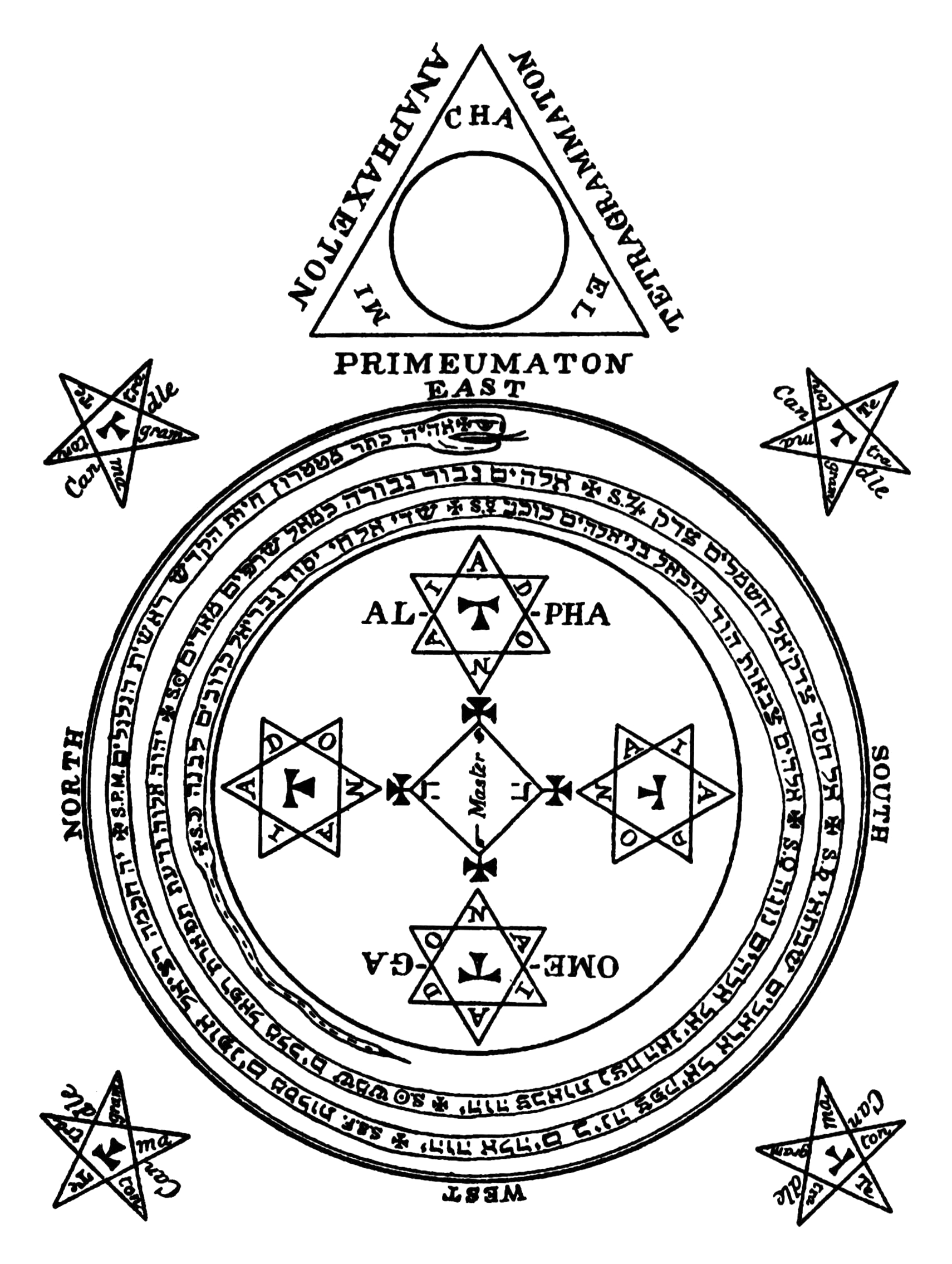
|
Evocation (other)
Evocation is the act of evoking, calling upon, or summoning a spirit, demon, deity or other supernatural agents, in the Western mystery tradition. Conjuration also refers to a summoning, often by the use of a magical spell. The conjuration of the ghosts or spirits of the dead for the purpose of divination is called necromancy. Comparable practices exist in many religions and magical traditions and may employ the use of mind-altering substances with and without uttered word formulas. Conjuration In traditional and most contemporary usage refers to a magical act of invoking spirits or using incantations or charms to cast magical spells. In the context of legerdemain, it may also refer to the performance of illusion or magic tricks for show. This article discusses mainly the original and primary usage, describing acts of a supernatural or paranormal nature. Within some magical traditions today, such as contemporary witchcraft, hoodoo and Hermeticism or ceremonial magic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in media such as comics, video games, movies, anime, and television series. Belief in demons probably goes back to the Paleolithic age, stemming from humanity's fear of the unknown, the strange and the horrific. ''A Dictionary of Comparative Religion'' edited by S.G.F. Brandon 1970 In ancient Near Eastern religions and in the Abrahamic religions, including early Judaism and ancient-medieval Christian demonology, a demon is considered a harmful spiritual entity which may cause demonic possession, calling for an exorcism. Large portions of Jewish demonology, a key influence on Christianity and Islam, originated from a later form of Zoroastrianism, and was transferred to Judaism during the Persian era. Demons may or may not also be considered to be devils: minions of the Devil. In ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonial Magic
Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an extension of ritual magic, and in most cases synonymous with it. Popularized by the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, it draws on such schools of philosophical and occult thought as Hermetic Qabalah, Enochian magic, Thelema, and the magic of various grimoires. Ceremonial magic is part of Hermeticism and Western esotericism. The synonym magick is a archaic spelling of 'magic' used during the Renaissance, which was revived by Aleister Crowley to show and differentiate the occult from performance magic. He defined it as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", including "mundane" acts of will as well as ritual magic. Crowley wrote that "it is theoretically possible to cause in any object any change of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke
Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke (15 January 195329 August 2012) was a British historian and professor of Western esotericism at the University of Exeter, best known for his authorship of several scholarly books on the history of Germany between the World Wars, esoteric and occult traditions. Early life and education Goodrick-Clarke was born in Lincoln, UK, on 15 January 1953, and was an Open Exhibitioner at Lancing College. He studied German, politics, and philosophy at the University of Bristol, and gained a B.A. with distinction. Moving to St. Edmund Hall, Oxford, Goodrick-Clarke took a Ph.D. with a dissertation on the modern Occult Revival and Theosophy at the end of the twentieth century. Career Goodrick-Clarke's Ph.D. dissertation was the basis for his most celebrated work, ''The Occult Roots of Nazism''. This book has been continually in print since its first publication in 1985, and has been translated into twelve languages. Later notable works include his well-regarded ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Book Of Abramelin
''The Book of Abramelin'' tells the story of an Egyptian mage named Abraham, or Abra-Melin, who taught a system of magic to Abraham of Worms, a Jew in Worms, Germany, presumed to have lived from –. The system of magic from this book regained popularity in the 19th and 20th centuries partly due to Samuel Liddell MacGregor Mathers' translation, ''The Book of the Sacred Magic of Abramelin the Mage''. The work was translated into English by Samuel L. MacGregor Mathers and more recently by Georg Dehn and Steven Guth. Dehn attributed authorship of ''The Book of Abramelin'' to Rabbi Yaakov Moelin (Hebrew ; ), a German Jewish Talmudist. This identification has since been disputed. Structure The grimoire is framed as a sort of epistolary novel or autobiography in which Abraham of Worms describes his journey from Germany to Egypt and reveals Abramelin's magical and Kabbalistic secrets to his son Lamech. Internally the text dates itself to the year 1458. The story involves Abraham o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemegeton
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known as ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymous grimoire on demonology. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials a couple of centuries older.''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis: The Lesser Key of Solomon, Detailing the Ceremonial Art of Commanding Spirits Both Good and Evil''; ed. Joseph H. Peterson; Weiser Books Maine; 2001. pp. xi–xvii.''The Goetia of Dr Rudd''; Thomas Rudd, Eds. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p. 399. It is divided into five books—the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. ''Ars Goetia'' Etymology The text is more properly called "Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis, or, The little Key of Solomon". The title most commonly used, "The Lesser Key of Solomon," does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A.E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Of Solomon
The ''Key of Solomon'' ( la, Clavicula Salomonis; he, מפתח שלמה []) (Also known as "The Greater Key of Solomon") is a pseudepigraphical grimoire (also known as a book of spells) attributed to Solomon, King Solomon. It probably dates back to the 14th or 15th century Italian Renaissance. It presents a typical example of Renaissance magic. It is possible that the ''Key of Solomon'' inspired later works, particularly the 17th-century grimoire also known as ''Clavicula Salomonis Regis'', ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', or ''Lemegeton'', although there are many differences between the books. Manuscripts and textual history Many such grimoires attributed to King Solomon were written during the Renaissance, ultimately being influenced by earlier works of Jewish kabbalists and Arab magicians. These, in turn, incorporated aspects of the Greco-Roman magic of Late Antiquity. Several versions of the ''Key of Solomon'' exist, in various translations, with minor to significant differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimoire
A grimoire ( ) (also known as a "book of spells" or a "spellbook") is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and how to summon or invoke supernatural entities such as angels, spirits, deities, and demons.Davies (2009:1) In many cases, the books themselves are believed to be imbued with magical powers, although in many cultures, other sacred texts that are not grimoires (such as the Bible) have been believed to have supernatural properties intrinsically. The only contents found in a grimoire would be information on spells, rituals, the preparation of magical tools, and lists of ingredients and their magical correspondences. In this manner, while all ''books on magic'' could be thought of as grimoires, not all ''magical books'' should be thought of as grimoires. While the term ''grimoire'' is originally European—and many Europeans throughout hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theurgy
Theurgy (; ) describes the practice of rituals, sometimes seen as magical in nature, performed with the intention of invoking the action or evoking the presence of one or more deities, especially with the goal of achieving henosis (uniting with the divine) and perfecting oneself. Definitions *Proclus (c. 480): theurgy is "a power higher than all human wisdom embracing the blessings of divination, the purifying powers of initiation and in a word all the operations of divine possession" * Keith Thomas: "Spiritual magic or theurgy was based on the idea that one could reach God in an ascent up the scale of creation made possible by a rigorous course of prayer, fasting and devotional preparation." * Pierre A. Riffard: "Theurgy is a type of magic. It consists of a set of magical practices performed to evoke beneficent spirits in order to see them or know them or in order to influence them, for instance by forcing them to animate a statue, to inhabit a human being (such as a mediu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplatonism
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonism, Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and Hellenistic religion, religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some ideas that are common to it. For example, the Monism, monistic idea that all of reality can be derived from a single principle, "the One". Neoplatonism began with Ammonius Saccas and his student Plotinus (c. 204/5 – 271 AD) and stretched to the 6th century AD. After Plotinus there were three distinct periods in the history of neoplatonism: the work of his student Porphyry (philosopher), Porphyry (3rd to early 4th century); that of Iamblichus (3rd to 4th century); and the period in the 5th and 6th centuries, when the Academies in Alexandria and Athens flourished. Neoplatonism had an enduring influence on the subsequent history of philosophy. In the Middle Ages, neoplatonic ideas were studied and discussed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Beard (classicist)
Dame Winifred Mary Beard, (born 1 January 1955) is an English scholar of Ancient Rome. She is a trustee of the British Museum and formerly held a personal professorship of Classics at the University of Cambridge. She is a fellow of Newnham College, Cambridge, and Royal Academy of Arts Professor of Ancient Literature. Beard is the classics editor of ''The Times Literary Supplement'', where she also writes a regular blog, "A Don's Life". Her frequent media appearances and sometimes controversial public statements have led to her being described as "Britain's best-known classicist". ''The New Yorker'' characterises her as "learned but accessible". Early life Mary Beard, an only child, was born on 1 January 1955 in Much Wenlock, Shropshire. Her mother, Joyce Emily Beard, was a headmistress and an enthusiastic reader. Her father, Roy Whitbread Beard, worked as an architect in Shrewsbury. She recalled him as "a raffish public-schoolboy type and a complete wastrel, but very engag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to Surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block the provision of supplies and the reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "Investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutelary Deity
A tutelary () (also tutelar) is a deity or a spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of "tutelary" expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the ''genius'', functions as the personal deity or ''daimon'' of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore. Ancient Greece Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or ''daimonion'': The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Ancient Rome Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |