|
FXN (gene)
Frataxin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FXN gene. It is located in the mitochondrion and Frataxin mRNA is mostly expressed in tissues with a high metabolic rate. The function of frataxin is not clear but it is involved in assembly of iron-sulfur clusters. It has been proposed to act as either an iron chaperone or an iron storage protein. Reduced expression of frataxin is the cause of Friedreich's ataxia. Structure X-ray crystallography has shown that human frataxin consists of a β-sheet that supports a pair of parallel α-helices, forming a compact αβ sandwich. Frataxin homologues in other species are similar, sharing the same core structure. However, the frataxin tail sequences, extending from the end of one helix, diverge in sequence and differ in length. Human frataxin has a longer tail sequence than frataxin found in bacteria or yeast. It is hypothesized that the purpose of the tail is to stabilize the protein. Like most mitochondrial proteins, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate (mathematics)
In mathematics, a rate is the ratio between two related quantities in different units. If the denominator of the ratio is expressed as a single unit of one of these quantities, and if it is assumed that this quantity can be changed systematically (i.e., is an independent variable), then the numerator of the ratio expresses the corresponding ''rate of change'' in the other (dependent) variable. One common type of rate is "per unit of time", such as speed, heart rate and flux. Ratios that have a non-time denominator include exchange rates, literacy rates, and electric field (in volts per meter). In describing the units of a rate, the word "per" is used to separate the units of the two measurements used to calculate the rate (for example a heart rate is expressed "beats per minute"). A rate defined using two numbers of the same units (such as tax rates) or counts (such as literacy rate) will result in a dimensionless quantity, which can be expressed as a percentage (for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small bits of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression (e.g. microRNA), or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules. Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. The length of the oligonucleotide is usually denoted by " -mer" (from Greek ''meros'', "part"). For example, an oligonucleotide of six nucleotides (nt) is a hexamer, while one of 25 nt wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
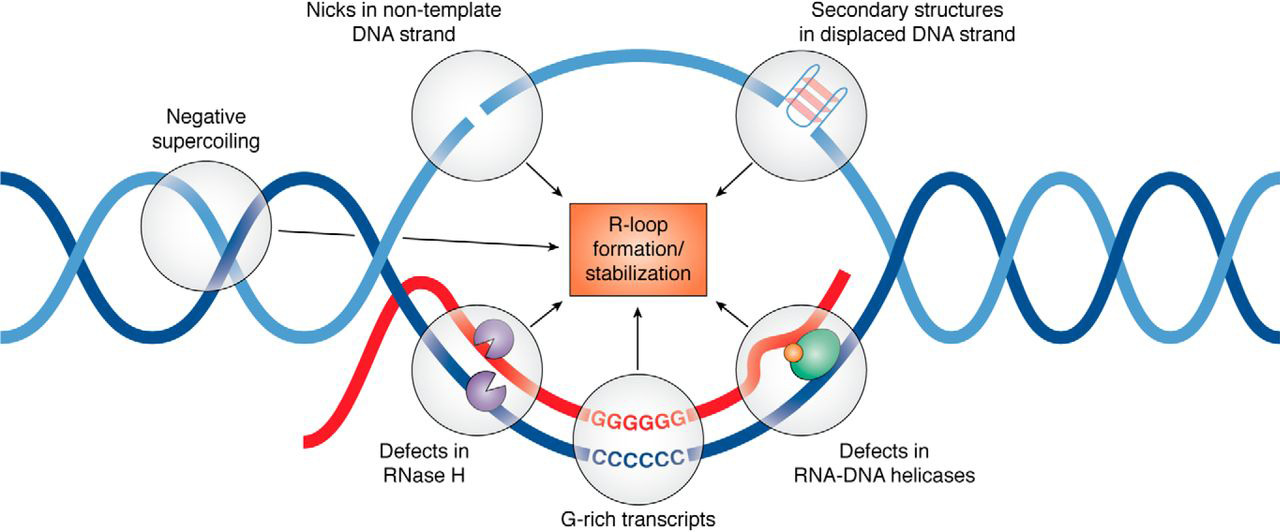
R-loop
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA:RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. The term "R-loop" was given to reflect the similarity of these structures to D-loops; the "R" in this case represents the involvement of an RNA moiety. In the laboratory, R-loops may also be created by the hybridization of mature mRNA with double-stranded DNA under conditions favoring the formation of a DNA-RNA hybrid; in this case, the intron regions (which have been spliced out of the mRNA) form single-stranded DNA loops, as they cannot hybridize with complementary sequence in the mRNA. History R-looping was first described in 1976. Independent R-looping studies from the laboratories of Richard J. Roberts and Phillip A. Sharp showed that protein coding adenovirus genes contained DNA sequences that were not present in the mature mRNA. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |