|
Common Lisp Object System
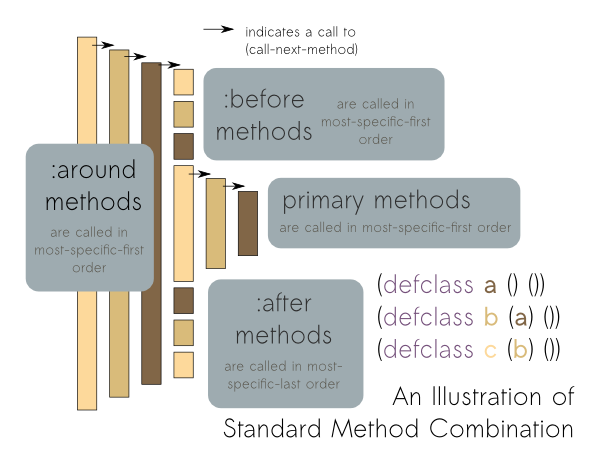
The Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) is the facility for object-oriented programming in American National Standards Institute, ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS is a powerful dynamic programming language, dynamic object system which differs radically from the OOP facilities found in more static languages such as C++ or Java (programming language), Java. CLOS was inspired by earlier Lisp object systems such as Flavors (computer science), MIT Flavors and CommonLoops, although it is more general than either. Originally proposed as an add-on, CLOS was adopted as part of the ANSI standard for Common Lisp and has been adapted into other Lisp dialects such as EuLisp or Emacs Lisp. Features The basic building blocks of CLOS are method (computer programming), methods, Class (computer programming), classes, instances of those classes, and generic functions. CLOS provides macros to define those: defclass, defmethod, and defgeneric. Instances are created with the method make-instance. Classes can hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Method (computer Science)
A method in object-oriented programming (OOP) is a procedure associated with an object, and generally also a message. An object consists of ''state data'' and ''behavior''; these compose an ''interface'', which specifies how the object may be used. A method is a behavior of an object parametrized by a user. Data is represented as properties of the object, and behaviors are represented as methods. For example, a Window object could have methods such as open and close, while its state (whether it is open or closed at any given point in time) would be a property. In class-based programming, methods are defined within a class, and objects are instances of a given class. One of the most important capabilities that a method provides is '' method overriding'' - the same name (e.g., area) can be used for multiple different kinds of classes. This allows the sending objects to invoke behaviors and to delegate the implementation of those behaviors to the receiving object. A method in Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect-oriented Programming
In computing, aspect-oriented programming (AOP) is a programming paradigm that aims to increase modularity by allowing the separation of cross-cutting concerns. It does so by adding behavior to existing code (an advice) ''without'' modifying the code, instead separately specifying which code is modified via a " pointcut" specification, such as "log all function calls when the function's name begins with 'set. This allows behaviors that are not central to the business logic (such as logging) to be added to a program without cluttering the code of core functions. AOP includes programming methods and tools that support the modularization of concerns at the level of the source code, while aspect-oriented software development refers to a whole engineering discipline. Aspect-oriented programming entails breaking down program logic into cohesive areas of functionality (so-called ''concerns''). Nearly all programming paradigms support some level of grouping and encapsulation of conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaobject
In computer science, a metaobject is an object that manipulates, creates, describes, or implements objects (including itself). The object that the metaobject pertains to is called the base object. Some information that a metaobject might define includes the base object's type, interface, class, methods, attributes, parse tree, etc. Metaobjects are examples of the computer science concept of reflection, where a system has access (usually at run time) to its own internal structure. Reflection enables a system to essentially rewrite itself on the fly, to alter its own implementation as it executes. Metaobject protocol A metaobject protocol (MOP) provides the vocabulary ( protocol) to access and manipulate the structure and behaviour of systems of objects. Typical functions of a metaobject protocol include: *Create or delete a new class *Create a new property or method *Cause a class to inherit from a different class ("change the class structure") *Generate or change the code defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prototype-based Language
Prototype-based programming is a style of object-oriented programming in which behavior reuse (known as inheritance) is performed via a process of reusing existing objects that serve as prototypes. This model can also be known as ''prototypal'', ''prototype-oriented,'' ''classless'', or ''instance-based'' programming. Prototype-based programming uses the process generalized objects, which can then be cloned and extended. Using fruit as an example, a "fruit" object would represent the properties and functionality of fruit in general. A "banana" object would be cloned from the "fruit" object and general properties specific to bananas would be appended. Each individual "banana" object would be cloned from the generic "banana" object. Compare to the class-based paradigm, where a "fruit" ''class'' would be extended by a "banana" ''class''. History The first prototype-based programming languages were Director a.k.a. Ani (on top of MacLisp) (1976-1979), and contemporaneously and not i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Pattern (computer Science)
In software engineering, a software design pattern or design pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem in many contexts in software design. A design pattern is not a rigid structure to be transplanted directly into source code. Rather, it is a description or a template for solving a particular type of problem that can be deployed in many different situations. Design patterns can be viewed as formalized best practices that the programmer may use to solve common problems when designing a software application or system. Object-oriented design patterns typically show relationships and interactions between classes or objects, without specifying the final application classes or objects that are involved. Patterns that imply mutable state may be unsuited for functional programming languages. Some patterns can be rendered unnecessary in languages that have built-in support for solving the problem they are trying to solve, and object-oriented patterns are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Problem
Multiple inheritance is a feature of some object-oriented computer programming languages in which an object or class can inherit features from more than one parent object or parent class. It is distinct from single inheritance, where an object or class may only inherit from one particular object or class. Multiple inheritance has been a controversial issue for many years, with opponents pointing to its increased complexity and ambiguity in situations such as the "diamond problem", where it may be ambiguous as to which parent class a particular feature is inherited from if more than one parent class implements said feature. This can be addressed in various ways, including using virtual inheritance. Alternate methods of object composition not based on inheritance such as mixins and traits have also been proposed to address the ambiguity. Details In object-oriented programming (OOP), ''inheritance'' describes a relationship between two classes in which one class (the ''child'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Inheritance
Multiple inheritance is a feature of some object-oriented computer programming languages in which an object or class can inherit features from more than one parent object or parent class. It is distinct from single inheritance, where an object or class may only inherit from one particular object or class. Multiple inheritance has been a controversial issue for many years, with opponents pointing to its increased complexity and ambiguity in situations such as the "diamond problem", where it may be ambiguous as to which parent class a particular feature is inherited from if more than one parent class implements said feature. This can be addressed in various ways, including using virtual inheritance. Alternate methods of object composition not based on inheritance such as mixins and traits have also been proposed to address the ambiguity. Details In object-oriented programming (OOP), ''inheritance'' describes a relationship between two classes in which one class (the ''child'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy (object-oriented Programming)
In object-oriented programming, inheritance is the mechanism of basing an object or class upon another object ( prototype-based inheritance) or class ( class-based inheritance), retaining similar implementation. Also defined as deriving new classes ( sub classes) from existing ones such as super class or base class and then forming them into a hierarchy of classes. In most class-based object-oriented languages like C++, an object created through inheritance, a "child object", acquires all the properties and behaviors of the "parent object", with the exception of: constructors, destructors, overloaded operators and friend functions of the base class. Inheritance allows programmers to create classes that are built upon existing classes, to specify a new implementation while maintaining the same behaviors ( realizing an interface), to reuse code and to independently extend original software via public classes and interfaces. The relationships of objects or classes through inheri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namespace
In computing, a namespace is a set of signs (''names'') that are used to identify and refer to objects of various kinds. A namespace ensures that all of a given set of objects have unique names so that they can be easily identified. Namespaces are commonly structured as hierarchies to allow reuse of names in different contexts. As an analogy, consider a system of naming of people where each person has a given name, as well as a family name shared with their relatives. If the first names of family members are unique only within each family, then each person can be uniquely identified by the combination of first name and family name; there is only one Jane Doe, though there may be many Janes. Within the namespace of the Doe family, just "Jane" suffices to unambiguously designate this person, while within the "global" namespace of all people, the full name must be used. Prominent examples for namespaces include file systems, which assign names to files. Some programming languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessor Method
In computer science, a mutator method is a method used to control changes to a variable. They are also widely known as setter methods. Often a setter is accompanied by a getter, which returns the value of the private member variable. They are also known collectively as accessors. The mutator method is most often used in object-oriented programming, in keeping with the principle of encapsulation. According to this principle, member variables of a class are made private to hide and protect them from other code, and can only be modified by a public member function (the mutator method), which takes the desired new value as a parameter, optionally validates it, and modifies the private member variable. Mutator methods can be compared to assignment operator overloading but they typically appear at different levels of the object hierarchy. Mutator methods may also be used in non-object-oriented environments. In this case, a reference to the variable to be modified is passed to the mut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |