|
Empada (Guinea-Bissau)
Empada is a town and a sector with the same name in the Quinara region of Guinea-Bissau. The city is located on the Buba river, the sector borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Originally, residents settled on the site of the town because of the presence of a natural spring, locally called "sanjuna". The Portuguese government tiled the well in 1946 and named it ''Fonte Frondosa'' (the leafy fountain). The city has 2267 inhabitants; the sector has 17,517 inhabitants (census 2009). Children under the age of five constituted 22% of the population. Illiteracy is high: 11% of men and 23% of women were unable to read and write in 2009. The inhabitants are mainly of the Beafada population with significant minorities of Mandinka and some Balanta and Fula. The city of Empada has two parts with a subdivision into three districts (''bairros''), each with a village elder. The sector Empada includes 85 towns, mainly rural villages (''tabancas''). The main locations are (population in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
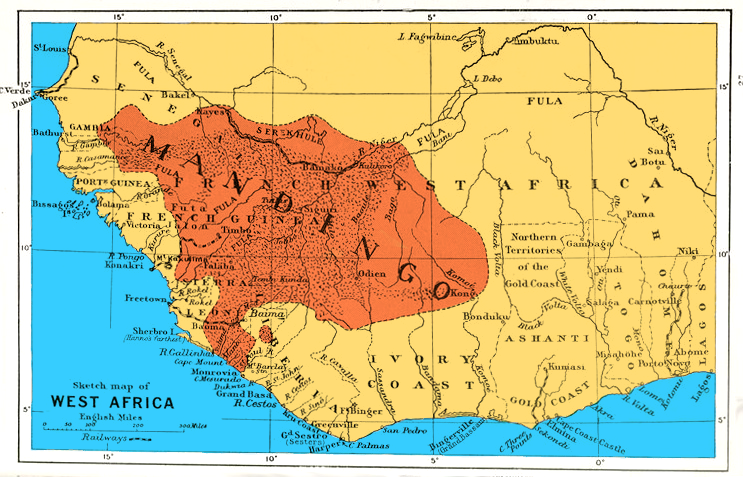
Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ), is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 1,726,000. It borders Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south-east. Guinea-Bissau was once part of the kingdom of Kaabu, as well as part of the Mali Empire. Parts of this kingdom persisted until the 18th century, while a few others were under some rule by the Portuguese Empire since the 16th century. In the 19th century, it was colonised as Portuguese Guinea. Portuguese control was restricted and weak until the early 20th century with the pacification campaigns, these campaigns solidified Portuguese sovereignty in the area. The final Portuguese victory over the remaining bastion of mainland resistance, the Papel ruled Kingdom of Bissau in 1915 by the Portu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau is divided into 8 regions (singular: ''região'', plural: ''regiões'') and 1 autonomous sector (''sector autónomo''). The regions are subdivided into a total of 37 sectors (singular: ''setor'', plural: ''setores'') ; which are further subdivided into smaller groups called ''sections'' (singular: ''secção'', plural: ''secções''); which are further subdivided into populated places (i.e.: towns, villages, localities, settlements, communities, etc.). Here are the following listed below: Regions The regions can also be grouped into 3 provinces: * ''Leste'' (East): Bafatá, Gabu * ''Norte'' (North): Biombo, Cacheu, Oio * ''Sul'' (South): Bolama, Quinara, Tombali See also *List of regions of Guinea-Bissau by Human Development Index This is a list of regions of Guinea-Bissau by Human Development Index as of 2019 with data for the year 2019. See also *List of countries by Human Development Index References {{Subnational entities by Human Development Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Savanna Climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of precipitation and also less than 100-\left (\frac \right)mm of precipitation. This latter fact is in a direct contrast to a tropical monsoon climate, whose driest month sees less than of precipitation but has ''more'' than 100-\left (\frac \right) of precipitation. In essence, a tropical savanna climate tends to either see less overall rainfall than a tropical monsoon climate or have more pronounced dry season(s). In tropical savanna climates, the dry season can become severe, and often drought conditions prevail during the course of the year. Tropical savanna climates often feature tree-studded grasslands due to its dryness, rather than thick jungle. It is this widespread occurrence of tall, coarse grass (called savanna) which has led to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sectors Of Guinea-Bissau
There are 39 sectors of Guinea-Bissau (singular: ''setor'', plural: ''setores'') which subdivide the regions. The sectors are further subdivided into smaller groups called ''sections'' (singular: ''secção'', plural: ''secções''); which are further subdivided into populated places (i.e.: towns, villages, localities, settlements, communities, etc.). Here are the following listed below, by region: Eastern Guinea-Bissau Bafata Region * Bafata * Bambadinca * Contuboel * Galomaro * Gamamundo * Xitole Gabú Region * Boe * Gabú * Piche * Pirada * Sonaco Northern Guinea-Bissau Biombo Region * Prabis * Quinhamel * Safim Cacheu Region * Bigene * Bula * Cacheu * Caio * Canghungo * São Domingos Oio Region * Bissorã * Farim * Mansaba * Mansôa * Nhacra Bissau Region * Bissau (autonomous sector) Southern Guinea-Bissau Bolama Region * Bolama * Bubaque * Caravela * Uno Quinara Region * Buba * Empada * Fulacunda * Tite Tombali Region * Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinara Region
Quinara is a region in central Guinea-Bissau and its capital is Fulacunda. There has not been any local administration since the civil war of 1998-99 and all the social services are done by organs of civil society and other government agencies. It is a coastal region covered with Mangrove swamps, rain forest and tangled forest and receives an annual rainfall of more than . As of 2009, the total population of the region was 60,777, with the urban population being 12,302 and rural being 48,475. The sex ratio of the region is 94 females for every hundred males. As of 2009, the net activity rate was 45.54 per cent, proportion of employed labour force was 33.16 per cent, proportion of labour force was 76.09 and the proportion of potentially active population was 33.16 per cent. The absolute poverty rate, people earning less than $2 a day, in the region stood at 79.6 per cent, with a regional contribution of 18 per cent to the national poverty totals. Geography Quinara is a low-lying c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Grande De Buba
The Rio Grande de Buba, also called the Rio Buba, Rio Grande, and Grande River, is an estuary of West Africa that is entirely contained within Guinea-Bissau, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean. It is about in total length and is wide at its mouth. It is an environment unique in West Africa, which has no other example of an arm of the sea extending so far inland, with a downstream depth of around , and its fauna is extremely rich and diversified. The Grande was commercially important in the late 16th century, but this soon changed: "Biafada and Mandinka traders along the Geba River The Geba is a river of West Africa that rises in the northernmost area of Guinea in the Fouta Djallon highlands, passes through southern Senegal, and reaches the Atlantic Ocean in Guinea-Bissau. It is about in total length. In Senegal, the r ... and the Papel of Bissau greatly benefited from the precipitous decline of Grande River trade as Bijago raiders increasingly disrupted Biafada an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biafada People
The Biafada people is an ethnic group of Guinea-Bissau, Senegal and Gambia. This group is often considered as a subgroup of the Tenda people. They are also known as Biafara, Beafada, Biafar, Bidyola, Dfola, Dyola, Fada, and Yola. Demography In Guinea Bissau, the Biafada are divided into four groups. A small group lives on the north bank of the Geba River and speaks the Gool dialect. Two large groups reside in Quinara Region, the southwestern part of the country, and they speak the Bubwas and Guinala dialects. The fourth group live in the southern province of Tombali, on the border with Guinea Conakry, and speaks the dialect Bagandada.The Joshuaproject: Biafada people Retrieved March 5, 2013, to 02: 18 pm. History They were once grouped into three kingdoms: Biguda, Guinal ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Senegal to Iv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanta People
The Balanta (Guinea-Bissau Creole and Portuguese: ''balanta''; ; lit. “those who resist” in Mandinka) are an ethnic group found in Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Senegal, Cape Verde and The Gambia. They are the largest ethnic group of Guinea-Bissau, representing more than one-quarter of the population. Despite their numbers, they have remained outside the colonial and postcolonial state because of their social organisation. The Balanta can be divided into six clans: Nhacra, Ganja (Mane), Naga, Patch, Sofa and Kentohe. The largest of which are the Balanta Kentohe. Archaeologists believe that the people who became the Balanta migrated to present-day Guinea-Bissau in small groups between the 10th and 14th centuries CE. During the 19th century, they spread throughout the area that is now Guinea-Bissau and southern Senegal in order to resist the expansion of the Kaabu kingdom. Today, the Balanta are found in the modern-day countries of Senegal, Cape Verde and Gambia but mostly reside in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 12 to 13 million – are pastoralism, pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)