|
Euler–Heisenberg Lagrangian
In physics, the Euler–Heisenberg Lagrangian describes the non-linear dynamics of electromagnetic fields in vacuum. It was first obtained by Werner Heisenberg and Hans Heinrich Euler in 1936. By treating the vacuum as a medium, it predicts rates of quantum electrodynamics (QED) light interaction processes. Physics It takes into account vacuum polarization to one loop, and is valid for electromagnetic fields that change slowly compared to the inverse electron mass, :\mathcal =-\mathcal -\frac\int_^\exp\left(-m^s\right)\left es)^\frac\mathcal-\frac(es)^\mathcal - 1\rightfrac. Here is the electron mass, the electron charge, \mathcal=\frac\left(\mathbf^2 - \mathbf^2\right), and \mathcal=\mathbf\cdot\mathbf. In the weak field limit, this becomes :\mathcal = \frac\left(\mathbf^-\mathbf^\right)+\frac\left left(\mathbf^2 - \mathbf^2\right)^ + 7 \left(\mathbf\cdot\mathbf\right)^\right It describes photon–photon scattering in QED; Robert Karplus and Maurice Neuman calculated the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear System
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Dark Matter
In cosmology and physics, cold dark matter (CDM) is a hypothetical type of dark matter. According to the current standard model of cosmology, Lambda-CDM model, approximately 27% of the universe is dark matter and 68% is dark energy, with only a small fraction being the ordinary baryonic matter that composes stars, planets, and living organisms. ''Cold'' refers to the fact that the dark matter moves slowly compared to the speed of light, while ''dark'' indicates that it interacts very weakly with ordinary matter and electromagnetic radiation. Proposed candidates for CDM include weakly interacting massive particles, primordial black holes, and axions. History The theory of cold dark matter was originally published in 1982 by James Peebles; while the warm dark matter picture was proposed independently at the same time by J. Richard Bond, Alex Szalay, and Michael Turner; and George Blumenthal, H. Pagels, and Joel Primack. A review article in 1984 by Blumenthal, Sandra Moore Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4U 0142+61
4U 0142+61 is a magnetar at an approximate distance of from Earth, located in the constellation Cassiopeia. In an article published in ''Nature'' on April 6, 2006, Deepto Chakrabarty ''et al.'' of MIT revealed that a circumstellar disk was discovered around the pulsar. This may prove that pulsar planets are common around neutron stars. The debris disk is likely to be composed of mainly heavier metals. The star had undergone a supernova event approximately 100,000 years ago. The disk orbits about 1.6 million kilometers away from the pulsar and probably contains about 10 Earth-masses of material. This also marks the first time that a pulsar has been discovered with a debris disk orbiting it. In May 2022, the first study by the IXPE Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer, commonly known as IXPE or SMEX-14, is a space observatory with three identical telescopes designed to measure the polarization of cosmic X-rays of black holes, neutron stars, and pulsars. The obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IXPE
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer, commonly known as IXPE or SMEX-14, is a space observatory with three identical telescopes designed to measure the polarization of cosmic X-rays of black holes, neutron stars, and pulsars. The observatory, which was launched on 9 December 2021, is an international collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). It is part of NASA's Explorers program, which designs low-cost spacecraft to study heliophysics and astrophysics. The mission will study exotic astronomical objects and permit mapping of the magnetic fields of black holes, neutron stars, pulsars, supernova remnants, magnetars, quasars, and active galactic nuclei. The high-energy X-ray radiation from these objects' surrounding environment can be polarized oscillating in a particular direction. Studying the polarization of X-rays reveals the physics of these objects and can provide insights into the high-temperature environments where they are created. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breit–Wheeler Process
The Breit–Wheeler process or Breit–Wheeler pair production is a physical process in which a positron–electron pair is created from the collision of two photons. It is the simplest mechanism by which pure light can be potentially transformed into matter. The process can take the form γ γ′ → e+ e− where γ and γ′ are two light quanta (for example, gamma photons). The multiphoton Breit–Wheeler process, also referred to as nonlinear Breit–Wheeler or strong field Breit–Wheeler in the literature, is the extension of the pure photon–photon Breit–Wheeler process when a high-energy probe photon decays into pairs propagating through an electromagnetic field (for example, a laser pulse). In contrast with the previous process, this one can take the form of γ + n ω → e+ e−, where ω represents the coherent photons of the laser field. The inverse process, e+ e− → γ γ′, in which an electron and a positron collide and annihilate to generate a pair of gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider
The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC ) is the first and one of only two operating heavy- ion colliders, and the only spin-polarized proton collider ever built. Located at Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) in Upton, New York, and used by an international team of researchers, it is the only operating particle collider in the US. By using RHIC to collide ions traveling at relativistic speeds, physicists study the primordial form of matter that existed in the universe shortly after the Big Bang. By colliding spin-polarized protons, the spin structure of the proton is explored. RHIC is as of 2019 the second-highest-energy heavy-ion collider in the world. As of November 7, 2010, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has collided heavy ions of lead at higher energies than RHIC. The LHC operating time for ions (lead–lead and lead–proton collisions) is limited to about one month per year. In 2010, RHIC physicists published results of temperature measurements from earlier exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
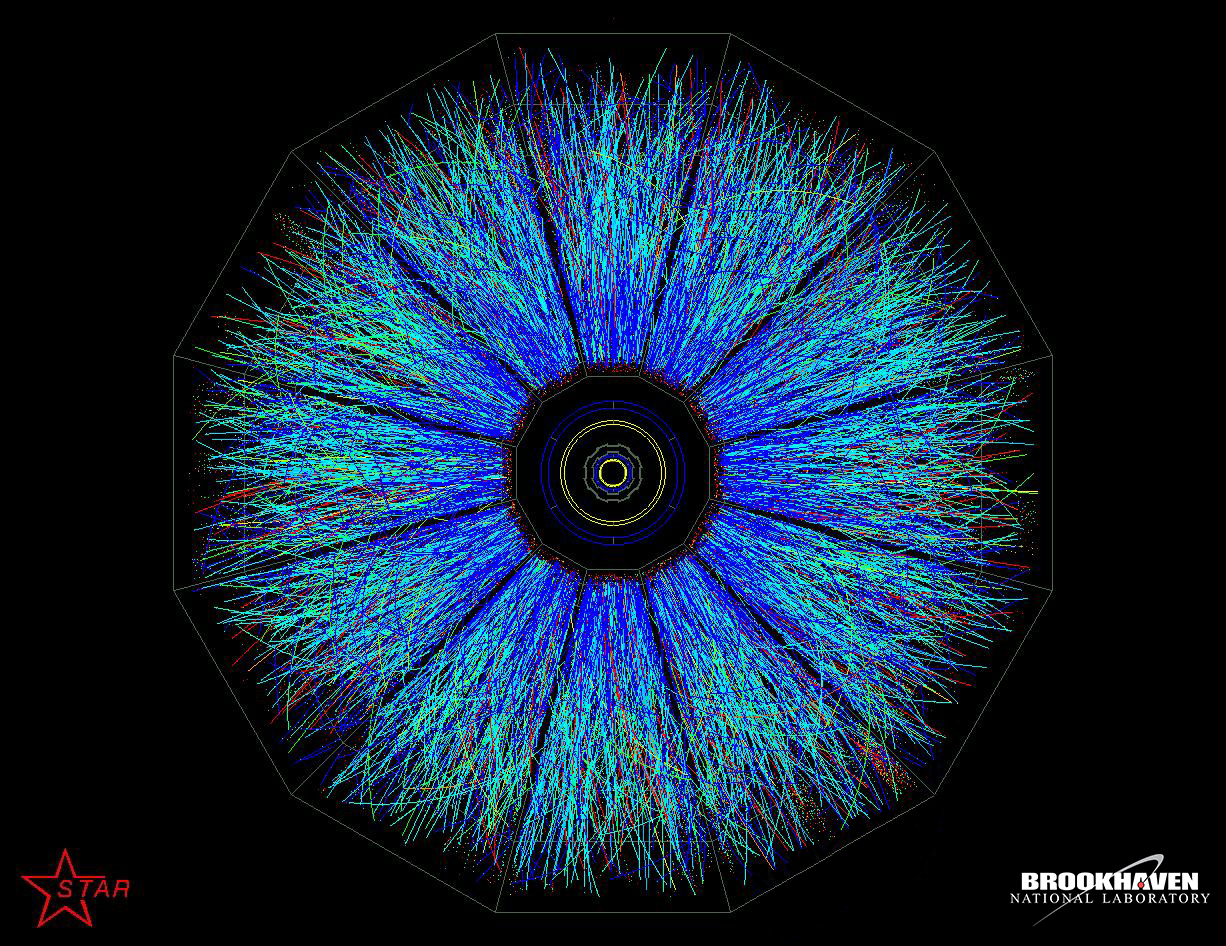
STAR Detector
The STAR detector (for Solenoidal Tracker at RHIC) is one of the four experiments at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) in Brookhaven National Laboratory, United States. The primary scientific objective of STAR is to study the formation and characteristics of the quark–gluon plasma (QGP), a state of matter believed to exist at sufficiently high energy densities. Detecting and understanding the QGP allows physicists to understand better the Universe in the seconds after the Big Bang, when the presently-observed symmetries (and asymmetries) of the Universe were established. Unlike other physics experiments where a theoretical prediction can be tested directly by a single measurement, STAR must make use of a variety of simultaneous studies in order to draw strong conclusions about the QGP. This is due both to the complexity of the system formed in the high-energy nuclear collision and the unexplored landscape of the physics studied. STAR therefore consists of several types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATLAS Collaboration
ATLAS is the largest general-purpose particle detector experiment at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), a particle accelerator at CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research) in Switzerland. The experiment is designed to take advantage of the unprecedented energy available at the LHC and observe phenomena that involve highly massive particles which were not observable using earlier lower-energy accelerators. ATLAS was one of the two LHC experiments involved in the discovery of the Higgs boson in July 2012. It was also designed to search for evidence of theories of particle physics beyond the Standard Model. The experiment is a collaboration involving 6,003 members, out of which 3,822 are physicists (last update: June 26, 2022) from 257 institutions in 42 countries. History Particle accelerator growth The first cyclotron, an early type of particle accelerator, was built by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1931, with a radius of just a few centimetres and a particle energy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Of Polarization
Degree of polarization (DOP) is a quantity used to describe the portion of an electromagnetic wave which is polarized. A perfectly polarized wave has a DOP of 100%, whereas an unpolarized wave has a DOP of 0%. A wave which is partially polarized, and therefore can be represented by a superposition of a polarized and unpolarized component, will have a DOP somewhere in between 0 and 100%. DOP is calculated as the fraction of the total power that is carried by the polarised component of the wave. DOP can be used to map the strain field in materials when considering the DOP of the photoluminescence. The polarization of the photoluminescence is related to the strain in a material by way of the given material's photoelasticity tensor. DOP is also visualized using the Poincaré sphere representation of a polarized beam. In this representation, DOP is equal to the length of the vector measured from the center of the sphere. See also * Axial ratio *Linear polarization *Circular po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |