|
Eutus Rastaca
Clofedanol ( INN) or chlophedianol (BAN) is a centrally acting cough suppressant used in the treatment of dry cough. Clofedanol has local anesthetic, antispasmodic, and antihistamine properties, and may have anticholinergic effects at high doses. Side effects Adverse effects may include irritability, drowsiness, nightmares, vertigo, nausea or vomiting, visual disturbances or hallucinations, and urticaria. There are potential interactions with other anticholinergics, CNS depressants, and alcohol. Pharmacology Unlike many other antitussive drugs such as dextromethorphan, it binds poorly to the sigma-1 receptor. Society and culture Chlophedianol was approved for OTC status in 1987 by the FDA OTC monograph process and its safety and efficacy data are limited. It was formerly sold over-the-counter in the United States under the trade name Ulo, as a syrup with a dosage of 25 mg/5 mL; however, it has been withdrawn from the market. It is marketed in Canada under the trade name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma-1 Receptor
The sigma-1 receptor (σ1R), one of two sigma receptor subtypes, is a chaperone protein at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that modulates calcium signaling through the IP3 receptor. In humans, the σ1 receptor is encoded by the ''SIGMAR1'' gene. The σ1 receptor is a transmembrane protein expressed in many different tissue types. It is particularly concentrated in certain regions of the central nervous system. It has been implicated in several phenomena, including cardiovascular function, schizophrenia, clinical depression, the effects of cocaine abuse, and cancer. Much is known about the binding affinity of hundreds of synthetic compounds to the σ1 receptor. An endogenous ligand for the σ1 receptor has yet to be conclusively identified, but tryptaminergic trace amines and neuroactive steroids have been found to activate the receptor. Especially progesterone, but also testosterone, pregnenolone sulfate, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) bind to the σ1 receptor. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications. Preparation The two main preparatory routes to aryl halides are direct halogenation and via diazonium salts. Direct halogenation In the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, Lewis acids serve as catalysts. Many metal chlorides are used, examples include iron(III) chloride or aluminium chloride. The most important aryl halide, chlorobenzene is produced by this route. Monochlorination of benzene is always accompanied by formation of the dichlorobenzene derivatives. Arenes with electron donating groups react with halogens even in the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H1 Receptor Antagonists
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action but are not true antihistamines. In common use, the term "antihistamine" refers only to H1-antihistamines. Virtually all H1-antihistamines function as inverse agonists at the histamine H1-receptor, as opposed to neutral antagonists, as was previously believed. Medical uses H1-antihistamines are clinically used in the treatment of histamine-mediated allergic conditions. These indications may include:Rossi S (Ed.) (2004). ''Australian Medicines Handbook 2004''. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook. * Allergic rhinitis * Allergic conjunctivitis * Allergic dermatological conditions (contact dermatitis) * Rhinorrhea (runny nose) * Urticaria * Angi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antitussives
Cold medicines are a group of medications taken individually or in combination as a treatment for the symptoms of the common cold and similar conditions of the upper respiratory tract. The term encompasses a broad array of drugs, including analgesics, antihistamines and decongestants, among many others. It also includes drugs which are marketed as cough suppressants or antitussives, but their effectiveness in reducing cough symptoms is unclear or minimal. While they have been used by 10% of American children in any given week, they are not recommended in Canada or the United States in children six years or younger because of lack of evidence showing effect and concerns of harm. In 2020, one version containing codeine and guaifenesin was the 377th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States with more than 400thousand prescriptions. Types There are a number of different cough and cold medications, which may be used for various coughing symptoms. The commercially a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azacyclonol
Azacyclonol (trade names Ataractan, Calmeran, Frenoton, Frenquel, Psychosan), also known as γ-pipradrol, is a drug which is an ataractive; an agent which diminishes hallucinations in psychotic individuals. It has also been called a tranquilizer and antipsychotic, though these definitions are not accurate as it does not actually possess such properties. Despite being a positional isomer of pipradrol, it is not a psychostimulant, and instead has mild depressant effects. The drug was introduced in Europe in the mid-1950s for the treatment of schizophrenia likely because it was found to attenuate the subjective psychedelic effects of LSD and mescaline in humans. However, due to poor and mixed clinical effectiveness, it never gained widespread acceptance and was eventually discontinued. Azacyclonol is also known as diphenylmethanolpiperidine and is the parent structure of the antihistamines fexofenadine and terfenadine. Terfenadine produces azacyclonol as a major active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
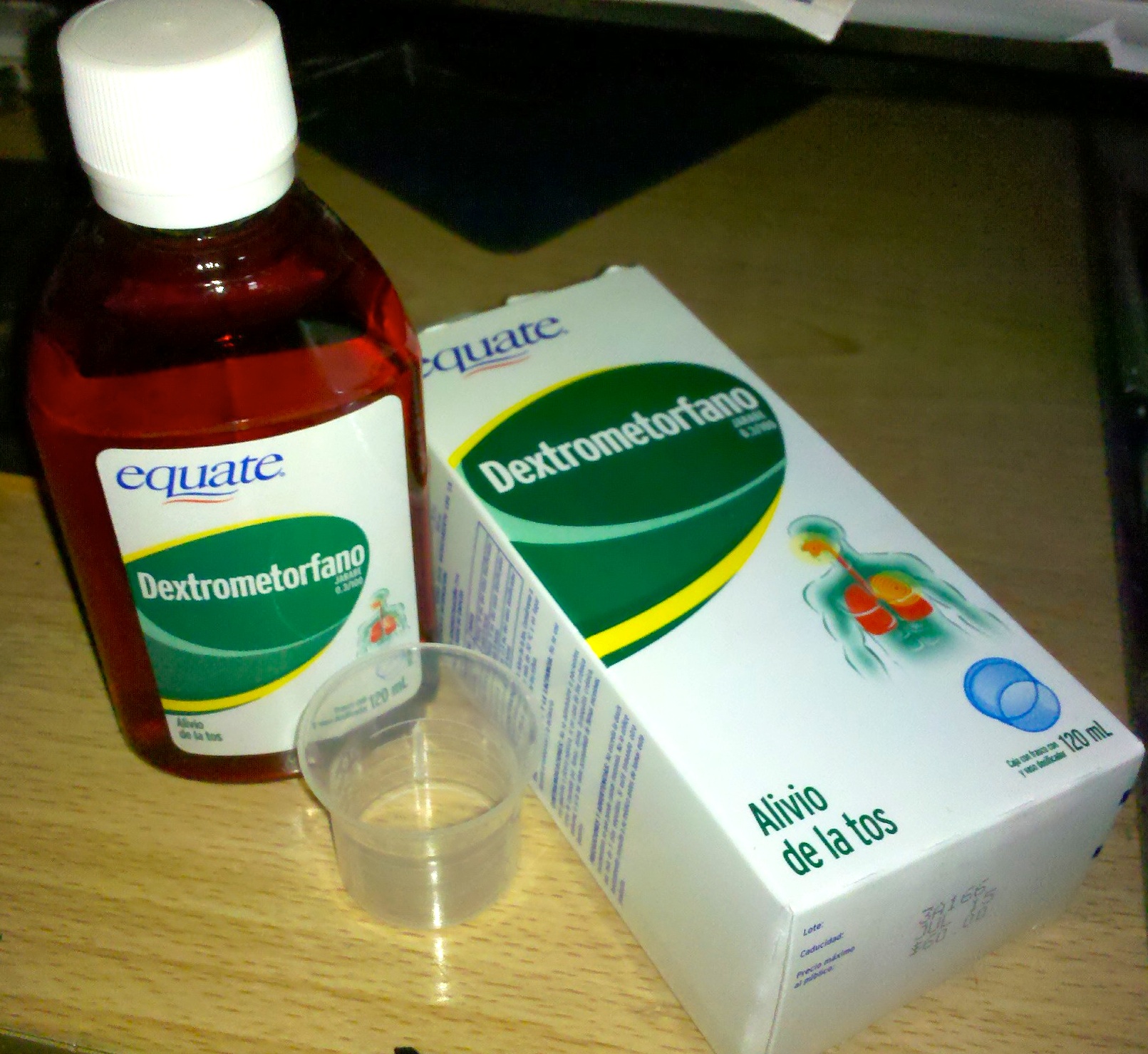
Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a medication most often used as a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It is sold in syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge forms. In 2022, the FDA approved a formulation of it combined with bupropion named Auvelity to serve as a rapid acting antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder. It is in the morphinan class of medications with sedative, dissociative, and stimulant properties (at lower doses). Dextromethorphan does not have a significant affinity for the mu-opioid receptor activity typical of morphinan compounds and exerts its therapeutic effects through several other receptors. In its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as a white powder. Dextromethorphan is also used recreationally. When exceeding approved dosages, dextromethorphan acts as a dissociative hallucinogen. It has multiple mechanisms of action, including actions as a nonselective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and a sigma-1 receptor agonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Approved Name
A British Approved Name (BAN) is the official, non-proprietary, or generic name given to a pharmaceutical substance, as defined in the British Pharmacopoeia (BP). The BAN is also the official name used in some countries around the world, because starting in 1953, proposed new names were evaluated by a panel of experts from WHO in conjunction with the BP commission to ensure naming consistency worldwide (an effort leading to the International Nonproprietary Name system). There is also a British Approved Name (Modified) (BANM). Combination preparations BANs are unique in that names are assigned for combination preparations as well as single-drug preparations. For example, the BAN Co-amoxiclav is assigned to preparations containing amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Most other pharmacopoeias simply refer to combination products by both ingredients in the preparation, in this example "amoxicillin with clavulanic acid". The prefix of "co-" is used for many combination drugs, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urticaria
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-lasting skin change. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs. Hives frequently occur following an infection or as a result of an allergic reaction such as to medication, insect bites, or food. Psychological stress, cold temperature, or vibration may also be a trigger. In half of cases the cause remains unknown. Risk factors include having conditions such as hay fever or asthma. Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. Prevention is by avoiding whatever it is that causes the condition. Treatment is typically with antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and cetirizine. In severe cases, corticosteroids or leukotriene inhibitors may also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the neurotransmitter called acetylcholine (ACh) at synapses in the central and peripheral nervous system. These agents inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system by selectively blocking the binding of ACh to its receptor in nerve cells. The nerve fibers of the parasympathetic system are responsible for the involuntary movement of smooth muscles present in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, lungs, sweat glands, and many other parts of the body. In broad terms, anticholinergics are divided into two categories in accordance with their specific targets in the central and peripheral nervous system and at the neuromuscular junction: antimuscarinic agents, and antinicotinic agents ( ganglionic blockers, neuromuscular blockers). The term "anticholinergic" is typically used to refer to antimuscarinics which competitively inhibit the binding of ACh to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors; such agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |