanthellae. Since the zooxanthellae produce the majority of coral colouration, the coral tissue becomes transparent, revealing the coral skeleton made of calcium carbonate. Most bleached corals appear bright white, but some are blue, yellow, or pink due to pigment proteins in the coral. The leading cause of coral bleaching is rising ocean temperature due to climate change. A temperature about 1 °C (or 2 °F) above average can cause bleaching. According to the United Nations Environment Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, ''Oodinium'' and ''Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
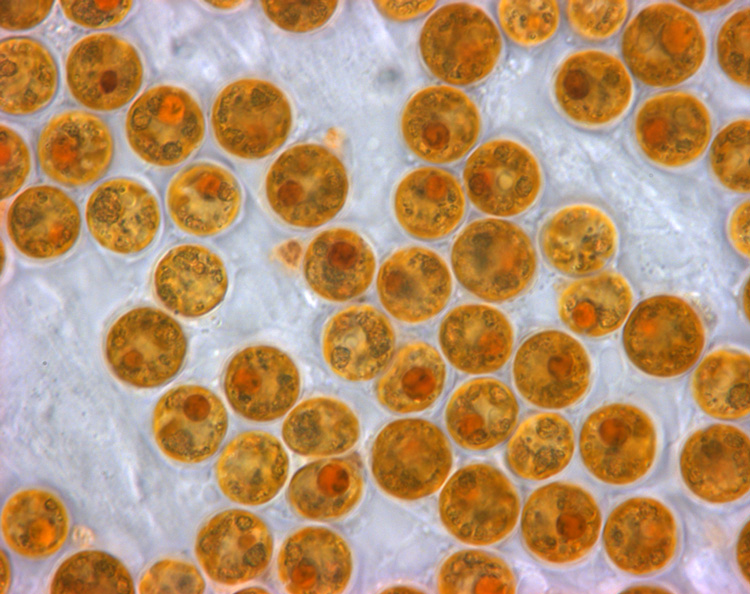
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
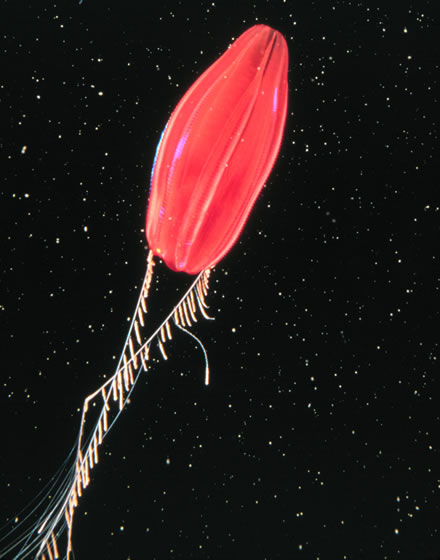
Tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions. A tentacle is similar to a cirrus, but a cirrus is an organ that usually lacks the tentacle's strength, size, flexibility, or sensitivity. A nautilus has cirri, but a squid has tentacles. Invertebrates Molluscs Many molluscs have tentacles of one form or another. The most familiar are those of the pulmonate land snails, which usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: when extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum (coral)
In coral Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and sec ...s, a septum (plural septa) is one of the radiating vertical plates lying within the corallite wall. Outside the corallite wall these plates are known as costae (singular costa). The septa may be thick, thin or vary in size. They may have teeth which range from needle-like to blade-like and are often characteristic of different genera. References {{reflist Cnidarian anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyp (zoology)
A polyp in zoology is one of two forms found in the phylum Cnidaria, the other being the medusa. Polyps are roughly cylindrical in shape and elongated at the axis of the vase-shaped body. In solitary polyps, the aboral (opposite to oral) end is attached to the substrate by means of a disc-like holdfast called a pedal disc, while in colonies of polyps it is connected to other polyps, either directly or indirectly. The oral end contains the mouth, and is surrounded by a circlet of tentacles. Classes In the class Anthozoa, comprising the sea anemones and corals, the individual is always a polyp; in the class Hydrozoa, however, the individual may be either a polyp or a medusa, with most species undergoing a life cycle with both a polyp stage and a medusa stage. In class Scyphozoa, the medusa stage is dominant, and the polyp stage may or may not be present, depending on the family. In those scyphozoans that have the larval planula metamorphose into a polyp, the polyp, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |