|
Euplerinae
Euplerinae, more commonly known as malagasy civets, is a subfamily of carnivorans that includes four species restricted to Madagascar. Together with the subfamily Galidiinae, which also only occurs on Madagascar, it forms the family Eupleridae. Members of this subfamily, which include the fossa (''Cryptoprocta ferox''), falanoucs (''Eupleres goudotii'' and ''Eupleres major'') and Malagasy civet (''Fossa fossana''), were placed in families like Felidae and Viverridae before genetic data indicated their consanguinity with other Madagascar carnivorans. Within the subfamily, the falanouc and Malagasy civet are more closely related to each other than to the fossa. Classification Phylogenetic tree The phylogenetic relationships of Malagasy civets (Euplerinae) are shown in the following cladogram: See also * List of mammals of Madagascar This is a list of the native wild mammal species recorded in Madagascar. As of June 2014 (following the IUCN reassessment of the lemurs) there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupleridae
Eupleridae is a family of carnivorans endemic to Madagascar and comprising 10 known living species in seven genera, commonly known as euplerids, Malagasy mongooses or Malagasy carnivorans. The best known species is the fossa (''Cryptoprocta ferox''), in the subfamily Euplerinae. All species of Euplerinae were formerly classified as viverrids, while all species in the subfamily Galidiinae were classified as herpestids. Recent molecular studies indicate that the 10 living species of Madagascar carnivorans evolved from one ancestor that is thought to have rafted over from mainland Africa 18–24 million years ago. This makes Malagasy carnivorans a clade. They are closely allied with the true herpestid mongooses, their closest living relatives. The fossa and the Malagasy civet (''Fossa fossana'') are each evolutionarily quite distinct from each other and from the rest of the clade. All Eupleridae are considered threatened species due to habitat destruction, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
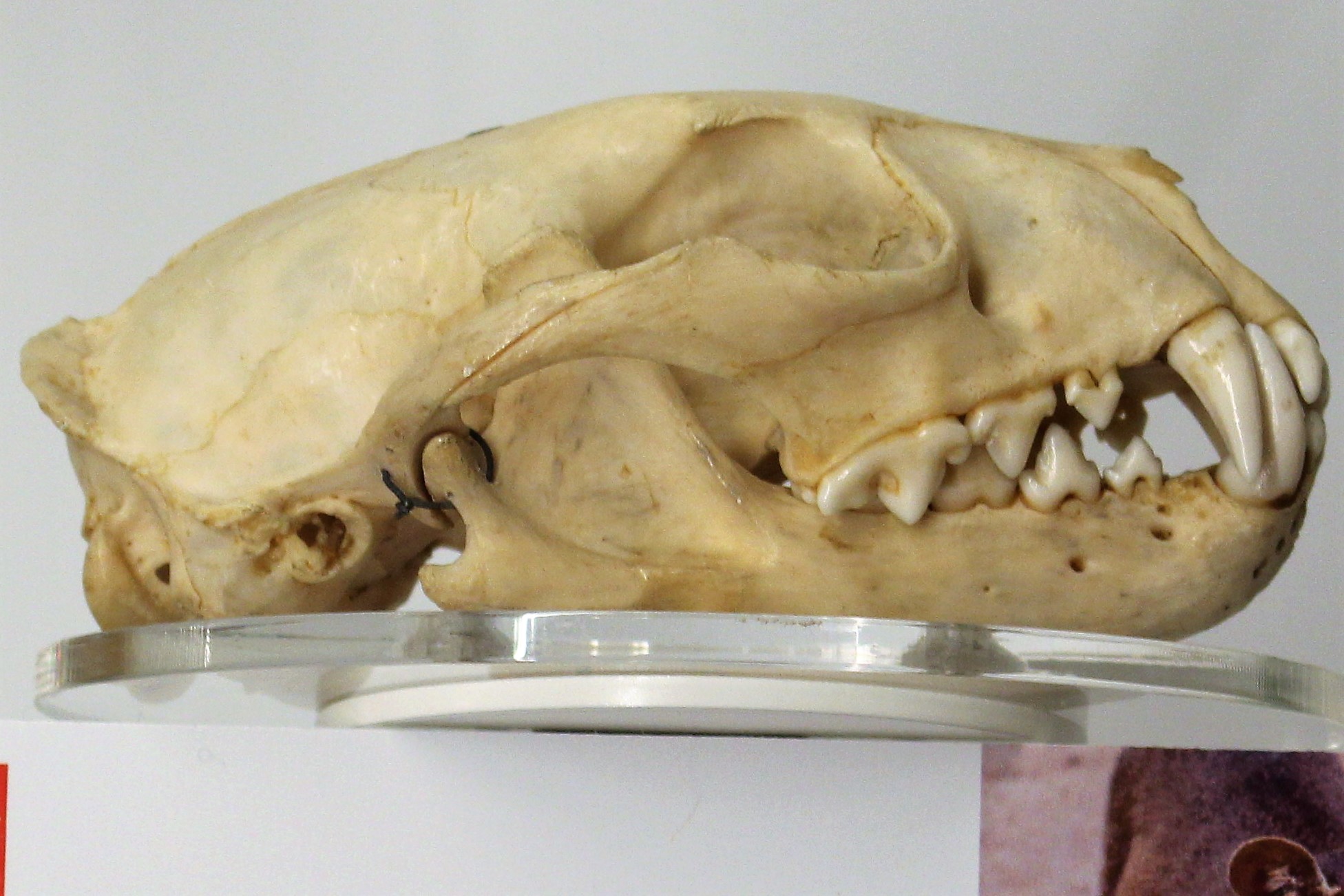
Fossa (animal)
The fossa (''Cryptoprocta ferox''; or ; ) is a slender, long-tailed, cat-like mammal that is endemic to Madagascar. It is a member of Eupleridae, the family of carnivorans, and closely related to the Malagasy civet. The fossa is the largest mammalian carnivore on Madagascar and has been compared to a small cougar, as it has convergently evolved many cat-like features. Adults have a head-body length of and weigh between , with the males larger than the females. It has semi-retractable claws (meaning it can extend but not retract its claws fully) and flexible ankles that allow it to climb up and down trees head-first, and also support jumping from tree to tree. A larger relative of the species, ''Cryptoprocta spelea'', probably became extinct before 1400. The species is widespread, although population densities are usually low. It is found solely in forested habitat, and actively hunts both by day and night. Over 50% of its diet consists of lemurs, the endemic primates found o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossa (animal)
The fossa (''Cryptoprocta ferox''; or ; ) is a slender, long-tailed, cat-like mammal that is endemic to Madagascar. It is a member of Eupleridae, the family of carnivorans, and closely related to the Malagasy civet. The fossa is the largest mammalian carnivore on Madagascar and has been compared to a small cougar, as it has convergently evolved many cat-like features. Adults have a head-body length of and weigh between , with the males larger than the females. It has semi-retractable claws (meaning it can extend but not retract its claws fully) and flexible ankles that allow it to climb up and down trees head-first, and also support jumping from tree to tree. A larger relative of the species, ''Cryptoprocta spelea'', probably became extinct before 1400. The species is widespread, although population densities are usually low. It is found solely in forested habitat, and actively hunts both by day and night. Over 50% of its diet consists of lemurs, the endemic primates found o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mammals Of Madagascar
This is a list of the native wild mammal species recorded in Madagascar. As of June 2014 (following the IUCN reassessment of the lemurs) there are 241 extant mammal species recognized in Madagascar, of which 22 are critically endangered, 62 are endangered, 32 are vulnerable, 9 are near threatened, 72 are of least concern and 44 are either data deficient or not evaluated. All of the critically endangered species are lemurs. The mammalian fauna of Madagascar is highly distinctive and largely endemic. The extant nonmarine, nonchiropteran taxa constitute (as of June 2014) 168 species, 40 genera and 9 families; of these, besides a probably introduced shrew, endemic taxa make up all the species, all the genera, and all but one of the families. This endemic terrestrial fauna, consisting of lemurs, tenrecs, nesomyine rodents and euplerid carnivorans, is thought to have colonized the island from Africa via four (or five, if aye-ayes arrived separately) rafting events. The other historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malagasy Civet
The Malagasy or striped civet (''Fossa fossana''), also known as the fanaloka (Malagasy, ) or jabady, is an euplerid endemic to Madagascar. It is the only species in genus ''Fossa''. The Malagasy civet is a small mammal, about long excluding the tail (which is only about ). It can weigh . It is endemic to the tropical forests of Madagascar. Malagasy civets are nocturnal. It eats small vertebrates, insects, aquatic animals, and eggs stolen from birds' nests. The mating season of the Malagasy civet is August to September and the gestation period is three months, ending with the birth of one young. The Malagasy civet is listed as Vulnerable by International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The Malagasy name ''fanaloka'' is related to the Malay word ''pelanduk'' "mousedeer" (via metathesis) likely due to their similar sizes and silhouette. Classification The Malagasy civet was to be placed in the subfamily Hemigalinae with the banded palm civets and then in its own sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falanouc
''Eupleres'' is a genus of two species of mongoose-like euplerid mammal native to Madagascar that are known as falanoucs. They are primarily terrestrial and consume mainly invertebrates. Species *Eastern falanouc, ''Eupleres goudotii'' - mesic forests of eastern Madagascar *Western falanouc, ''Eupleres major'' - xeric areas in northwestern Madagascar Conservation status The IUCN Red List lists ''E. goudotii'' as vulnerable, while ''E. major'' has been assessed as endangered An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inva .... References Carnivorans of Africa Euplerids Endemic fauna of Madagascar Taxa named by Louis Michel François Doyère {{carnivora-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupleres Major
The western falanouc (''Eupleres major'') is a rare mongoose-like mammal endemic to Madagascar. Until recently, the eastern falanouc (''Eupleres goudotii'') was the only recognized species in the genus ''Eupleres''. In 2010, Goodman and Helgen provided morphological evidence showing the two falanoucs are each a separate species and are found in separate geographical locations. ''E. major'' is larger and browner compared to ''E. goudotii'' and has a diet consisting mainly of invertebrates such as worms, snails, and slugs. Knowledge of the western falanouc's ecology is limited, but its range is believed to be limited to dry deciduous forest, flooded palm savanna, and wetlands. ''E. major'' is known to occur in Ankarafantsika National Park and is believed to also be found in or near other local national parks and reserves. The main predators of the western falanouc are feral dogs and humans. ''E. major'' is currently listed as ''endangered'' on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Falanouc
The Eastern falanouc (''Eupleres goudotii'') is a rare mongoose-like mammal in the carnivoran family Eupleridae endemic to Madagascar . It is classified alongside the Western falanouc (''Eupleres major''), recognized only in 2010, in the genus ''Eupleres''. Falanoucs have several peculiarities. They have no anal or perineal glands (unlike their closest relative, the fanaloka), nonretractile claws, and a unique dentition: the canines and premolars are backwards-curving and flat. This is thought to be related to their prey, mostly invertebrates, such as worms, slugs, snails, and larvae. It lives primarily in the lowland rainforests of eastern Madagascar, while ''E. major'' is found in northwest Madagascar. It is solitary and territorial, but whether nocturnal or diurnal is unknown. It is small (about 50 centimetres long with a 24-centimetre-long tail) and shy (clawing, not biting, in self-defence). It most closely resembles the mongooses with its long snout and low body, though its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptoprocta Ferox
''Cryptoprocta'' is a genus of carnivoran endemic to Madagascar. It contains the living fossa and its larger, recently extinct relative, the giant fossa ''Cryptoprocta spelea'', also known as the giant fossa, is an extinct species of carnivore from Madagascar in the family Eupleridae which is most closely related to the mongooses and includes all Malagasy carnivorans. It was first described in 19 .... The fossas are the largest of Madagascar's mammalian carnivores. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q141424 Mammal genera Mammal genera with one living species Euplerids Taxa named by Edward Turner Bennett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptoprocta Spelea
''Cryptoprocta spelea'', also known as the giant fossa, is an extinct species of carnivore from Madagascar in the family Eupleridae which is most closely related to the mongooses and includes all Malagasy carnivorans. It was first described in 1902, and in 1935 was recognized as a separate species from its closest relative, the living fossa (''Cryptoprocta ferox''). ''C. spelea'' was larger than the fossa, but otherwise similar. The two have not always been accepted as distinct species. When and how ''C. spelea'' became extinct is unknown; there is some anecdotal evidence, including reports of very large fossas, that there is more than one surviving species. The species is known from subfossil bones found in a variety of caves in northern, western, southern, and central Madagascar. In some sites, it occurs with remains of ''C. ferox'', but there is no evidence that the two lived in the same places at the same time. Living species of comparably sized, related carnivores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_skulls.jpg)
_(44120142915)_2.jpg)
.jpg)