|
Eurybacteria
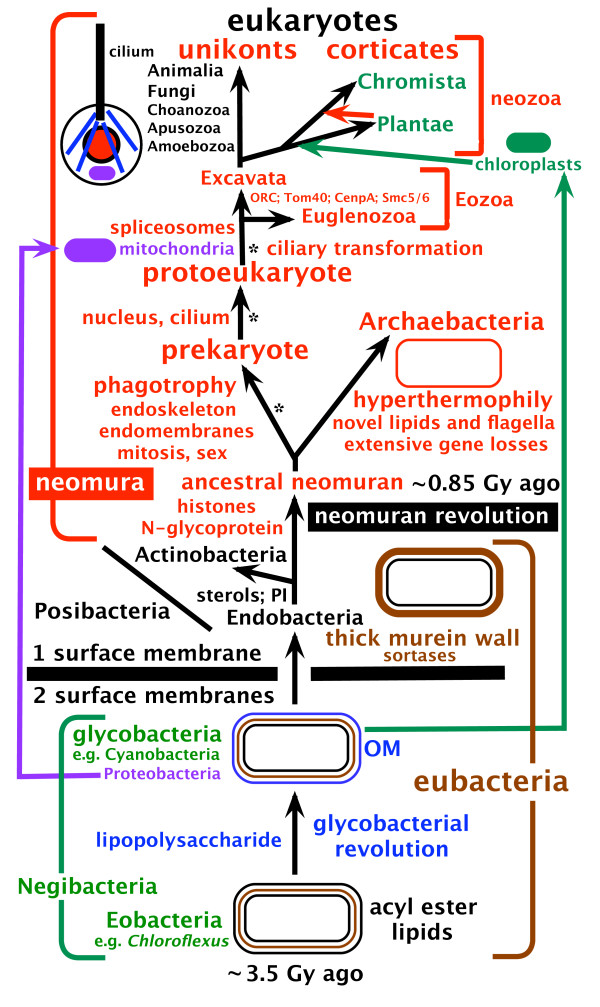
Eurybacteria is a taxon created by Cavalier-Smith, which includes several groups of Gram-negative bacteria. In this model, it is the ancestor of gram positive bacteria. Their endospores are characterized by producing and presenting external flagella or mobility by bacterial displacement. Members Specifically, it includes: * Fusobacteria. For example, '' Leptotrichia'' and ''Fusobacterium'' * Togobacteria. For example, ''Thermotoga''. In the standard classification, Selenobacteria are usually included in the phylum Bacillota, whereas fusobacteria and togobacteria are classified as their own groups. Relationships The following graph shows Cavalier-Smith Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to disc ...'s version of the tree of life, indicating the status of eurybacteria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermotogota
The Thermotogota are a phylum of the domain Bacteria. The phylum Thermotogota is composed of Gram-negative staining, anaerobic, and mostly thermophilic and hyperthermophilic bacteria.Gupta, RS (2014) The Phylum Thermotogae. The Prokaryotes 989-1015. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. Characteristics The name of this phylum is derived from the existence of many of these organisms at high temperatures along with the characteristic sheath structure, or "toga", surrounding the cells of these species.Reysenbach, A.-L. (2001) Phylum BII. Thermotogae phy. nov. In: Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, pp. 369-387. Eds D. R. Boone, R. W. Castenholz. Springer-Verlag: Berlin. Recently, some Thermotogota existing at moderate temperatures have also been identified. Although Thermotogota species exhibit Gram-negative staining, they are bounded by a single-unit lipid membrane, hence they are monoderm bacteria. Because of the ability of some Thermotogota species to thrive at high temperatures, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusobacteriota
Fusobacteriota are obligately anaerobic non-sporeforming Gram-negative bacilli. Since the first reports in the late nineteenth century, various names have been applied to these organisms, sometimes with the same name being applied to different species. More recently, not only have there been changes to the nomenclature, but also attempts to differentiate between species which are believed to be either pathogenic or commensal or both. Because of their asaccharolytic nature, and a general paucity of positive results in routine biochemical tests, laboratory identification of the Fusobacteriota has been difficult. However, the application of novel molecular biological techniques to taxonomy has established a number of new species, together with the subspeciation of ''Fusobacterium necrophorum'' and ''F. nucleatum'', and provided new methods for identification. The involvement of Fusobacteriota in a wide spectrum of human infections causing tissue necrosis and septicaemia has long bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endospores
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not an offspring). It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of ''Bacillus marismortui'' in salt crystals approximately 250 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusobacterium
''Fusobacterium'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-negative, non-sporeforming bacteria belonging to Gracilicutes. Individual cells are slender, rod-shaped bacilli with pointed ends. Strains of ''Fusobacterium'' cause several human diseases, including periodontal diseases, Lemierre's syndrome, and topical skin ulcers. Although older sources state that ''Fusobacterium'' is part of the normal flora of the human oropharynx, the current consensus is that ''Fusobacterium'' should always be treated as a pathogen. ''F. prausnitzii'', a gut commensal associated with healthy patients, was completely reclassified as ''Faecalibacterium'' (''Clostridiales'':''Ruminococcaceae'') in 2002. Clinical relevance ''Fusobacterium'' is often associated with ulcerative colitis. Research of colon cancer has also shown an overrepresentation of ''Fusobacterium'', both in feces of patients and tumor issue itself. Whether ''Fusobacterium'' causes these diseases or only colonizes existing tumours, remains undete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermotoga
''Thermotoga'' is a genus of the phylum ''Thermotogota''. Members of ''Thermotoga'' are hyperthermophilic bacteria whose cell is wrapped in a unique sheath-like outer membrane, called a "toga". The members of the phylum stain Gram-negative as they possess a thin peptidoglycan in between two lipid bilayers, albeit both peculiar. The peptidoglycan is unusual as the crosslink is not only meso-diaminopimelate as occurs in Pseudomonadota, but D-lysine.All proteinogenic amino acids have the L- configuration; in peptidoglycan some amino acids with the D- configuration are present. Lysine is synthesised from meso-diaminopimelate by Diaminopimelate decarboxylase The species are anaerobes with varying degrees of oxygen tolerance. They are capable of reducing elemental sulphur (S0) to hydrogen sulphide, which in turn can be used. Whether thermophily is an innovation of the lineage or an ancestral trait is unclear and cannot be determined. The genome of '' Thermotoga maritima'' was sequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenobacteria
The Negativicutes are a class of bacteria in the phylum Bacillota, whose members have a peculiar cell wall with a lipopolysaccharide outer membrane which stains gram-negative, unlike most other members of the Bacillota. Although several neighbouring ''Clostridia'' species (firmicute bacteria) also stain gram-negative, the proteins responsible for the unusual diderm structure of the ''Negativicutes'' may have actually been laterally acquired from Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria). Additional research is required to confirm the origin of the diderm cell envelope in the Negativicutes. Most members of this class are obligate anaerobes, and occur in habitats such as rivers, lakes, and the intestines of vertebrates. They range from spherical forms, such as ''Megasphaera'' and ''Veillonella'', to curved rods, as typified by the selenomonads. ''Selenomonas'' has a characteristic crescent shape, with flagella inserted on the concave side, while ''Sporomusa'' is similar, but nonmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The name "Firmicutes" was derived from the Latin words for "tough skin," referring to the thick cell wall typical of bacteria in this phylum. Scientists once classified the Firmicutes to include all gram-positive bacteria, but have recently defined them to be of a core group of related forms called the low- G+C group, in contrast to the Actinomycetota. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Firmicutes, such as ''Megasphaera'', ''Pectinatus'', ''Selenomonas'' and ''Zymophilus'', have a porous pseudo-outer membrane that causes them to stain gram-negative. Many Bacillota (Firmicutes) produce endospores, which are resistant to desiccation and can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |