|
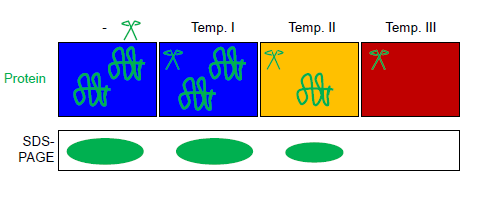
Fast Parallel Proteolysis (FASTpp)
Fast parallel proteolysis (FASTpp) is a method to determine the thermostability of proteins by measuring which fraction of protein resists rapid proteolytic digestion. History and background Proteolysis is widely used in biochemistry and cell biology to probe protein structure. In "limited trypsin proteolysis", low amounts of protease digest both folded and unfolded protein but at largely different rates: unstructured proteins are cut more rapidly, while structured proteins are cut at a slower rate (sometimes by orders of magnitude). Recently, several other assays of protein stability based on proteolysis have been proposed, exploiting other proteases with high specificity for cleaving unfolded proteins. These include Pulse Proteolysis, Proteolytic Scanning Calorimetry and FASTpp. How it works FASTpp measures the quantity of protein that resists digestion under various conditions. To this end, a thermostable protease is used, which cleaves specifically at exposed hydrophobi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand Binding Assay
A ligand binding assay (LBA) is an assay, or an analytic procedure, which relies on the binding of ligand molecules to receptors, antibodies or other macromolecules. A detection method is used to determine the presence and extent of the ligand-receptor complexes formed, and this is usually determined electrochemically or through a fluorescence detection method. This type of analytic test can be used to test for the presence of target molecules in a sample that are known to bind to the receptor. There are numerous types of ligand binding assays, both radioactive and non-radioactive.Joseph R. Lakowicz. (1991) Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Biochemical applications. As such, ligand binding assays are a superset of radiobinding assays, which are the conceptual inverse of radioimmunoassays (RIA). Some newer types are called "mix-and-measure" assays because they do not require separation of bound from unbound ligand. Ligand binding assays are used primarily in pharmacology to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology. The term ''biophysics'' was originally introduced by Karl Pearson in 1892. Roland Glaser. Biophysics: An Introduction'. Springer; 23 April 2012. . The term ''biophysics'' is also regularly used in academia to indicate the study of the physical quantities (e.g. electric current, temperature, stress, entropy) in biological systems. Other biological sciences also perform research on the biophysical properties of living organisms including molecular biology, cell biology, chemical biology, and biochemistry. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In addition, other kinds of proteins include antibodies that protect an organism from infection, and hormones that send important signals throughout the body. The proteome is the entire set of proteins produced or modified by an organism or system. Proteomics enables the identification of ever-increasing numbers of proteins. This varies with time and distinct requirements, or stresses, that a cell or organism undergoes. Proteomics is an interdisciplinary domain that has benefited greatly from the genetic information of various genome projects, including the Human Genome Project. It covers the exploration of proteomes from the overall level of protein composition, structure, and activity, and is an important component of functional genomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology Techniques
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting these long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyzes proteins. Trypsin is formed in the small intestine when its proenzyme form, the trypsinogen produced by the pancreas, is activated. Trypsin cuts peptide chains mainly at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine. It is used for numerous biotechnological processes. The process is commonly referred to as trypsin proteolysis or trypsinization, and proteins that have been digested/treated with trypsin are said to have been trypsinized. Trypsin was discovered in 1876 by Wilhelm Kühne and was named from the Ancient Greek word for rubbing since it was first isolated by rubbing the pancreas with glycerin. Function In the duodenum, trypsin catalyzes the hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermolysin
Thermolysin (, ''Bacillus thermoproteolyticus neutral proteinase'', ''thermoase'', ''thermoase Y10'', ''TLN'') is a thermostable neutral metalloproteinase enzyme produced by the Gram-positive bacteria ''Bacillus thermoproteolyticus''. It requires one zinc ion for enzyme activity and four calcium ions for structural stability. Thermolysin specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds containing hydrophobic amino acids. However thermolysin is also widely used for peptide bond formation through the reverse reaction of hydrolysis. Thermolysin is the most stable member of a family of metalloproteinases produced by various ''Bacillus'' species. These enzymes are also termed 'neutral' proteinases or thermolysin -like proteinases (TLPs). Synthesis Like all bacterial extracellular proteases thermolysin is first synthesised by the bacterium as a pre-proenzyme. Thermolysin is synthesized as a pre-proenzyme consisting of a signal peptide 28 amino acids long, a pro-peptide 204 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula H2N(CH2CO2H)2sub>2. This white, water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-soluble complexes even at neutral pH. It is thus used to dissolve Fe- and Ca-containing scale as well as to deliver iron ions under conditions where its oxides are insoluble. EDTA is available as several salts, notably disodium EDTA, sodium calcium edetate, and tetrasodium EDTA, but these all function similarly. Uses Textile industry In industry, EDTA is mainly used to sequester (bind or confine) metal ions in aqueous solution. In the textile industry, it prevents metal ion impurities from modifying colours of dyed products. In the pulp and paper industry, EDTA inhibits the ability of metal ions, especially Mn2+, from catalysing the disproportionation of hydrogen peroxide, which is used in chlorine-free bleaching. In a similar manner, EDTA is added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
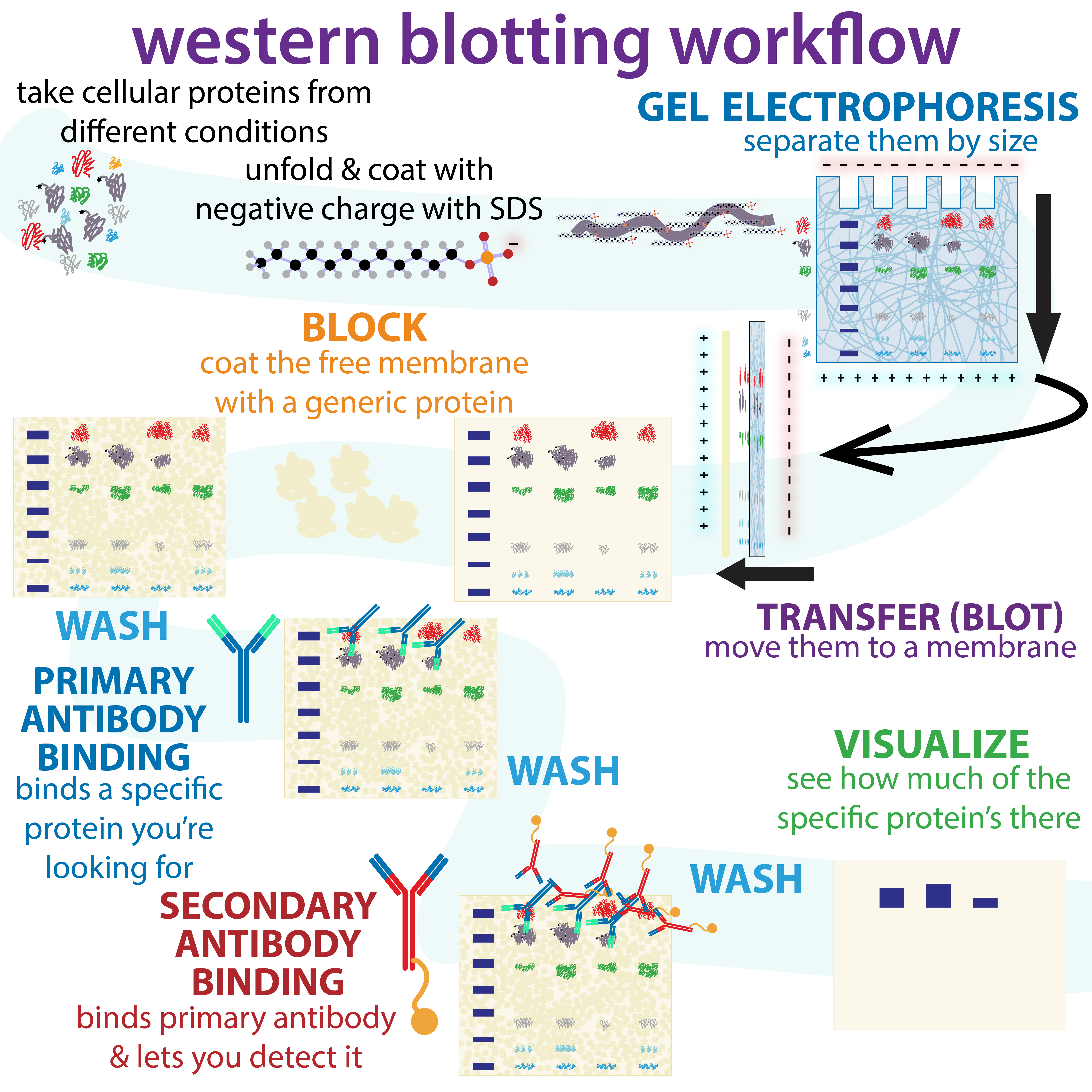
Western Blot
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missense Mutations
In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution. Substitution of protein from DNA mutations Missense mutation refers to a change in one amino acid in a protein, arising from a point mutation in a single nucleotide. Missense mutation is a type of nonsynonymous substitution in a DNA sequence. Two other types of nonsynonymous substitution are the nonsense mutations, in which a codon is changed to a premature stop codon that results in truncation of the resulting protein, and the nonstop mutations, in which a stop codon erasement results in a longer, nonfunctional protein. Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, and such mutations are responsible for human diseases such as Epidermolysis bullosa, sickle-cell disease, SOD1 mediated ALS, and a substantial number of cancers. In the most common variant of sickle-cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)