Ceremonial Magic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of
Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of



 The
The 


 James Lees (August 22, 1939 – 2015) was an English magician known for discovering the system he called English Qaballa.
Lees was born in Bolton, Lancashire. He established a career as an analytic chemistry, analytic chemist. In his search for truth, he also studied psychology. Not finding the answers he wanted from science, he turned to the study of astrology, even making a living for a time as a horary astrology, horary astrologer.
Still resolved to discover further answers, Lees decided to study Kabbalah and the Tree of life (Kabbalah), Tree of Life. From here he proceeded to experiment with invocations from the ''Key of Solomon''. Satisfied with the results, he proceeded to perform the 18-month working described in ''The Book of Abramelin'' by means of the Bornless Ritual. Having successfully invoked his Holy Guardian Angel, he turned his attention to ascending the 'Middle Pillar' of the Tree of Life, culminating with an experience known as crossing the abyss.
Then, in November 1976, Lees discovered the "order & value of the English Alphabet." Following this discovery, Lees founded the O∴A∴A∴ in order to assist others in the pursuit of their own spiritual paths. The first public report of the system known as English Qaballa (EQ) was published in 1979 by Ray Sherwin in an editorial in the final issue of his journal, ''The New Equinox''. Lees subsequently assumed the role of publisher of ''The New Equinox'' and, starting in 1981, published additional material about the EQ system over the course of five issues of the journal, extending into 1982.
In 1904, Aleister Crowley wrote out the text of the foundational document of his world-view, known as ''Liber AL vel Legis'', ''
James Lees (August 22, 1939 – 2015) was an English magician known for discovering the system he called English Qaballa.
Lees was born in Bolton, Lancashire. He established a career as an analytic chemistry, analytic chemist. In his search for truth, he also studied psychology. Not finding the answers he wanted from science, he turned to the study of astrology, even making a living for a time as a horary astrology, horary astrologer.
Still resolved to discover further answers, Lees decided to study Kabbalah and the Tree of life (Kabbalah), Tree of Life. From here he proceeded to experiment with invocations from the ''Key of Solomon''. Satisfied with the results, he proceeded to perform the 18-month working described in ''The Book of Abramelin'' by means of the Bornless Ritual. Having successfully invoked his Holy Guardian Angel, he turned his attention to ascending the 'Middle Pillar' of the Tree of Life, culminating with an experience known as crossing the abyss.
Then, in November 1976, Lees discovered the "order & value of the English Alphabet." Following this discovery, Lees founded the O∴A∴A∴ in order to assist others in the pursuit of their own spiritual paths. The first public report of the system known as English Qaballa (EQ) was published in 1979 by Ray Sherwin in an editorial in the final issue of his journal, ''The New Equinox''. Lees subsequently assumed the role of publisher of ''The New Equinox'' and, starting in 1981, published additional material about the EQ system over the course of five issues of the journal, extending into 1982.
In 1904, Aleister Crowley wrote out the text of the foundational document of his world-view, known as ''Liber AL vel Legis'', ''
 A
A
 A magical formula or 'word of power' is a word that is believed to have specific supernatural effects. They are words whose meaning illustrates principles and degrees of understanding that are often difficult to relay using other forms of speech or writing. It is a concise means to communicate very abstract information through the medium of a word or phrase.
These words often have no intrinsic meaning in and of themselves. However, when deconstructed, each individual letter may refer to some universal concept found in the system that the formula appears. Additionally, in grouping certain letters together one is able to display meaningful sequences that are considered to be of value to the spiritual system that utilizes them (e.g., spiritual hierarchies, historiographic data, psychological stages, etc.)
A formula's potency is understood and made usable by the magician only through prolonged meditation on its levels of meaning. Once these have been interiorized by the magician, they may then utilize the formula to maximum effect.
A magical formula or 'word of power' is a word that is believed to have specific supernatural effects. They are words whose meaning illustrates principles and degrees of understanding that are often difficult to relay using other forms of speech or writing. It is a concise means to communicate very abstract information through the medium of a word or phrase.
These words often have no intrinsic meaning in and of themselves. However, when deconstructed, each individual letter may refer to some universal concept found in the system that the formula appears. Additionally, in grouping certain letters together one is able to display meaningful sequences that are considered to be of value to the spiritual system that utilizes them (e.g., spiritual hierarchies, historiographic data, psychological stages, etc.)
A formula's potency is understood and made usable by the magician only through prolonged meditation on its levels of meaning. Once these have been interiorized by the magician, they may then utilize the formula to maximum effect.
 Invocation is the bringing in or identifying with a particular deity or spirit. Crowley wrote of two keys to success in this arena: to "inflame thyself in praying" and to "invoke often". For Crowley, the single most important invocation, or any act of magic for that matter, was the invocation of one's Holy Guardian Angel, or "secret self", which allows the adept to know his or her true will.
Crowley describes the experience of invocation:
Crowley (''Magick, Book 4'') discusses three main categories of invocation, although "in the great essentials these three methods are one. In each case the magician identifies himself with the Deity invoked."
*''Devotion''—where "identity with the God is attained by love and by surrender, by giving up or suppressing all irrelevant (and illusionary) parts of yourself."
*''Calling forth''—where "identity is attained by paying special attention to the desired part of yourself."
*''Drama''—where "identity is attained by sympathy. It is very difficult for the ordinary man to lose himself completely in the subject of a play or of a novel; but for those who can do so, this method is unquestionably the best."
Another invocatory technique that the magician can employ is called the assumption of godforms — where with "concentrated imagination of oneself in the symbolic shape of any God, one should be able to identify oneself with the idea which [the god] represents." A general method involves positioning the body in a position that is typical for a given god, imagining that the image of the god is coinciding with or enveloping the body, accompanied by the practice of "vibration" of the appropriate god-name(s).
Invocation is the bringing in or identifying with a particular deity or spirit. Crowley wrote of two keys to success in this arena: to "inflame thyself in praying" and to "invoke often". For Crowley, the single most important invocation, or any act of magic for that matter, was the invocation of one's Holy Guardian Angel, or "secret self", which allows the adept to know his or her true will.
Crowley describes the experience of invocation:
Crowley (''Magick, Book 4'') discusses three main categories of invocation, although "in the great essentials these three methods are one. In each case the magician identifies himself with the Deity invoked."
*''Devotion''—where "identity with the God is attained by love and by surrender, by giving up or suppressing all irrelevant (and illusionary) parts of yourself."
*''Calling forth''—where "identity is attained by paying special attention to the desired part of yourself."
*''Drama''—where "identity is attained by sympathy. It is very difficult for the ordinary man to lose himself completely in the subject of a play or of a novel; but for those who can do so, this method is unquestionably the best."
Another invocatory technique that the magician can employ is called the assumption of godforms — where with "concentrated imagination of oneself in the symbolic shape of any God, one should be able to identify oneself with the idea which [the god] represents." A general method involves positioning the body in a position that is typical for a given god, imagining that the image of the god is coinciding with or enveloping the body, accompanied by the practice of "vibration" of the appropriate god-name(s).
 Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of
Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an extension of ritual magic, and in most cases synonymous with it. Popularized by the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn
The Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn ( la, Ordo Hermeticus Aurorae Aureae), more commonly the Golden Dawn (), was a secret society devoted to the study and practice of occult Hermeticism and metaphysics during the late 19th and early 20th ...
, it draws on such schools of philosophical and occult thought as Hermetic Qabalah
Hermetic Qabalah () is a Western esoteric tradition involving mysticism and the occult. It is the underlying philosophy and framework for magical societies such as the Golden Dawn, Thelemic orders, mystical-religious societies such as the Bu ...
, Enochian magic
Enochian magic is a system of ceremonial magic based on the 16th-century writings of John Dee and Edward Kelley, who wrote that their information, including the revealed Enochian language, was delivered to them directly by various angels. Dee's ...
, Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word ' ...
, and the magic of various grimoire
A grimoire ( ) (also known as a "book of spells" or a "spellbook") is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and ...
s. Ceremonial magic is part of Hermeticism
Hermeticism, or Hermetism, is a philosophical system that is primarily based on the purported teachings of Hermes Trismegistus (a legendary Hellenistic combination of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth). These teachings are containe ...
and Western esotericism
Western esotericism, also known as esotericism, esoterism, and sometimes the Western mystery tradition, is a term scholars use to categorise a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas ...
.
The synonym magick is a archaic spelling of 'magic' used during the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, which was revived by Aleister Crowley
Aleister Crowley (; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 – 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, painter, novelist, and mountaineer. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the pr ...
to show and differentiate the occult from performance magic. He defined it as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", including "mundane" acts of will as well as ritual magic. Crowley wrote that "it is theoretically possible to cause in any object any change of which that object is capable by nature". John Symonds and Kenneth Grant attach a deeper occult significance to this preference.
Crowley saw magic as the essential method for a person to reach true understanding of the self and to act according to one's true will, which he saw as the reconciliation "between freewill and destiny." Crowley describes this process in his '' Magick, Book 4''.
Definitions and general purpose
The term ''magick'' is anEarly Modern English
Early Modern English or Early New English (sometimes abbreviated EModE, EMnE, or ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transition from Middle E ...
spelling for magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
, used in works such as the 1651 translation of Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim (; ; 14 September 1486 – 18 February 1535) was a German polymath, physician, legal scholar, soldier, theologian, and occult writer. Agrippa's '' Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' published in 1533 dre ...
's ''De Occulta Philosophia'', '' Three Books of Occult Philosophy, or Of Magick''. Aleister Crowley
Aleister Crowley (; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 – 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, painter, novelist, and mountaineer. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the pr ...
chose the spelling to differentiate his practices and rituals from stage magic (which may be more appropriately termed "illusion") and the term has since been re-popularised by those who have adopted elements of his teachings. Crowley defined Magick as "the science and art of causing change to occur in conformity with will."
History

Renaissance magic
The term originates in 16th-centuryRenaissance magic
Renaissance magic was a resurgence in Hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of the magical arts which arose along with Renaissance humanism in the 15th and 16th centuries CE. These magical arts (called '' artes magicae'') were divided into sev ...
, referring to practices described in various Medieval and Renaissance grimoire
A grimoire ( ) (also known as a "book of spells" or a "spellbook") is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and ...
s and in collections such as that of Johannes Hartlieb
Johannes Hartlieb (c. 1410Hartlieb's year of birth is unknown; his existence is first attested as the author of ''Kunst der Gedächtnüß'', written during 1430–32, and an estimate of his year of birth as either "c. 1400" or "c. 1410" can be ...
. Georg Pictor uses the term synonymously with '' goetia''.
James Sanford in his 1569 translation of Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim (; ; 14 September 1486 – 18 February 1535) was a German polymath, physician, legal scholar, soldier, theologian, and occult writer. Agrippa's '' Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' published in 1533 dre ...
's 1526 ''De incertitudine et vanitate scientiarum'' has "The partes of ceremoniall Magicke be Geocie, and Theurgie". For Agrippa, ceremonial magic was in opposition to natural magic
Natural magic in the context of Renaissance magic is that part of the occult which deals with natural forces directly, as opposed to ceremonial magic which deals with the summoning of spirits. Natural magic sometimes makes use of physical substa ...
. While he had his misgivings about natural magic, which included astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
, alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
, and also what we would today consider fields of natural science, such as botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
, he was nevertheless prepared to accept it as "the highest peak of natural philosophy". Ceremonial magic, on the other hand, which included all sorts of communication with spirits, including necromancy
Necromancy () is the practice of magic or black magic involving communication with the dead by summoning their spirits as apparitions or visions, or by resurrection for the purpose of divination; imparting the means to foretell future even ...
and witchcraft
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have ...
, he denounced in its entirety as impious disobedience towards God.

Francis Barrett
Among the various sources for ceremonial magic, Francis Barrett, a late 18th-century Englishman, called himself a student of chemistry,metaphysics
Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that studies the fundamental nature of reality, the first principles of being, identity and change, space and time, causality, necessity, and possibility. It includes questions about the nature of conscio ...
, and natural occult philosophy. Barrett was enthusiastic about reviving interest in the occult arts, and published a magical textbook called '' The Magus''. ''The Magus'' dealt with the natural magic of herbs and stones, magnetism, talismanic magic, alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
, numerology, the elements, and biographies of famous adept
An adept is an individual identified as having attained a specific level of knowledge, skill, or aptitude in doctrines relevant to a particular author or organization.
He or she stands out from others with their great abilities. All human quali ...
s from history. It was a compilation, almost entirely consisting of selections from Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim (; ; 14 September 1486 – 18 February 1535) was a German polymath, physician, legal scholar, soldier, theologian, and occult writer. Agrippa's '' Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' published in 1533 drew ...
's ''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'', the ''Fourth Book of Occult Philosophy'' attributed to Agrippa, and Robert Turner's 1655 translation of the ''Heptameron of Peter of Abano''. Barrett made modifications and modernized spelling and syntax. Possibly influencing the novelist Edward Bulwer-Lytton, the book gained little other notice until it influenced Eliphas Levi Eliphaz is one of Esau's sons in the Bible.
Eliphaz or Eliphas is also the given name of:
* Eliphaz (Job), another person in the Bible
* Eliphaz Dow (1705-1755), the first male executed in New Hampshire, for murder
* Eliphaz Fay (1797–1854), fo ...
.

Éliphas Lévi
Éliphas Lévi
Éliphas Lévi Zahed, born Alphonse Louis Constant (8 February 1810 – 31 May 1875), was a French esotericist, poet, and author of more than 20 books on magic, Kabbalah, alchemical studies, and occultism. He pursued an ecclesiastical career i ...
(1810–1875) conceived the notion of writing a treatise on magic with his friend Bulwer-Lytton Bulwer-Lytton is a surname, and may refer to:
* Edward Bulwer-Lytton, 1st Baron Lytton (1803–1873), novelist and politician
* Rosina Bulwer Lytton (1802–1882), feminist writer and wife of Edward Bulwer-Lytton
* Robert Bulwer-Lytton, 1st Earl of ...
. This appeared in 1855 under the title ''Dogme et Rituel de la Haute Magie
''Dogme et Rituel de la Haute Magie'' ( en, Dogma and Ritual of High Magic) is the title of Éliphas Lévi's first published treatise on ritual magic, which appeared in two volumes between 1854 (''Dogme'') and 1856 (''Rituel''). Each volume is ...
'', and was translated into English by Arthur Edward Waite
Arthur Edward Waite (2 October 1857 – 19 May 1942) was a British poet and scholarly mystic who wrote extensively on occult and esoteric matters, and was the co-creator of the Rider–Waite tarot deck (also called the Rider–Waite–Smith ...
as ''Transcendental Magic, its Doctrine and Ritual''.
In 1861, he published a sequel, ''La Clef des Grands Mystères'' (''The Key to the Great Mysteries''). Further magical works by Lévi include ''Fables et Symboles'' (''Stories and Images''), 1862, and ''La Science des Esprits'' (''The Science of Spirits''), 1865. In 1868, he wrote ''Le Grand Arcane, ou l'Occultisme Dévoilé'' (''The Great Secret, or Occultism Unveiled''); this, however, was only published posthumously in 1898.
Lévi's version of magic became a great success, especially after his death. That Spiritualism
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and Mind-body dualism, dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (w ...
was popular on both sides of the Atlantic from the 1850s contributed to his success. His magical teachings were free from obvious fanaticisms, even if they remained rather murky; he had nothing to sell, and did not pretend to be the initiate of some ancient or fictitious secret society. He incorporated the Tarot
The tarot (, first known as '' trionfi'' and later as ''tarocchi'' or ''tarocks'') is a pack of playing cards, used from at least the mid-15th century in various parts of Europe to play card games such as Tarocchini. From their Italian roots ...
cards into his magical system, and as a result the Tarot has been an important part of the paraphernalia of Western magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
ians. He had a deep impact on the magic of the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn and later Aleister Crowley, and it was largely through this impact that Lévi is remembered as one of the key founders of the twentieth century revival of magic.
Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn
 The
The Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn
The Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn ( la, Ordo Hermeticus Aurorae Aureae), more commonly the Golden Dawn (), was a secret society devoted to the study and practice of occult Hermeticism and metaphysics during the late 19th and early 20th ...
(founded 1888) was a secret society devoted to the study and practice of the occult, metaphysics
Metaphysics is the branch of philosophy that studies the fundamental nature of reality, the first principles of being, identity and change, space and time, causality, necessity, and possibility. It includes questions about the nature of conscio ...
, and paranormal
Paranormal events are purported phenomena described in popular culture, folk, and other non-scientific bodies of knowledge, whose existence within these contexts is described as being beyond the scope of normal scientific understanding. Not ...
activities during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Known as a magical order
A magical organization or magical order is an organization created for the practice of ceremonial or other forms of occult magic or to further the knowledge of magic among its members. Magical organizations can include Hermetic orders, Wiccan ...
, the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn was active in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
and focused its practices on theurgy
Theurgy (; ) describes the practice of rituals, sometimes seen as magical in nature, performed with the intention of invoking the action or evoking the presence of one or more deities, especially with the goal of achieving henosis (uniting w ...
and spiritual development. Many present-day concepts of ritual and magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
that are at the centre of contemporary traditions, such as Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and w ...
and Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word ' ...
, were inspired by the Golden Dawn, which became one of the largest single influences on 20th century Western occultism.
The three founders, William Robert Woodman, William Wynn Westcott, and Samuel Liddell Mathers
Samuel Liddell (or Liddel) MacGregor Mathers (8 or 11 January 1854 – 5 or 20 November 1918), born Samuel Liddell Mathers, was a British occultist. He is primarily known as one of the founders of the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, a cerem ...
, were Freemasons. Westcott appears to have been the initial driving force behind the establishment of the Golden Dawn.
The "Golden Dawn" was the first of three Orders, although all three are often collectively referred to as the "Golden Dawn". The First Order taught esoteric philosophy based on the Hermetic Qabalah
Hermetic Qabalah () is a Western esoteric tradition involving mysticism and the occult. It is the underlying philosophy and framework for magical societies such as the Golden Dawn, Thelemic orders, mystical-religious societies such as the Bu ...
and personal development through study and awareness of the four classical elements, as well as the basics of astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
, tarot divination
Tarot card reading is a form of cartomancy whereby practitioners use tarot cards to purportedly gain insight into the past, present or future. They formulate a question, then draw cards to interpret them for this end. A traditional tarot deck con ...
, and geomancy
Geomancy ( Greek: γεωμαντεία, "earth divination") is a method of divination that interprets markings on the ground or the patterns formed by tossed handfuls of soil, rocks, or sand. The most prevalent form of divinatory geomancy in ...
. The Second or Inner Order, the , taught magic, including scrying
Scrying, also known by various names such as "seeing" or "peeping", is the practice of looking into a suitable medium in the hope of detecting significant messages or visions. The objective might be personal guidance, prophecy, revelation, or in ...
, astral travel, and alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
.

Aleister Crowley
English author and occultist Aleister Crowley (1875–1947) often introduced new terminology for spiritual and magical practices and theory. For example, he termedtheurgy
Theurgy (; ) describes the practice of rituals, sometimes seen as magical in nature, performed with the intention of invoking the action or evoking the presence of one or more deities, especially with the goal of achieving henosis (uniting w ...
'high magic' and thaumaturgy
Thaumaturgy is the purported capability of a magician to work magic or other paranormal events or a saint to perform miracles. It is sometimes translated into English as wonderworking.
A practitioner of thaumaturgy is a "thaumaturge", "thauma ...
'low magic'. In ''The Book of the Law
''Liber AL vel Legis'' (), commonly known as ''The Book of the Law'', is the central sacred text of Thelema. Aleister Crowley said that it was dictated to him by a beyond-human being who called himself ' Aiwass'. Rose Edith Kelly, Crowley's ...
'' and ''The Vision and the Voice
''The Vision and the Voice'' (Liber 418) is a book by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947). It chronicles the mystical journey of the author as he explored the 30 Enochian aethyrs originally developed by John Dee and Edward Kelley in the 16th century. ...
'', the Aramaic magical formula ''Abracadabra
''Abracadabra'' is a magic word, historically used as an incantation on amulets and common today in stage magic.
Etymology
''Abracadabra'' is of unknown origin, but according to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', its first known occurrence ...
'' was changed to ''Abrahadabra
Abrahadabra is a word that first publicly appeared in ''The Book of the Law'' (1904), the central sacred text of Thelema. Its author, Aleister Crowley, described it as "the Word of the Aeon, which signifieth The Great Work accomplished." This ...
'', which he called the new formula of the Aeon of Horus. He also famously spelled magic in the archaic manner, as 'magick', to differentiate "the true science of the Magi from all its counterfeits." He also stated that "The spirits of the Goetia are portions of the human brain."
His book '' Magick, Liber ABA, Book 4'', is a lengthy treatise on magic in which he which also presents his own system of Western occult practice, synthesised from many sources, including Yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consci ...
, Hermeticism
Hermeticism, or Hermetism, is a philosophical system that is primarily based on the purported teachings of Hermes Trismegistus (a legendary Hellenistic combination of the Greek god Hermes and the Egyptian god Thoth). These teachings are containe ...
, medieval grimoires
A grimoire ( ) (also known as a "book of spells" or a "spellbook") is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and ...
, contemporary magical theories from writers like Eliphas Levi Eliphaz is one of Esau's sons in the Bible.
Eliphaz or Eliphas is also the given name of:
* Eliphaz (Job), another person in the Bible
* Eliphaz Dow (1705-1755), the first male executed in New Hampshire, for murder
* Eliphaz Fay (1797–1854), fo ...
and Helena Blavatsky
Helena Petrovna Blavatsky, uk, Олена Петрівна Блаватська, Olena Petrivna Blavatska (; – 8 May 1891), often known as Madame Blavatsky, was a Russian mystic and author who co-founded the Theosophical Society in 187 ...
, and his own original contributions. It consists of four parts: Mysticism, Magick (Elementary Theory), Magick in Theory and Practice, and ΘΕΛΗΜΑ—the Law (The Equinox of The Gods). It also includes numerous appendices presenting many rituals and explicatory papers.
Dion Fortune

Dion Fortune
Dion Fortune (born Violet Mary Firth, 6 December 1890 – 6 January 1946) was a British occultist, ceremonial magician, novelist and author. She was a co-founder of the Fraternity of the Inner Light, an occult organisation that promoted ph ...
(1890–1946) was a Welsh occultist
The occult, in the broadest sense, is a category of esoteric supernatural beliefs and practices which generally fall outside the scope of religion and science, encompassing phenomena involving otherworldly agency, such as magic and mysticism a ...
, ceremonial magician, novelist and author. She was a co-founder of the Fraternity of the Inner Light, an occult organisation that promoted philosophies which she claimed had been taught to her by spiritual entities known as the Ascended Masters. A prolific writer, she produced a large number of articles and books on her occult ideas and also authored seven novels, several of which expound occult themes.
Fortune was a ceremonial magician. The magical principles on which her Fraternity was based were adopted from the late nineteenth century Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, with other influences coming from Theosophy and Christian Science. The magical ceremonies performed by Fortune's Fraternity were placed into two categories: initiations, in which the candidate was introduced to magical forces, and evocation, in which these forces were manipulated for a given purpose.
The Fraternity's rituals at their Bayswater temple were carried out under a dim light, as Fortune believed that bright light disperses etheric forces. An altar was placed in the centre of a room, with the colours of the altar-cloth and the symbols on the altar varying according to the ceremony being performed. A light was placed on the altar while incense, usually frankincense, was burned. The senior officers sat in a row along the eastern end of the room, while officers—who were believed to be channels for cosmic forces—were positioned at various positions on the floor. The lodge was opened by walking around the room in a circle chanting, with the intent of building a psychic force up as a wall. Next, the cosmic entities would be invoked, with the members believing that these entities would manifest in astral
Astral may refer to:
Concepts of the non-physical
* Astral body, a subtle body posited by many religious philosophers
* Astral journey (or ''astral trip''), the same as having an ''out-of-body experience''
* Astral plane (AKA astral world), a ...
form and interact with the chosen officers.
Fortune was particularly concerned with the issue of sex. She believed that this erotic attraction between men and women could be harnessed for use in magic. She urged her followers to be naked under their robes when carrying out magical rituals, for this would increase the creative sexual tension between the men and women present. Although sex features in her novels, it is never described in graphic detail. The scholar Andrew Radford noted that Fortune's "reactionary and highly heteronormative" view of "sacralised sexuality" should be seen as part of a wider tradition among esoteric currents, going back to the ideas of Emanuel Swedenborg
Emanuel Swedenborg (, ; born Emanuel Swedberg; 29 March 1772) was a Swedish pluralistic-Christian theologian, scientist, philosopher and mystic. He became best known for his book on the afterlife, ''Heaven and Hell'' (1758).
Swedenborg had a ...
and Andrew Jackson Davis
Andrew Jackson Davis (August 11, 1826January 13, 1910) was an American Spiritualist, born in Blooming Grove, New York.
Early years
Davis had little education. In 1843 he heard lectures in Poughkeepsie on animal magnetism, the precursor of hy ...
and also being found in the work of occultists like Paschal Beverly Randolph
Paschal Beverly Randolph (October 8, 1825 – July 29, 1875) was an American medical doctor, occultist, spiritualist, trance medium, and writer. He is notable as perhaps the first person to introduce the principles of erotic alchemy to North A ...
and Ida Craddock.
The religious studies scholar Hugh Urban
Hugh Bayard Urban is a professor of religious studies at Ohio State Universities Department of Comparative Studies and author of eight books and several academic articles, including a history of the Church of Scientology, published by Princeton ...
noted that Fortune was "one of the key links" between early twentieth-century ceremonial magic and the developing Pagan religion of Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and w ...
. Similarly, the Wiccan high priestess Vivianne Crowley
Vivianne Crowley is an author, university lecturer, psychologist, and a High Priestess and teacher of the Wiccan religion. She was initiated into the London coven of Alex Sanders (founder of the Alexandrian tradition of Wicca) at the age of eig ...
characterised Fortune as a "proto-Pagan". The scholar and esotericist Nevill Drury stated that Fortune "in many ways anticipated feminist ideas in contemporary Wicca", particularly through her belief that all goddesses were a manifestation of a single Great Goddess. Graf agreed, adding that Fortune's works found "resonance" in the work of the later feminist Wiccan Starhawk
Starhawk (born Miriam Simos on June 17, 1951) is an American feminist and author. She is known as a theorist of feminist Neopaganism and ecofeminism.
In 2013, she was listed in Watkins' ''Mind Body Spirit'' magazine as one of the 100 Most Spir ...
, and in particular in the latter's 1979 book, ''The Spiral Dance
''The Spiral Dance: a Rebirth of the Ancient Religion of the Great Goddess'' is a book about Neopagan beliefs and practices written by Starhawk. It was first published in 1979, with a second edition in 1989 and a third edition in 1999. It is a ...
''.
In researching ceremonial magic orders and other esoteric groups active in the London area during the 1980s, Luhrmann found that within them, Fortune's novels were treated as "fictionalized ideals" and that they were recommended to newcomers as the best way to understand magic. The Pagan studies Pagan studies is the multidisciplinary academic field devoted to the study of modern paganism, a broad assortment of modern religious movements, which are typically influenced by or claiming to be derived from the various pagan beliefs of premodern ...
scholar Joanne Pearson added that Fortune's books, and in particular the novels ''The Sea Priestess'' and ''Moon Magic'', were owned by many Wiccans and other Pagans. The religious studies scholar Graham Harvey compared ''The Sea Priestess'' to the Wiccan Gerald Gardner
Gerald Brosseau Gardner (13 June 1884 – 12 February 1964), also known by the craft name Scire, was an English Wiccan, as well as an author and an amateur anthropology, anthropologist and archaeology, archaeologist. He was instrumental in bri ...
's 1949 novel ''High Magic's Aid'', stating that while neither were "great literature", they "evoke Paganism better than later more didactic works".
Fortune's priestesses were an influence on the characters of Marion Zimmer Bradley
Marion Eleanor Zimmer Bradley (June 3, 1930 – September 25, 1999) was an American author of fantasy, historical fantasy, science fiction, and science fantasy novels, and is best known for the Arthurian fiction novel ''The Mists of Avalon'' an ...
's ''The Mists of Avalon
''The Mists of Avalon'' is a 1983 historical fantasy novel by American writer Marion Zimmer Bradley, in which the author relates the Arthurian legends from the perspective of the female characters. The book follows the trajectory of Morgaine (M ...
'', and her ideas were adopted as the basis for the Aquarian Order of the Restoration
Aquarian may refer to:
*Aquarius (astrology), a sign of the zodiac
*Aquarian Tabernacle Church, a Wiccan church in Index, Washington, U.S.
*''The Aquarian Weekly'', a weekly newspaper in New Jersey, U.S.
*Aquarii, Christians who substituted water f ...
, a ceremonial magic group led by Bradley. Her works also influenced Bradley's collaborator and fellow Order member Diana Paxson. As of 2007, Fortune's latter three novels remained in print and had a wide readership.

Jack Parsons
John Whiteside Parsons
John Whiteside Parsons (born Marvel Whiteside Parsons; October 2, 1914 – June 17, 1952) was an American rocket engineer, chemist, and Thelemite occultist. Associated with the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Parsons was one of t ...
(1914–1952) was an American rocket engineer, chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe t ...
, and Thelemite occultist. Parsons converted to Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word ' ...
, the new religious movement
A new religious movement (NRM), also known as alternative spirituality or a new religion, is a religious or spiritual group that has modern origins and is peripheral to its society's dominant religious culture. NRMs can be novel in origin or th ...
founded by the English occultist Aleister Crowley. Together with his first wife, Helen Northrup, Parsons joined the Agape Lodge, the Californian branch of the Thelemite Ordo Templi Orientis
Ordo Templi Orientis (O.T.O.; ) is an occult initiatory organization founded at the beginning of the 20th century. The origins of the O.T.O. can be traced back to the German-speaking occultists Carl Kellner, Heinrich Klein, Franz Hartmann and T ...
(O.T.O.) in 1941. At Crowley's bidding, Parsons replaced Wilfred Talbot Smith as its leader in 1942 and ran the Lodge from his mansion on Orange Grove Boulevard.
Parsons identified four obstacles that prevented humans from achieving and performing their true will, all of which he connected with fear: the fear of incompetence, the fear of the opinion of others, the fear of hurting others, and the fear of insecurity. He insisted that these must be overcome, writing that "The Will must be freed of its fetters. The ruthless examination and destruction of taboos, complexes, frustrations, dislikes, fears and disgusts hostile to the Will is essential to progress."
In 1945, Parsons separated from Helen, after having an affair with her sister Sara; when Sara left him for L. Ron Hubbard
Lafayette Ronald Hubbard (March 13, 1911 – January 24, 1986) was an American author, primarily of science fiction and fantasy stories, who is best known for having founded the Church of Scientology. In 1950, Hubbard authored '' Dianeti ...
, Parsons conducted the Babalon Working, a series of rituals intended to invoke the Thelemic goddess Babalon
Babalon (also known as the Scarlet Woman, Great Mother or Mother of Abominations) is a goddess found in the occult system of Thelema, which was established in 1904 with the writing of '' The Book of the Law'' by English author and occultist ...
on Earth. The Babalon Working was a series of magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
ceremonies
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan origin, via the Latin '' caerimonia''.
Church and civil (secular ...
or ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized ...
s performed from January to March 1946 by Parsons and Scientology
Scientology is a set of beliefs and practices invented by American author L. Ron Hubbard, and an associated movement. It has been variously defined as a cult, a Scientology as a business, business, or a new religious movement. The most recent ...
founder L. Ron Hubbard
Lafayette Ronald Hubbard (March 13, 1911 – January 24, 1986) was an American author, primarily of science fiction and fantasy stories, who is best known for having founded the Church of Scientology. In 1950, Hubbard authored '' Dianeti ...
. This ritual was essentially designed to manifest an individual incarnation
Incarnation literally means ''embodied in flesh'' or ''taking on flesh''. It refers to the conception and the embodiment of a deity or spirit in some earthly form or the appearance of a god as a human. If capitalized, it is the union of divinit ...
of the archetypal divine feminine called Babalon
Babalon (also known as the Scarlet Woman, Great Mother or Mother of Abominations) is a goddess found in the occult system of Thelema, which was established in 1904 with the writing of '' The Book of the Law'' by English author and occultist ...
. The project was based on the ideas of Crowley, and his description of a similar project in his 1917 novel ''Moonchild''.
When Parsons declared that the first of the series of rituals was complete and successful, he almost immediately met Marjorie Cameron in his own home, and regarded her as the elemental
An elemental is a mythic being that is described in occult and alchemical works from around the time of the European Renaissance, and particularly elaborated in the 16th century works of Paracelsus. According to Paracelsus and his subsequent fo ...
that he and Hubbard had called through the ritual. Soon Parsons began the next stage of the series, an attempt to conceive a child through sex magic
Sex magic (sometimes spelled sex magick) is any type of sexual activity used in magical, ritualistic or otherwise religious and spiritual pursuits. One practice of sex magic is using sexual arousal or orgasm with visualization of a desired re ...
workings. Although no child was conceived, this did not affect the result of the ritual to that point. Parsons and Cameron, who Parsons now regarded as the Scarlet Woman, ''Babalon
Babalon (also known as the Scarlet Woman, Great Mother or Mother of Abominations) is a goddess found in the occult system of Thelema, which was established in 1904 with the writing of '' The Book of the Law'' by English author and occultist ...
'', called forth by the ritual, soon married.
The rituals performed drew largely upon rituals and sex magic described by Crowley. Crowley was in correspondence with Parsons during the course of the Babalon Working, and warned Parsons of his potential overreactions to the magic he was performing, while simultaneously deriding Parsons' work to others.
A brief text entitled ''Liber 49'', self-referenced within the text as ''The Book of Babalon'', was written by Jack Parsons as a transmission from the goddess or force called 'Babalon' received by him during the Babalon Working. Parsons wrote that ''Liber 49'' constituted a fourth chapter of Crowley's ''Liber AL Vel Legis (The Book of the Law
''Liber AL vel Legis'' (), commonly known as ''The Book of the Law'', is the central sacred text of Thelema. Aleister Crowley said that it was dictated to him by a beyond-human being who called himself ' Aiwass'. Rose Edith Kelly, Crowley's ...
)'', the holy text of Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word ' ...
.
Phyllis Seckler
Phyllis Seckler
Phyllis Evalina Seckler (18 June 1917 – 31 May 2004), also known as Soror Meral, was a ninth degree (IX°) member of the Sovereign Sanctuary of the Gnosis of Ordo Templi Orientis (O.T.O.), and a lineage holder in the A∴A∴ tradition. She wa ...
(1917–2004), also known as 'Soror Meral', was a ninth degree (IX°) member of the Sovereign Sanctuary of the Gnosis of Ordo Templi Orientis
Ordo Templi Orientis (O.T.O.; ) is an occult initiatory organization founded at the beginning of the 20th century. The origins of the O.T.O. can be traced back to the German-speaking occultists Carl Kellner, Heinrich Klein, Franz Hartmann and T ...
(O.T.O.), and a lineage holder in the A∴A∴
The A∴A∴ ( ) is a magical organization described in 1907 by occultist Aleister Crowley. Its members are dedicated to the advancement of humanity by perfection of the individual on every plane through a graded series of universal initiation ...
tradition. She was a student of Jane Wolfe
Sarah Jane Wolfe (March 21, 1875 – March 29, 1958) was an American silent film character actress who is considered an important female figure in magick. She was a friend and a colleague of Aleister Crowley and a founding member of Agape Lodg ...
, herself a student of Aleister Crowley.
Sekler was a member of O.T.O. Agape Lodge, the only working Lodge of the O.T.O. at the time of Aleister Crowley's death. Seckler was also instrumental in preserving important parts of Crowley's literary heritage, typing parts of his ''Confessions'', and the complete texts of ''The Vision and the Voice
''The Vision and the Voice'' (Liber 418) is a book by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947). It chronicles the mystical journey of the author as he explored the 30 Enochian aethyrs originally developed by John Dee and Edward Kelley in the 16th century. ...
'' and ''Magick Without Tears
''Magick Without Tears'', a series of letters, was the last book written by English occultist Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), although it was not published until after his death. It was written in 1943 and published in 1954 with a foreword by it ...
'' during the 1950s. Seckler was also instrumental in re-activing the O.T.O. with Grady Louis McMurtry
Grady Louis McMurtry (October 18, 1918 – July 12, 1985) was a student of author and occultist Aleister Crowley and an adherent of Thelema. He is best known for reviving the fraternal organization Ordo Templi Orientis, which he headed from 197 ...
, during the early-mid 1970s, following the death of Crowley's appointed successor, Karl Germer
Karl Johannes Germer (22 January 1885 – 25 October 1962), also known as ''Frater Saturnus'', was a German occultist and the United States representative and later a successor of author and occultist Aleister Crowley as the Outer Head of the Ord ...
.
Seckler continued her lifelong work with the A∴A∴
The A∴A∴ ( ) is a magical organization described in 1907 by occultist Aleister Crowley. Its members are dedicated to the advancement of humanity by perfection of the individual on every plane through a graded series of universal initiation ...
, founding the ''College of Thelema'' and co-founding (with James A. Eshelman) the ''Temple of Thelema'', and later warranting the formation of the ''Temple of the Silver Star''. Seeking to guide her students to an understanding of the Law of Thelema, especially deeper understanding of oneself and of one's magical will, Sekler published the bi-annual Thelemic journal ''In the Continuum'' which featured her essays on Thelema and initiation as well as instructional articles for the students of the A.:.A.:., illustrations and essays which help to clarify some of Crowley's thoughts and aid in the understanding of Thelemic principles expressed in Liber AL. Printed for 20 years from 1976 through 1996, ''In the Continuum'' also published rare works by Aleister Crowley which at the time were out of print or hard to find.
Seckler served as a master of 418 Lodge of O.T.O. in California from its inception in 1979 until her death.
Kenneth Grant
Kenneth Grant (1924–2011) was an English ceremonial magician and advocate of theThelemic
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word '' ...
religion. A poet, novelist, and writer, he founded his own Thelemic organisation, the Typhonian Ordo Templi Orientis—later renamed the Typhonian Order—with his wife Steffi Grant.
Grant was fascinated by the work of the occultist Aleister Crowley, having read a number of his books. Eager to meet Crowley, Grant wrote letters to Crowley's publishers, asking that they pass his letters on to Crowley himself. These eventually resulted in the first meeting between the two, in autumn 1944, at the Bell Inn in Buckinghamshire. After several further meetings and an exchange of letters, Grant agreed to work for Crowley as his secretary and personal assistant. Now living in relative poverty, Crowley was unable to pay Grant for his services in money, instead paying him in magical instruction.
In March 1945, Grant moved into a lodge cottage in the grounds of Netherwood, a Sussex boarding house where Crowley was living. He continued living there with Crowley for several months, dealing with the old man's correspondences and needs. In turn, he was allowed to read from Crowley's extensive library on occult subjects, and performed ceremonial magic workings with him, becoming a high initiate of Crowley's magical group, the Ordo Templi Orientis
Ordo Templi Orientis (O.T.O.; ) is an occult initiatory organization founded at the beginning of the 20th century. The origins of the O.T.O. can be traced back to the German-speaking occultists Carl Kellner, Heinrich Klein, Franz Hartmann and T ...
(O.T.O.). Crowley saw Grant as a potential leader of O.T.O. in the UK, writing in his diary, "value of Grant. If I die or go to the USA, there must be a trained man to take care of the English O.T.O."
Grant drew eclectically on a range of sources in devising his teachings. Although based in Thelema, Grant's Typhonian tradition has been described as "a ''bricolage'' of occultism, Neo-Vedanta, Hindu tantra, Western sexual magic, Surrealism, ufology and Lovecraftian gnosis". According to Djurdjevic, Grant's writing style is notorious for being opaque with "verbal and conceptual labyrinths". The historian of religion Manon Hedenborg White noted that "Grant's writings to not lend themselves easily to systematization". She added that he "deliberately employs cryptic or circuitous modes of argumentation", and lacks clear boundaries between fact and fiction.
Grant promoted what he termed the Typhonian or Draconian tradition of magic, and wrote that Thelema was only a recent manifestation of this wider tradition. In his books, he portrayed the Typhonian tradition as the world's oldest spiritual tradition, writing that it had ancient roots in Africa. The religious studies scholar Gordan Djurdjevic noted that Grant's historical claims regarding Typhonian history were "at best highly speculative" and lacked any supporting evidence, however he suggested that Grant may never have intended these claims to be taken literally.
Grant adopted a perennialist interpretation of the history of religion. Grant's wrote that Indian spiritual traditions like Tantra and Yoga correlate to Western esoteric traditions, and that both stem from a core, ancient source, has parallels in the perennial philosophy promoted by the Traditionalist School
The Traditionalist or Perennialist School is a group of 20th- and 21st-century thinkers who believe in the existence of a perennial wisdom or perennial philosophy, primordial and universal truths which form the source for, and are shared by, al ...
of esotericists. He believed that by mastering magic, one masters this illusory universe, gaining personal liberation and recognising that only the Self really exists. Doing so, according to Grant, leads to the discovery of one's true will, the central focus of Thelema.
Grant further wrote that the realm of the Self was known as "the Mauve Zone", and that it could be reached while in a state of deep sleep, where it has the symbolic appearance of a swamp. He also believed that the reality of consciousness, which he deemed the only true reality, was formless and thus presented as a void, although he also taught that it was symbolised by the Hindu goddess Kali
Kali (; sa, काली, ), also referred to as Mahakali, Bhadrakali, and Kalika ( sa, कालिका), is a Hindu goddess who is considered to be the goddess of ultimate power, time, destruction and change in Shaktism. In this tra ...
and the Thelemic goddess Nuit
Nuit (alternatively Nu, Nut, or Nuith) is a goddess in Thelema, the speaker in the first Chapter of ''The Book of the Law'', the sacred text written or received in 1904 by Aleister Crowley.
Based on the Ancient Egyptian sky goddess Nut, who ...
.
Grant's views on sex magic
Sex magic (sometimes spelled sex magick) is any type of sexual activity used in magical, ritualistic or otherwise religious and spiritual pursuits. One practice of sex magic is using sexual arousal or orgasm with visualization of a desired re ...
drew heavily on the importance of sexual dimorphism among humans and the subsequent differentiation of gender roles. Grant taught that the true secret of sex magic were bodily secretions, the most important of which was a woman's menstrual blood. In this he differed from Crowley, who viewed semen as the most important genital secretion. Grant referred to female sexual secretions as ''kalas'', a term adopted from Sanskrit. He thought that because women have kalas, they have oracular and visionary powers. The magical uses of female genital secretions are a recurring theme in Grant's writings.
James Lees
 James Lees (August 22, 1939 – 2015) was an English magician known for discovering the system he called English Qaballa.
Lees was born in Bolton, Lancashire. He established a career as an analytic chemistry, analytic chemist. In his search for truth, he also studied psychology. Not finding the answers he wanted from science, he turned to the study of astrology, even making a living for a time as a horary astrology, horary astrologer.
Still resolved to discover further answers, Lees decided to study Kabbalah and the Tree of life (Kabbalah), Tree of Life. From here he proceeded to experiment with invocations from the ''Key of Solomon''. Satisfied with the results, he proceeded to perform the 18-month working described in ''The Book of Abramelin'' by means of the Bornless Ritual. Having successfully invoked his Holy Guardian Angel, he turned his attention to ascending the 'Middle Pillar' of the Tree of Life, culminating with an experience known as crossing the abyss.
Then, in November 1976, Lees discovered the "order & value of the English Alphabet." Following this discovery, Lees founded the O∴A∴A∴ in order to assist others in the pursuit of their own spiritual paths. The first public report of the system known as English Qaballa (EQ) was published in 1979 by Ray Sherwin in an editorial in the final issue of his journal, ''The New Equinox''. Lees subsequently assumed the role of publisher of ''The New Equinox'' and, starting in 1981, published additional material about the EQ system over the course of five issues of the journal, extending into 1982.
In 1904, Aleister Crowley wrote out the text of the foundational document of his world-view, known as ''Liber AL vel Legis'', ''
James Lees (August 22, 1939 – 2015) was an English magician known for discovering the system he called English Qaballa.
Lees was born in Bolton, Lancashire. He established a career as an analytic chemistry, analytic chemist. In his search for truth, he also studied psychology. Not finding the answers he wanted from science, he turned to the study of astrology, even making a living for a time as a horary astrology, horary astrologer.
Still resolved to discover further answers, Lees decided to study Kabbalah and the Tree of life (Kabbalah), Tree of Life. From here he proceeded to experiment with invocations from the ''Key of Solomon''. Satisfied with the results, he proceeded to perform the 18-month working described in ''The Book of Abramelin'' by means of the Bornless Ritual. Having successfully invoked his Holy Guardian Angel, he turned his attention to ascending the 'Middle Pillar' of the Tree of Life, culminating with an experience known as crossing the abyss.
Then, in November 1976, Lees discovered the "order & value of the English Alphabet." Following this discovery, Lees founded the O∴A∴A∴ in order to assist others in the pursuit of their own spiritual paths. The first public report of the system known as English Qaballa (EQ) was published in 1979 by Ray Sherwin in an editorial in the final issue of his journal, ''The New Equinox''. Lees subsequently assumed the role of publisher of ''The New Equinox'' and, starting in 1981, published additional material about the EQ system over the course of five issues of the journal, extending into 1982.
In 1904, Aleister Crowley wrote out the text of the foundational document of his world-view, known as ''Liber AL vel Legis'', ''The Book of the Law
''Liber AL vel Legis'' (), commonly known as ''The Book of the Law'', is the central sacred text of Thelema. Aleister Crowley said that it was dictated to him by a beyond-human being who called himself ' Aiwass'. Rose Edith Kelly, Crowley's ...
''. In this text was the injunction found at verse 2:55; "Thou shalt obtain the order & value of the English Alphabet, thou shalt find new symbols to attribute them unto" which was understood by Crowley as referring to an English Qabalah yet to be developed or revealed.
The "order & value" discovered by James Lees lays the letters out on the grid superimposed on the page of manuscript of ''Liber AL'' on which this verse (Ch. III, v. 47) appears (sheet 16 of Chapter III). Also appearing on this page are a diagonal line and a circled cross. ''The Book of the Law'' states that the book should only be printed with Crowley's hand-written version included, suggesting that there are mysteries in the "chance shape of the letters and their position to one another" of Crowley's handwriting. Whichever top-left to bottom-right diagonal is read the magickal order of the letters is obtained.
Little further material on English Qaballa was published until the appearance of Jake Stratton-Kent's book, ''The Serpent Tongue: Liber 187'', in 2011. This was followed in 2016 by ''The Magickal Language of the Book of the Law: An English Qaballa Primer'' by Cath Thompson. The discovery, exploration, and continuing research and development of the system up to 2010, by James Lees and members of his group in England, are detailed in her 2018 book, ''All This and a Book''.
Nema Andahadna
Nema Andahadna (1939-2018) practiced and wrote about magic (magical working, as defined by Aleister Crowley) for over thirty years. In 1974, she Mediumship#Channeling, channelled a short book called ''Wikisource:Liber Pennae Praenumbra, Liber Pennae Praenumbra''. From her experience withThelemic
Thelema () is a Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. The word '' ...
magic, she developed her own system of magic called "Maat Magick" which has the aim of transforming the human race. In 1979, she co-founded the Horus-Maat Lodge. The Lodge and her ideas have been featured in the writings of Kenneth Grant.
Her writings have appeared in many publications, including the ''Cincinnati Journal of Ceremonial Magick'', ''Aeon'', and ''Starfire''. According to Donald Michael Kraig:
Components
Grimoires
 A
A grimoire
A grimoire ( ) (also known as a "book of spells" or a "spellbook") is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and ...
is a textbook of magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical Spell (paranormal), spells, Spell (paranormal), charms and divination, and how to evocation, summon or invocation, invoke supernatural entities such as angels, Ghost, spirits, Deity, deities, and demons. In many cases, the books themselves are believed to be imbued with magical powers, although in many cultures, other sacred texts that are not grimoires (such as the Bible) have been believed to have supernatural properties intrinsically. The only contents found in a grimoire would be information on spells, rituals, the preparation of magical tools, and lists of ingredients and their magical correspondences. In this manner, while all ''books on magic'' could be thought of as grimoires, not all ''magical books'' should be thought of as grimoires.
While the term ''grimoire'' is originally European—and many Europeans throughout history, particularly ceremonial magicians and cunning folk, have used grimoires—the historian Owen Davies (historian), Owen Davies noted that similar books can be found all around the world, ranging from Jamaica to Sumatra. He also noted that in this sense, the world's first grimoires were created in Europe and the Ancient Near East.
Magical formulae
 A magical formula or 'word of power' is a word that is believed to have specific supernatural effects. They are words whose meaning illustrates principles and degrees of understanding that are often difficult to relay using other forms of speech or writing. It is a concise means to communicate very abstract information through the medium of a word or phrase.
These words often have no intrinsic meaning in and of themselves. However, when deconstructed, each individual letter may refer to some universal concept found in the system that the formula appears. Additionally, in grouping certain letters together one is able to display meaningful sequences that are considered to be of value to the spiritual system that utilizes them (e.g., spiritual hierarchies, historiographic data, psychological stages, etc.)
A formula's potency is understood and made usable by the magician only through prolonged meditation on its levels of meaning. Once these have been interiorized by the magician, they may then utilize the formula to maximum effect.
A magical formula or 'word of power' is a word that is believed to have specific supernatural effects. They are words whose meaning illustrates principles and degrees of understanding that are often difficult to relay using other forms of speech or writing. It is a concise means to communicate very abstract information through the medium of a word or phrase.
These words often have no intrinsic meaning in and of themselves. However, when deconstructed, each individual letter may refer to some universal concept found in the system that the formula appears. Additionally, in grouping certain letters together one is able to display meaningful sequences that are considered to be of value to the spiritual system that utilizes them (e.g., spiritual hierarchies, historiographic data, psychological stages, etc.)
A formula's potency is understood and made usable by the magician only through prolonged meditation on its levels of meaning. Once these have been interiorized by the magician, they may then utilize the formula to maximum effect.
Magical weapons
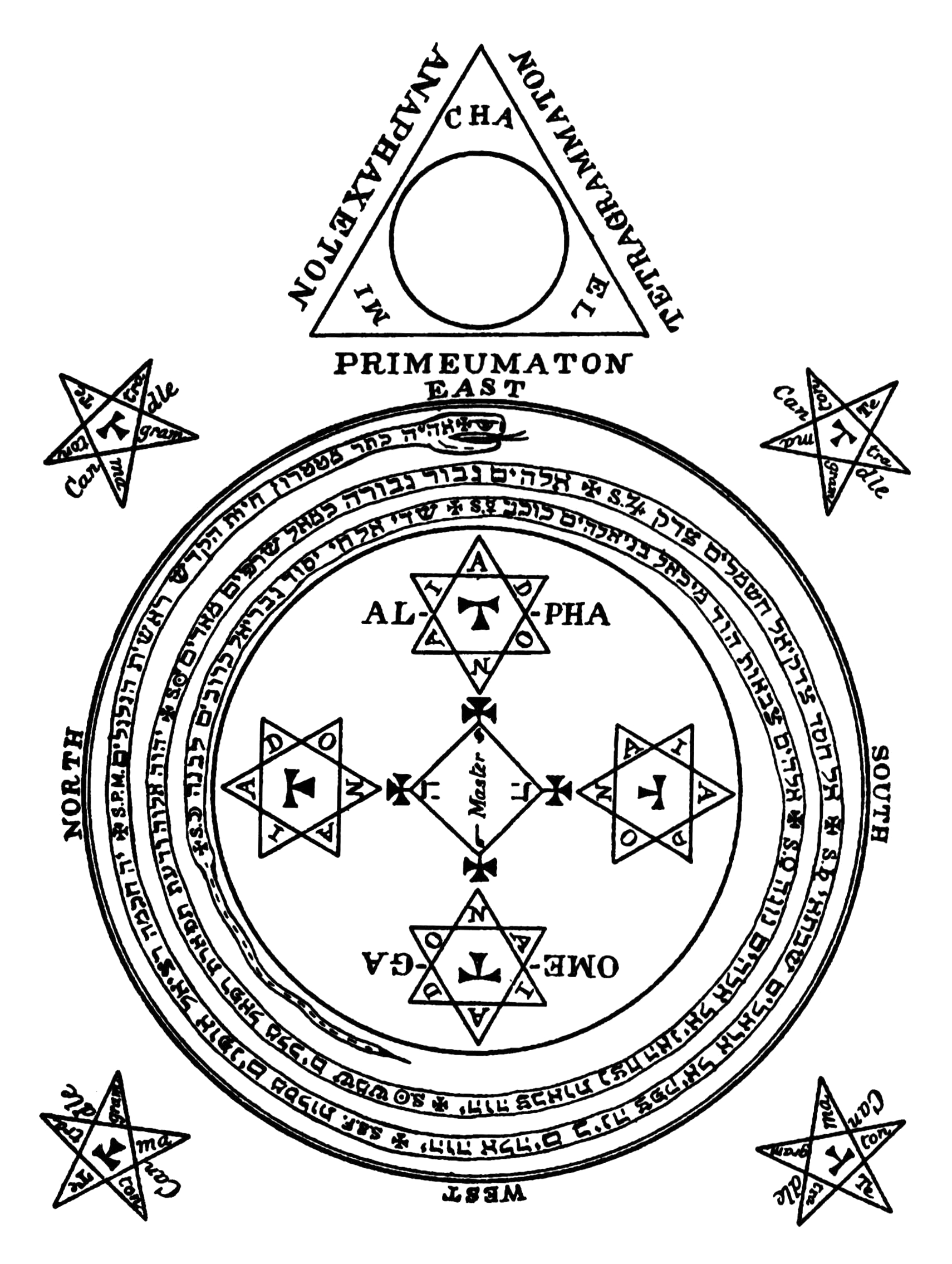
The practice of ceremonial magic often requires tools made or consecrated specifically for this use, called magical weapons, which are required for a particular ritual or series of rituals. They may be a symbolic representation of psychological elements of the magician or of metaphysical concepts. In ''Magick (Book 4)'', Part II ''(Magick)'', Aleister Crowley lists the tools required as a magic circle drawn on the ground and inscribed with the names of god, an altar, a wand, cup, sword, and pentacle, to represent his true will, his Binah (Kabbalah), understanding, his reason, and the lower parts of his being respectively. On the altar, too, is a phial of Abramelin oil, oil to represent his aspiration, and for consecrating items to his intent. The magician is surrounded by a scourge, dagger, and chain intended to keep his intent pure. An oil lamp, Grimoire, book of conjurations and bell are required, as is the wearing of a crown, robe, and Lamen (magic), lamen. The crown affirms his divinity, the robe symbolizes silence, and the lamen declare his work. The book of conjurations is his magical record, his karma. In the East is the Thurible, magic fire in which all burns up at last.Vibration of god-names
In magical rituals involving the invocation of deities, a vocal technique called ''vibration'' is commonly used. This was a basic aspect of magical training for Crowley, who described it in "Liber O." According to that text, vibration involves a physical set of steps, starting in a standing position, breathing in through the nose while imagining the name of the god entering with the breath, imagining that breath travelling through the entire body, stepping forward with the left foot while throwing the body forward with arms outstretched, visualizing the name rushing out when spoken, ending in an upright stance, with the right forefinger placed upon the lips. According to Crowley in "Liber O", success in this technique is signaled by physical exhaustion and "though only by the student himself is it perceived, when he hears the name of the God vehemently roared forth, as if by the concourse of ten thousand thunders; and it should appear to him as if that Great Voice proceeded from the Universe, and not from himself." In general ritual practice, ''vibration'' can also refer to a technique of saying a god-name or a magical formula in a long, drawn-out fashion (i.e. with a full, deep breath) that employs the nasal passages, such that the sound feels and sounds "vibrated'.Techniques
According to Crowley, there is a single definition of the purpose for ritual magic: to achieve Union with God through "the uniting of the Microcosm with the Macrocosm." Since this process is so arduous, it is also acceptable to use magic to develop the self (i.e. one's body of light) or to create ideal circumstances for the Work (e.g. having access to a place in which to do ritual undisturbed). There are many kinds of magic, but the categories of ritual that are recommended by Crowley include: # Banishing—the elimination of unwanted forces. "The Magician must therefore take the utmost care in the matter of purification, firstly, of himself, secondly, of his instruments, thirdly, of the place of working." # Invocation, where the magician identifies with the Deity invoked. There are three methods: #* ''Buddhist devotion, Devotion'' —where "identity with the God is attained by love and by surrender, by giving up or suppressing all irrelevant (and illusionary) parts of yourself." #* ''Calling forth''—where "identity is attained by paying special attention to the desired part of yourself: positive, as the first method is negative." (e.g. assumption of godforms) #* ''Drama''—where "identity is attained by sympathy. It is very difficult for the ordinary man to lose himself completely in the subject of a play or of a novel; but for those who can do so, this method is unquestionably the best." (e.g. many initiations and the Gnostic Mass) # Evocation—which is bringing a spiritual being ''before'', not ''into'', the magician (e.g. goetia) # Eucharisticritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized ...
—which "consists in taking common things, transmuting them into things divine, and consuming them."
# Consecration—"the active dedication of a thing to a single purpose."
# Divination—such as the use of the Thoth Tarot or other tools used to gather information.
Banishing
The purpose of banishing rituals is to eliminate forces that might interfere with a magical operation, and they are often performed at the beginning of an important event or ceremony (although they can be performed for their own sake as well). The area of effect can be a magic circle or a room. The general theory of magic proposes that there are various forces which are represented by the classical elements (air, earth, fire, and water), the planets, the signs of the Zodiac, and adjacent spaces in the astral world. There are many banishing rituals, but most are some variation on two of the most common—"The Star Ruby" and the Lesser Banishing Ritual of the Pentagram. Crowley describes banishing in his ''Magick, Book 4'' (ch.13): He further states:Purification
Purification is similar in theme to banishing, but is a more rigorous process of preparing the self and her temple for serious spiritual work. Crowley mentions that ancient magicians would purify themselves through arduous programs, such as through special diets, fasting, sexual abstinence, keeping the body meticulously tidy, and undergoing a complicated series of prayers. He goes on to say that purification no longer requires such activity, since the magician can purify the self via willed intention. Specifically, the magician labors to purify the mind and body of all influences which may interfere with the Great Work: Crowley recommended symbolically ritual practices, such as bathing and robing before a main ceremony: "The bath signifies the removal of all things extraneous or antagonistic to the one thought. The putting on of the robe is the positive side of the same operation. It is the assumption of the frame of mind suitable to that one thought."Consecration
Consecration is an equally important magical operation. It is essentially the dedication, usually of a ritual instrument or space, to a specific purpose. In ''Magick, Book 4'' (ch.13), Crowley writes:Invocation
 Invocation is the bringing in or identifying with a particular deity or spirit. Crowley wrote of two keys to success in this arena: to "inflame thyself in praying" and to "invoke often". For Crowley, the single most important invocation, or any act of magic for that matter, was the invocation of one's Holy Guardian Angel, or "secret self", which allows the adept to know his or her true will.
Crowley describes the experience of invocation:
Crowley (''Magick, Book 4'') discusses three main categories of invocation, although "in the great essentials these three methods are one. In each case the magician identifies himself with the Deity invoked."
*''Devotion''—where "identity with the God is attained by love and by surrender, by giving up or suppressing all irrelevant (and illusionary) parts of yourself."
*''Calling forth''—where "identity is attained by paying special attention to the desired part of yourself."
*''Drama''—where "identity is attained by sympathy. It is very difficult for the ordinary man to lose himself completely in the subject of a play or of a novel; but for those who can do so, this method is unquestionably the best."
Another invocatory technique that the magician can employ is called the assumption of godforms — where with "concentrated imagination of oneself in the symbolic shape of any God, one should be able to identify oneself with the idea which [the god] represents." A general method involves positioning the body in a position that is typical for a given god, imagining that the image of the god is coinciding with or enveloping the body, accompanied by the practice of "vibration" of the appropriate god-name(s).
Invocation is the bringing in or identifying with a particular deity or spirit. Crowley wrote of two keys to success in this arena: to "inflame thyself in praying" and to "invoke often". For Crowley, the single most important invocation, or any act of magic for that matter, was the invocation of one's Holy Guardian Angel, or "secret self", which allows the adept to know his or her true will.
Crowley describes the experience of invocation:
Crowley (''Magick, Book 4'') discusses three main categories of invocation, although "in the great essentials these three methods are one. In each case the magician identifies himself with the Deity invoked."
*''Devotion''—where "identity with the God is attained by love and by surrender, by giving up or suppressing all irrelevant (and illusionary) parts of yourself."
*''Calling forth''—where "identity is attained by paying special attention to the desired part of yourself."
*''Drama''—where "identity is attained by sympathy. It is very difficult for the ordinary man to lose himself completely in the subject of a play or of a novel; but for those who can do so, this method is unquestionably the best."
Another invocatory technique that the magician can employ is called the assumption of godforms — where with "concentrated imagination of oneself in the symbolic shape of any God, one should be able to identify oneself with the idea which [the god] represents." A general method involves positioning the body in a position that is typical for a given god, imagining that the image of the god is coinciding with or enveloping the body, accompanied by the practice of "vibration" of the appropriate god-name(s).
Evocation
There is a distinct difference between invocation and evocation, as Crowley explains: Generally, evocation is used for two main purposes: to gather information and to obtain the services or obedience of a spirit or demon. Crowley believed that the most effective form of evocation was found in the grimoire on Goetia (see below), which instructs the magician in how to safely summon forth and command 72 infernal spirits. However, it is equally possible to evoke angelic beings, gods, and other intelligences related to planets, elements, and the Zodiac. Unlike with invocation, which involves a calling in, evocation involves a calling forth, most commonly into what is called the "triangle of art."Eucharist
The word ''eucharist'' originally comes from the Greek word for thanksgiving. However, within magic, it takes on a special meaning—the transmutation of ordinary things (usually food and drink) into divine sacraments, which are then consumed. The object is to infuse the food and drink with certain properties, usually embodied by various deities, so that the adept takes in those properties upon consumption. Crowley describes the process of the regular practice of eucharistic ritual: There are several eucharistic rituals within the magical canon. Two of the most well known are The Mass of the Phoenix and The Gnostic Mass. The first is a ritual designed for the individual, which involves sacrificing a "Cake of Light" (a type of bread that serves as the host) to Ra (i.e. the Sun) and infusing a second Cake with the adept's own blood (either real or symbolic, in a gesture reflecting the myth of the Pelican cutting its own breast to feed its young) and then consuming it with the words, "There is no grace: there is no guilt: This is the Law: Do what thou wilt!" The other ritual, The Gnostic Mass, is a very popular public ritual (although it can be practiced privately) that involves a team of participants, including a Priest and Priestess. This ritual is an enactment of the mystical journey that culminates with the Mystic Marriage and the consumption of a Cake of Light and a goblet of wine (a process termed "communication"). Afterwards, each Communicant declares, "There is no part of me that is not of the gods!"Divination
The art of divination is generally employed for the purpose of obtaining information that can guide the adept in his Great Work (Hermeticism), Great Work. The underlying theory states that there exists intelligences (either outside of or inside the mind of the diviner) that can offer accurate information within certain limits using a language of symbols. Normally, divination within magic is not the same as fortune telling, which is more interested in predicting future events. Rather, divination tends to be more about discovering information about the nature and condition of things that can help the magician gain insight and to make better decisions. There are literally hundreds of different divinatory techniques in the world. However, Western occult practice mostly includes the use ofastrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
(calculating the influence of heavenly bodies), bibliomancy (reading random passages from a book, such as Liber Legis or the I Ching), Thoth Tarot (a deck of 78 cards, each with symbolic meaning, usually laid out in a meaningful pattern), and geomancy
Geomancy ( Greek: γεωμαντεία, "earth divination") is a method of divination that interprets markings on the ground or the patterns formed by tossed handfuls of soil, rocks, or sand. The most prevalent form of divinatory geomancy in ...
(a method of making random marks on paper or in earth that results in a combination of sixteen patterns).
It is an accepted truism within magic that divination is imperfect. As Crowley writes, "In estimating the ultimate value of a divinatory judgment, one must allow for more than the numerous sources of error inherent in the process itself. The judgment can do no more than the facts presented to it warrant. It is naturally impossible in most cases to make sure that some important factor has not been omitted [...] One must not assume that the oracle is omniscient."
Other magical practices
Qabalah and the Tree of Life
The Tree of Life is a tool used to categorize and organize various Mysticism, mystical concepts. At its most simple level, it is composed of ten spheres, or emanations, called Sephirot (Kabbalah), sephiroth (sing. "sephira") which are connected by twenty two paths. The sephiroth are represented by the planets and the paths by the characters of the Hebrew alphabet, which are subdivided by the four classical elements, the seven classical planets, and the twelve signs of the Zodiac. Within the western magical tradition, the Tree is used as a kind of conceptual filing cabinet. Each sephira and path is assigned various ideas, such as gods, cards of the Tarot, astrological planets and signs, elements, etc. Crowley considered a deep understanding of the Tree of Life to be essential to the magician: Similar to yoga, learning the Tree of Life is not so much magic as it is a way to map out one's spiritual universe. As such, the adept may use the Tree to determine a destination for astral travel, to choose which gods to invoke for what purposes, et cetera. It also plays an important role in modeling the spiritual journey, where the adept begins in Malkuth, which is the every-day material world of phenomena, with the ultimate goal being at Kether, the sphere of Unity with the All.Body of light
The body of light, sometimes called the 'astral body' or the 'subtle body,' is a "quasi material" aspect of the human body, being neither solely physical nor solely spiritual, posited by a number of philosophers, and elaborated on according to various Western esotericism, esoteric, occult, and mysticism, mystical teachings. Other terms used for this body include body of glory, spirit-body, radiant body, luciform body, ''augoeides'' ('radiant'), ''astroeides'' ('starry' or 'sidereal body'), and celestial body. Crowley referred to the ''augoeides'', a Greek term for the body of light, and connected it with 'the Knowledge & Conversation of the Holy Guardian Angel' associated with each human being. He stressed that the body of light must be built up though the use of imagination, and that it must then be animated, exercised, and disciplined. According to Asprem (2017):Magical record
A magical record is a journal or other source of documentation containing magical events, experiences, ideas, and any other information that the magician may see fit to add. There can be many purposes for such a record, such as recording evidence to verify the effectiveness of specific procedures (per the scientific method that Aleister Crowley claimed should be applied to the practice of magic) or to ensure that data may propagate beyond the lifetime of the magician. Benefits of this process vary, but usually include future analysis and further education by the individual and/or associates with whom the magician feels comfortable in revealing such intrinsically private information. Crowley was highly insistent upon the importance of this practice. As he writes in Liber E, "It is absolutely necessary that all experiments should be recorded in detail during, or immediately after, their performance ... The more scientific the record is, the better. Yet the emotions should be noted, as being some of the conditions. Let then the record be written with sincerity and care; thus with practice it will be found more and more to approximate to the ideal." Other items he suggests for inclusion include the physical and mental condition of the experimenter, the time and place, and environmental conditions, including the weather.See also
* * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Citations
Works cited
Primary sources
* * * * * * * * * * Contains a lengthy account of the writing of Nema's ''Liber Pennae Praenumbra''. * Contains a photo facsimile of ''Liber Pennae Praenumbra''. * *Secondary sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *. * * * *Further reading
* * * * {{Witchcraft Ceremonial magic, Magic (supernatural) Thelema Western esotericism Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn