|
Exertion
Exertion is the physical or perceived use of energy.Newton's Third Law, Elert, Glenn. “Forces.” ''Viscosity – The Physics Hypertextbook'', physics.info/newton-first/. Exertion traditionally connotes a strenuous or costly ''effort'', resulting in generation of force, initiation of motion, or in the performance of work. It often relates to muscular activity and can be quantified, empirically and by measurable metabolic response. Physical In physics, ''exertion'' is the expenditure of energy against, or inductive of, inertia as described by Isaac Newton's third law of motion. In physics, force exerted equivocates work done. The ability to do work can be either positive or negative depending on the direction of exertion relative to gravity. For example, a force exerted upwards, like lifting an object, creates positive work done on that object. Exertion often results in force generated, a contributing dynamic of general motion. In mechanics it describes the use of force against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating Of Perceived Exertion
In sports, health and particularly exercise testing, the rating of perceived exertion (RPE), as measured by the ''Borg rating of perceived exertion scale'' (RPE scale), is a frequently used quantitative measure of perceived exertion during physical activity. In medicine this is used to document the patient's exertion during a test for the severity of diseases, and sports coaches use the scale to assess the intensity of training and competition as well as endurance. The original scale introduced by Gunnar Borg rated exertion on a scale of 6-20. Borg then constructed a newer category (C) ratio (R) scale, the Borg CR10 scale, rated on a scale from 1-10. This is especially used in clinical diagnosis and severity assessment of breathlessness and dyspnea, chest pain, angina and musculo-skeletal pain. The CR-10 scale is best suited when there is an overriding sensation arising either from a specific area of the body rather than overall exertion, for example, muscle pain, ache or fatigue in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
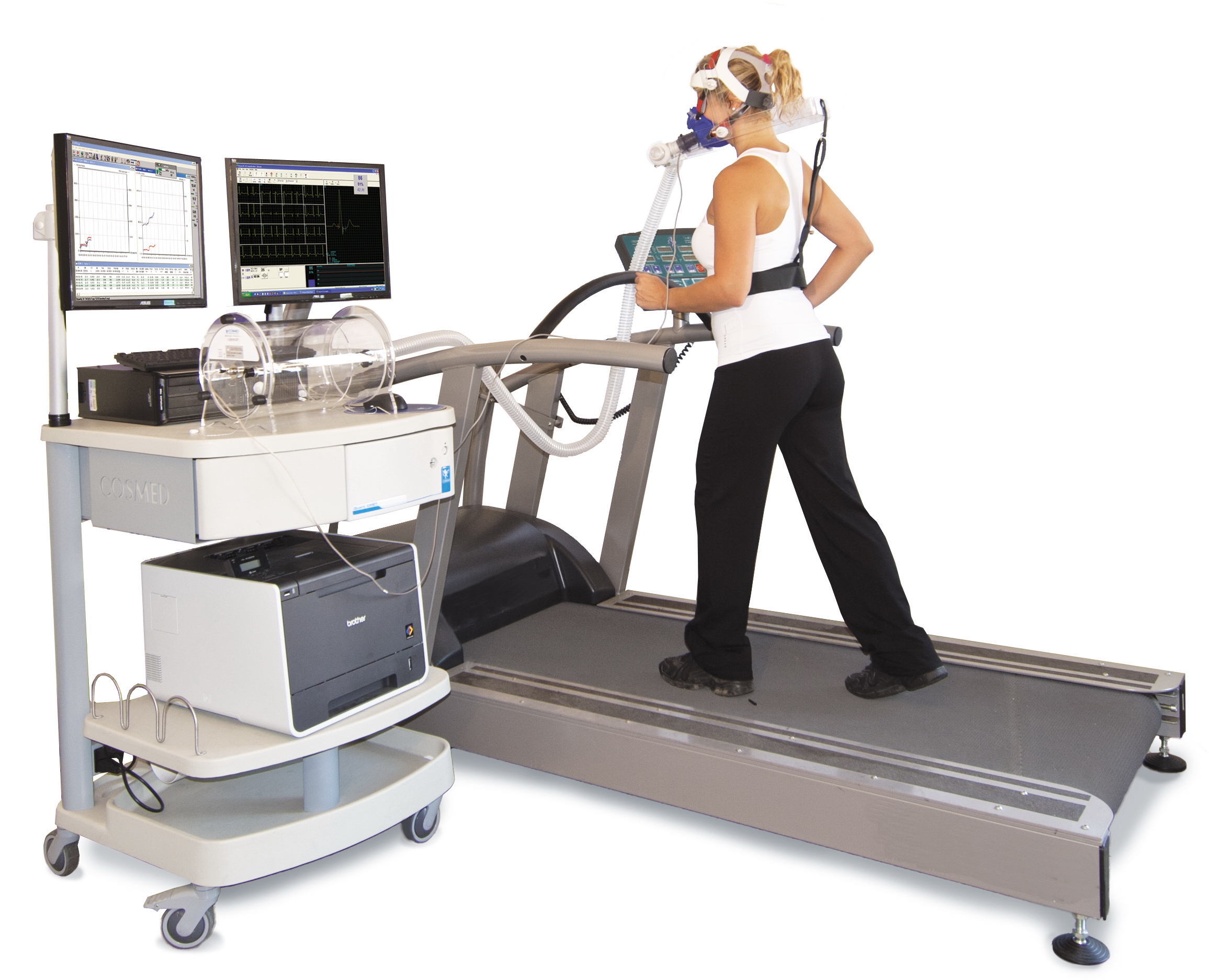
Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise professionals and utilise education, lifestyle intervention and specific forms of exercise to rehabilitate and manage acute and chronic injuries and conditions. Understanding the effect of exercise involves studying specific changes in muscular, cardiovascular, and neurohumoral systems that lead to changes in functional capacity and strength due to endurance training or strength training. The effect of training on the body has been defined as the reaction to the adaptive responses of the body arising from exercise or as "an elevation of metabolism produced by exercise". Exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. History British phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactate Dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells. LDH catalyzes the conversion of lactate to pyruvate and back, as it converts NAD+ to NADH and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another. LDH exists in four distinct enzyme classes. This article is specifically about the NAD(P)-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase. Other LDHs act on D-lactate and/or are dependent on cytochrome c: D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) and L-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome). LDH is expressed extensively in body tissues, such as blood cells and heart muscle. Because it is released during tissue damage, it is a marker of common injuries and disease such as heart failure. Reaction Lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and lactate with concomitant interconversion of NADH and NAD+. It converts pyruvate, the final product of glycolysis, to lactate when oxygen is absent or in short supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Work
In physics, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force strength and the distance traveled. A force is said to do ''positive work'' if when applied it has a component in the direction of the displacement of the point of application. A force does ''negative work'' if it has a component opposite to the direction of the displacement at the point of application of the force. For example, when a ball is held above the ground and then dropped, the work done by the gravitational force on the ball as it falls is positive, and is equal to the weight of the ball (a force) multiplied by the distance to the ground (a displacement). If the ball is thrown upwards, the work done by its weight is negative, and is equal to the weight multiplied by the displacement in the upwards direction. When the force is consta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borg Scale
The Borg are an alien group that appear as recurring antagonists in the '' Star Trek'' fictional universe. The Borg are cybernetic organisms (cyborgs) linked in a hive mind called "the Collective". The Borg co-opt the technology and knowledge of other alien species to the Collective through the process of " assimilation": forcibly transforming individual beings into "drones" by injecting nanoprobes into their bodies and surgically augmenting them with cybernetic components. The Borg's ultimate goal is "achieving perfection".Star Trek: First Contact Aside from being recurring antagonists in the '' Next Generation'' television series, they are depicted as the main threat in the film '' Star Trek: First Contact''. In addition, they played major roles in the '' Voyager'' and '' Picard'' series. ''The Borg'' have become a symbol in popular culture for any juggernaut against which "resistance is futile", a common phrase uttered by the Borg. Concept The Borg represented a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone. It is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is produced in other tissues in lower quantities. It is released with a diurnal cycle and its release is increased in response to stress and low blood-glucose concentration. It functions to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis, to suppress the immune system, and to aid in the metabolism of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. It also decreases bone formation. Many of these functions are carried out by cortisol binding to glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid receptors inside the cell, which then bind to DNA to impact gene expression. Health effects Metabolic response Metabolism of glucose In general, cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis (the synthesis of 'new' glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, which occurs mainly in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sport Psychology
Sport psychology was defined by the European Federation of Sport in 1996, as the study of the psychological basis, processes, and effects of sport. Otherwise, sport is considered as any physical activity where the individuals engage for competition and health. Sport psychology is recognized as an interdisciplinary science that draws on knowledge from many related fields including biomechanics, physiology, kinesiology and psychology. It involves the study of how psychological factors affect performance and how participation in sport and exercise affect psychological and physical factors. Sport psychologists teach cognitive and behavioral strategies to athletes in order to improve their experience and performance in sports. In addition to instruction and training of psychological skills for performance improvement, applied sport psychology may include work with athletes, coaches, and parents regarding injury, rehabilitation, communication, team building, and career transitions. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness. It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic skills, weight loss or maintenance, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many individuals choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, the amount of recommended exercise depends upon the goal, the type of exercise, and the age of the person. Even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the human body: * Aerobic exercise is any physical activity that uses large muscle groups and causes the body to use more oxygen than it would while resting. The goal of aerobic exercise is to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humility And Struggle
Humility is the quality of being humble. Dictionary definitions accentuate humility as a low self-regard and sense of unworthiness. In a religious context humility can mean a recognition of self in relation to a deity (i.e. God), and subsequent submission to that deity as a member of that religion.Humility, The Catholic encyclopedia, Herbermann et al. (Editors), Vol 7, 1910, pp 543-544Humility, The Protestant theological and ecclesiastical encyclopedia, Herzog et al (Editors), Vol 2, 1860, pp 598-599 Outside of a religious context, humility is defined as being "unselved", a liberation from consciousness of self, a form of temperance that is neither having pride (or haughtiness) nor indulging in self-deprecation. Humility is an outward expression of an appropriate inner, or self regard, and is contrasted with humiliation which is an imposition, often external, of shame upon a person. Humility may be misappropriated as ability to suffer humiliation through self-denouncements which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost
In production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this case, money is the input that is gone in order to acquire the thing. This acquisition cost may be the sum of the cost of production as incurred by the original producer, and further costs of transaction as incurred by the acquirer over and above the price paid to the producer. Usually, the price also includes a mark-up for profit over the cost of production. More generalized in the field of economics, cost is a metric that is totaling up as a result of a process or as a differential for the result of a decision. Hence cost is the metric used in the standard modeling paradigm applied to economic processes. Costs (pl.) are often further described based on their t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |