|
EuLisp
EuLisp is a statically and dynamically Scope (programming), scoped Lisp (programming language), Lisp dialect developed by a loose formation of industrial and academic Lisp users and developers from around Europe. The Standardization, standardizers intended to create a new Lisp (programming language), Lisp "less encumbered by the past" (compared to Common Lisp), and not so Minimalism (computing), minimalist as Scheme (programming language), Scheme. Another objective was to integrate the object-oriented programming paradigm well. It is a third-generation programming language. Origin The language definition process first began in a meeting in 1985 in Paris and took several years. The complete specification and a first implementation (Interpreter (computing), interpreted-only) were made available in 1990. Distinguishing features Its main traits are that it is a Lisp-1 (no separate function and variable namespaces), has a ''Common Lisp Object System'' (CLOS) style generic-function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisp (programming Language)
Lisp (historically LISP) is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1960, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket and Clojure. Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order functions, recursion, the self-hosting compiler, and the rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
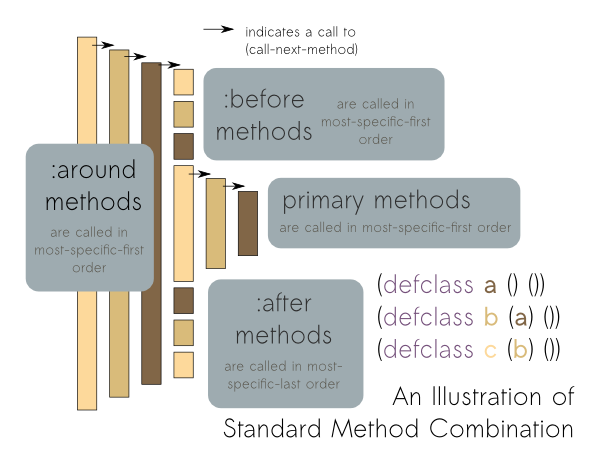
Common Lisp Object System
The Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) is the facility for object-oriented programming which is part of ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS is a powerful dynamic object system which differs radically from the OOP facilities found in more static languages such as C++ or Java. CLOS was inspired by earlier Lisp object systems such as MIT Flavors and CommonLoops, although it is more general than either. Originally proposed as an add-on, CLOS was adopted as part of the ANSI standard for Common Lisp and has been adapted into other Lisp dialects such as EuLisp or Emacs Lisp. Features The basic building blocks of CLOS are methods, classes, instances of those classes, and generic functions. CLOS provides macros to define those: defclass, defmethod, and defgeneric. Instances are created with the method make-instance. Classes can have multiple superclasses, a list of slots (member variables in C++/Java parlance) and a special metaclass. Slots can be allocated by class (all instances of a class sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISLISP
ISLISP (also capitalized as ISLisp) is a programming language in the Lisp family standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) joint working group ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 22/WG 16 (commonly termed simply SC22/WG16 or WG16). The primary output of this working group was an international standard, published by ISO. The standard was updated in 2007 and republished as ISO/IEC 13816:2007(E). Although official publication was through ISO, versions of the ISLISP language specification are available that are believed to be in the public domain. The goal of this standards effort was to define a small, core language to help bridge the gap between differing dialects of Lisp. It attempted to accomplish this goal by studying primarily Common Lisp, EuLisp, Le Lisp, and Scheme and standardizing only those features shared between them. Design goals ISLISP has these design goals: * Compatible with extant Lisp dialects w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Lisp
Common Lisp (CL) is a dialect of the Lisp programming language, published in ANSI standard document ''ANSI INCITS 226-1994 (S20018)'' (formerly ''X3.226-1994 (R1999)''). The Common Lisp HyperSpec, a hyperlinked HTML version, has been derived from the ANSI Common Lisp standard. The Common Lisp language was developed as a standardized and improved successor of Maclisp. By the early 1980s several groups were already at work on diverse successors to MacLisp: Lisp Machine Lisp (aka ZetaLisp), Spice Lisp, NIL and S-1 Lisp. Common Lisp sought to unify, standardise, and extend the features of these MacLisp dialects. Common Lisp is not an implementation, but rather a language specification. Several implementations of the Common Lisp standard are available, including free and open-source software and proprietary products. Common Lisp is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm programming language. It supports a combination of procedural, functional, and object-oriented programming para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oaklisp
Oaklisp is a portable object-oriented Scheme developed by Kevin J. Lang and Barak A. Pearlmutter while Computer Science PhD students at Carnegie Mellon University. Oaklisp uses a superset of Scheme syntax. It is based on generic operations rather than functions, and features anonymous classes, multiple inheritance, a strong error system, setters and locators for operations, and a facility for dynamic binding. Version 1.2 includes an interface, bytecode compiler, run-time system In computer programming, a runtime system or runtime environment is a sub-system that exists both in the computer where a program is created, as well as in the computers where the program is intended to be run. The name comes from the compile t ... and documentation. References * * * {{cite book , author=Barak A. Pearlmutter and Kevin J. Lang , editor=Peter Lee , title=Topics in Advanced Language Implementation , year=1991 , publisher=MIT Press , location=Cambridge MA , isbn=978-0-262-12151 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T (programming Language)
T is a dialect of the Scheme programming language developed in the early 1980s by Jonathan A. Rees, Kent M. Pitman, and Norman I. Adams of Yale University as an experiment in language design and implementation. Rationale T's purpose is to test the thesis developed by Guy L. Steele Jr. and Gerald Jay Sussman in their series of papers about Scheme: that Scheme may be used as the basis for a practical programming language of exceptional expressive power, and that implementations of Scheme could perform better than other Lisp systems, and competitively with implementations of programming languages, such as C and BLISS, which are usually considered to be inherently more efficient than Lisp on conventional machine architectures. Much of this occurs via an optimizing compiler named Orbit. T contains some features that modern Scheme lacks. For example, T is object-oriented, and it has first-class environments, called ''locales'', which can be modified non-locally and used as a module sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme (programming Language)
Scheme is a dialect of the Lisp family of programming languages. Scheme was created during the 1970s at the MIT AI Lab and released by its developers, Guy L. Steele and Gerald Jay Sussman, via a series of memos now known as the Lambda Papers. It was the first dialect of Lisp to choose lexical scope and the first to require implementations to perform tail-call optimization, giving stronger support for functional programming and associated techniques such as recursive algorithms. It was also one of the first programming languages to support first-class continuations. It had a significant influence on the effort that led to the development of Common Lisp.Common LISP: The Language, 2nd Ed., Guy L. Steele Jr. Digital Press; 1981. . "Common Lisp is a new dialect of Lisp, a successor to MacLisp, influenced strongly by ZetaLisp and to some extent by Scheme and InterLisp." The Scheme language is standardized in the official IEEE standard1178-1990 (Reaff 2008) IEEE Standard for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dylan (programming Language)
Dylan is a multi-paradigm programming language that includes support for functional and object-oriented programming (OOP), and is dynamic and reflective while providing a programming model designed to support generating efficient machine code, including fine-grained control over dynamic and static behaviors. It was created in the early 1990s by a group led by Apple Computer. Dylan derives from Scheme and Common Lisp and adds an integrated object system derived from the Common Lisp Object System (CLOS). In Dylan, all values (including numbers, characters, functions, and classes) are first-class objects. Dylan supports multiple inheritance, polymorphism, multiple dispatch, keyword arguments, object introspection, pattern-based syntax extension macros, and many other advanced features. Programs can express fine-grained control over dynamism, admitting programs that occupy a continuum between dynamic and static programming and supporting evolutionary development (allowing for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-generation Programming Language
A third-generation programming language (3GL) is a high-level computer programming language that tends to be more machine-independent and programmer-friendly than the machine code of the first-generation and assembly languages of the second-generation, while having a less specific focus to the fourth and fifth generations. Examples of common and historical third-generation programming languages are ALGOL, BASIC, C, COBOL, Fortran, Java, and Pascal. Characteristics 3GLs are much more machine-independent and more programmer-friendly. This includes features like improved support for aggregate data types, and expressing concepts in a way that favors the programmer, not the computer. A third generation language improves over a second-generation language by having the computer take care of non-essential details. 3GLs are more abstract than previous generations of languages, and thus can be considered higher-level languages than their first- and second-generation counterparts. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimalism (computing)
In computing, minimalism refers to the application of minimalist philosophies and principles in the design and use of hardware and software. Minimalism, in this sense, means designing systems that use the least hardware and software resources possible. History In the late 1970s and early 1980s, programmers worked within the confines of relatively expensive and limited resources of common platforms. Eight or sixteen kilobytes of RAM was common; 64 kilobytes was considered a vast amount and was the entire address space accessible to the 8-bit CPUs predominant during the earliest generations of personal computers. The most common storage medium was the 5.25 inch floppy disk holding from 88 to 170 kilobytes. Hard drives with capacities from five to ten megabytes cost thousands of dollars. Over time, personal-computer memory capacities expanded by orders of magnitude and mainstream programmers took advantage of the added storage to increase their software's capabilities a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpreter (computing)
In computer science, an interpreter is a computer program that directly execution (computers), executes instructions written in a Programming language, programming or scripting language, without requiring them previously to have been Compiler, compiled into a machine language program. An interpreter generally uses one of the following strategies for program execution: # Parse the source code and perform its behavior directly; # Translator (computing), Translate source code into some efficient intermediate representation or object code and immediately execute that; # Explicitly execute stored precompiled bytecode made by a compiler and matched with the interpreter Virtual Machine. Early versions of Lisp programming language and BASIC interpreter, minicomputer and microcomputer BASIC dialects would be examples of the first type. Perl, Raku (programming language), Raku, Python (programming language), Python, MATLAB, and Ruby (programming language), Ruby are examples of the second, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |