|
Esen Buqa–Ayurbarwada War
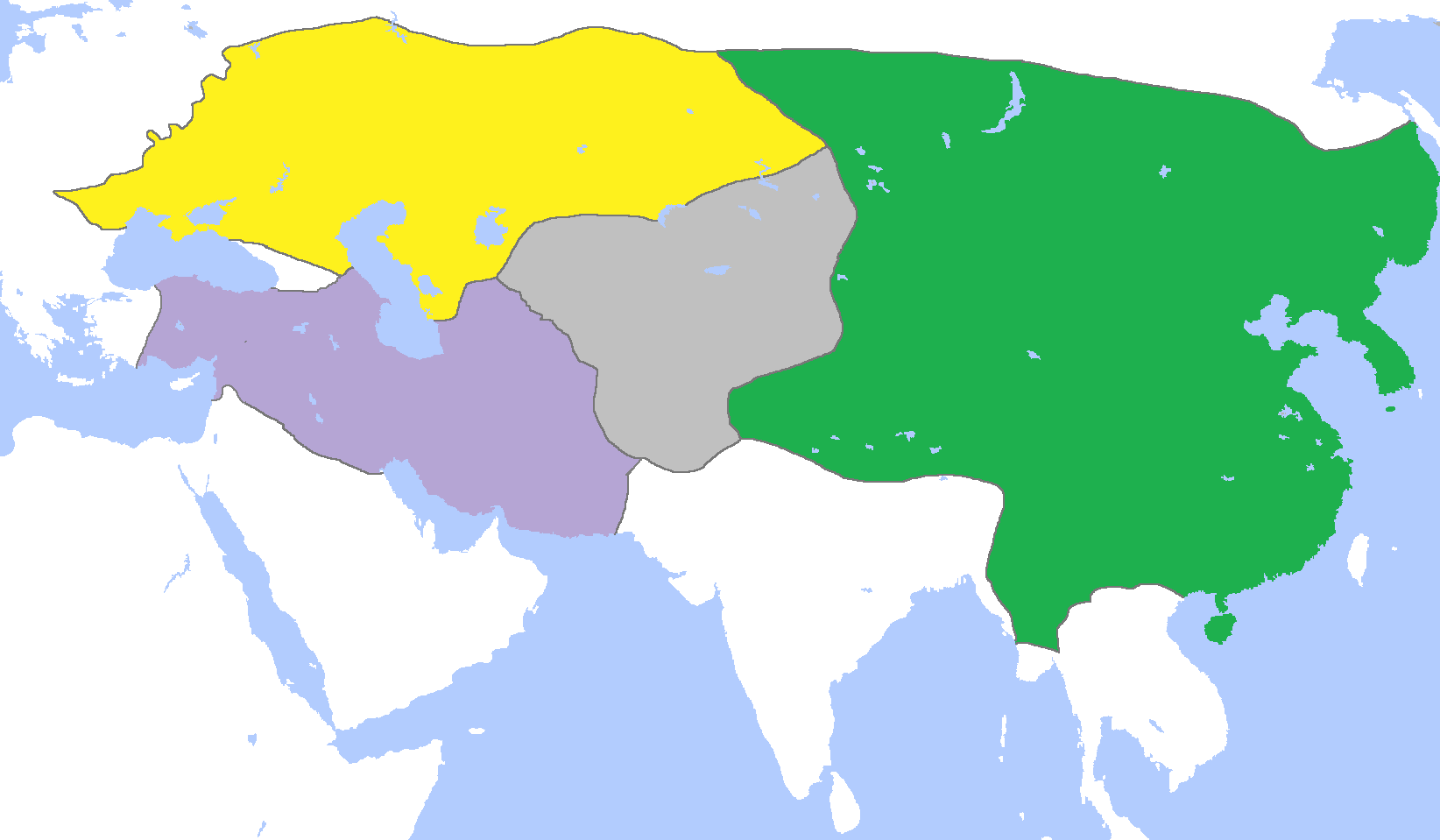
The Esen Buqa–Ayurbarwada war was a war between the Chagatai Khanate under Esen Buqa I and the Yuan dynasty under Ayurbarwada Buyantu Khan (Emperor Renzong) and its ally the Ilkhanate under Öljaitü. The war ended with the victory for the Yuan and the Ilkhanate, but the peace only came after the death of Esen Buqa in 1318. Background The Yuan emperor Ayurbarwarda maintained friendly relations with Öljaitü, ruler of the Ilkhanate. As for the relations with the Chagatai Khanate, the Yuan forces had, in fact, already for a long time been entrenched in the east. This was originally meant to keep Chapar in submission, but since the latter's defeat in 1310, the garrisons were perceived as a threat to the Chaghadaid state. In order to solve the shortages of pasture grounds, Esen Buqa I, ruler of the Chagatai Khanate sent envoys in an attempt to negotiate with the border garrison commander Tughaji Jinsank in order to convince them to adjust their position in 1312. The negotiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamanism
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world through Altered state of consciousness, altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct Non-physical entity, spirits or Energy (esotericism), spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as "shamanic" have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers and psychologists. Hundreds of books and Academic publishing#Scholarly paper, academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. In the 20th century, non-Indigenous Peoples, Indigenous Westerners involved in countercultural movements, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taraz
Taraz ( kz, Тараз, تاراز, translit=Taraz ; known to Europeans as Talas) is a city and the administrative center of Jambyl Region in Kazakhstan, located on the Talas (river), Talas (Taraz) River in the south of the country near the border with Kyrgyzstan. It had a population of 330,100 as of the 1999 census, up 9% from 1989, making it one of the fastest-growing cities in the country, after Astana and Turkistan (city), Turkistan. One of the oldest cities in Kazakhstan and in Transoxania, built and populated by the ancient Sogdians, Taraz celebrated its official 2,000th anniversary (recognized by UNESCO) in 2001, dating from a fortress built in the area by a Xiongnu Chanyu named Zhizhi, and was a site of the Battle of Zhizhi in 36 BCE. The city was first recorded under the name "Talas" in 568 CE by Menander Protector. The medieval city of Talas was a major trade centre along the Silk Road. Talas was later described by Buddhist monk and traveller Xuanzang, who passed Talas i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd Kōh'') in the fertile valley of the Hari River in the western part of the country. An ancient civilization on the Silk Road between the Middle East, Central and South Asia, it serves as a regional hub in the country's west. Herat dates back to Avestan times and was traditionally known for its wine. The city has a number of historic sites, including the Herat Citadel and the Musalla Complex. During the Middle Ages Herat became one of the important cities of Khorasan, as it was known as the ''Pearl of Khorasan''. After the conquest of Tamerlane, the city became an important center of intellectual and artistic life in the Islamic world. Under the rule of Shah Rukh the city served as the focal point of the Timurid Renaissance, whose glor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murgab River
The Marghab River (Persian/Pashto: مرغاب, ''Morqâb''), anciently the Margiana (Ancient Greek: Μαργιανή, ''Margianḗ''), is an long river in Central Asia. It rises in the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safīd Kūh'') in Ghor Province, flows through the Marghab District in central Afghanistan, then runs northwest towards the Bala Murghab. Reaching the oasis of Mary in the Karakum Desert of Turkmenistan, the Marghab debouches into the Karakum Canal, a diversion of water from the Amu Darya. The catchment area of the Marghab is estimated at . Geography The Marghab River originates in the Ghor Province of central Afghanistan, on a plateau among the chain of mountains of Paropamisus, Gharjistan and Band-i Turkestan. In its higher course, the river runs from east to west, towards Mukhamedkhan, for about in a narrow, steep valley measuring less than one kilometer in width, with narrow gorges in some places. Between Darband-i Kilrekht and Mukhammedkhan, the Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasa'ur
Yasa'ur (died 1320) was a Chagatai prince who launched a revolt against the Ilkhan Abu Sa'id. He was the son of Chübei, and a great-great-grandson of Chagatai Khan. Yasa'ur had originally resided within the Chagatai ''ulus''. In 1314 he participated in a campaign against the Ilkhanate, together with the Chagatai Khan's brother Kebek and a Neguderi prince Daud Khwaja(a son of Qutlugh Khwaja) who had been expelled from his territories by the Ilkhan the previous year. Their forces defeated the Ilkhan army near the banks of the Murgab River; they then marched to Herat. The Ilkhan Öljeitü then set off with an army for the east, while the Chagataiid forces were recalled by the khan Esen Buqa. Around this time Yasa'ur, who had been accused by Kebek of cooperated with the Ilkhanid forces during the invasion, defected to Öljeitü. His forces engaged in battle with the Chagataiid troops; an Ilkhanid army that had crossed the Oxus joined the fighting and secured victory for Yasa'ur. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. , Demographics of Afghanistan, its population is 40.2 million (officially estimated to be 32.9 million), composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qutlugh Khwaja
Qutlugh Khwaja (d. 1299/1300) was a son of Duwa, the Mongol khan of Chagatai Khanate, division of the Mongol Empire. He became a chief of the Qara'unas in Afghanistan after Abdullah was recalled by the Khan to Central Asia in around 1298–1299. It seems that later Ilkhans allowed him to settle with his Qaranaus in Afghanistan, though they were struggling with each other. He launched several attacks on both the Delhi Sultanate and Ilkhanate. According to Rashid ad-Din, he was a threat to Mamluks in Delhi. In the end of 1299, a larger force under Khwaja reached the very outskirts of Delhi, leading to the Battle of Kili. Sultan Alauddin Khalji led his entire army to give battle to the Mongols — he engaged the Mongol center while his left wing broke the Mongol formation opposite them and penetrated into their rear lines. This created panic in the rest of the army and the Mongols retreated from Delhi. Qutlugh Khwaja was mortally wounded during his return from India in 1299–1300. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qaraunas
The Qara'unas or Negüderi were a Mongol people who settled in Afghanistan after moving from Turkestan and Mongolia. Foundation The word Qarauna derived from the Mongolian word ''Qara'' meaning black in Mongolian. At first they were subjects of the Great Khan and served as ''tamnas'' or ''tamachis'' in Afghanistan. The Great Khan appointed their leaders from non- Chingisid generals such as Dayir and Mungudei. In 1238, they settled near India to face the military forces of the Delhi Sultanate. In the 1250s their leader was Sali Noyan who was of Tatar origin. Möngke Khan ordered Sali Noyan and his tamna soldiers to join Hulegu's army in 1253. In 1260, Jochid Baval, the father of Nogai Khan, was executed on the orders of Hulegu Khan after gaining permission from Berke who was the khan of the Golden Horde. Soon after that, Kuli and Tutar, also Golden Horde princes, died under suspicious circumstances. Golden Horde soldiers who served Hulgeu feared for their lives and began to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Khorasan
Greater Khorāsān,Dabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 or Khorāsān ( pal, Xwarāsān; fa, خراسان ), is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau between Western and Central Asia. The name ''Khorāsān'' is Persian and means "where the sun arrives from" or "the Eastern Province".Sykes, M. (1914). "Khorasan: The Eastern Province of Persia". ''Journal of the Royal Society of Arts'', 62(3196), 279-286.A compound of ''khwar'' (meaning "sun") and ''āsān'' (from ''āyān'', literally meaning "to come" or "coming" or "about to come"). Thus the name ''Khorasan'' (or ''Khorāyān'' ) means "sunrise", viz. " Orient, East"Humbach, Helmut, and Djelani Davari, "Nāmé Xorāsān", Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz; Persian translation by Djelani Davari, published in Iranian Languages Studies Website. MacKenzie, D. (1971). ''A Concise Pahlavi Dictionary'' (p. 95). London: Oxford University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizir
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a helper but afterwards became the representative and successor of the ''dapir'' (official scribe or secretary) of the Sassanian kings. In modern usage, the term has been used for government ministers in much of the Middle East and beyond. Several alternative spellings are used in English, such as ''vizir'', ''wazir'', and ''vezir''. Etymology Vizier is suggested to be an Iranian word, from the Pahlavi root of ''vičir'', which originally had the meaning of a ''decree'', ''mandate'', and ''command'', but later as its use in Dinkard also suggests, came to mean ''judge'' or ''magistrate''. Arthur Jeffery considers the word to be a "good Iranian" word, as has a well-established root in Avestan language. The Pahlavi ''viči ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hami City
Hami (Kumul) is a prefecture-level city in Eastern Xinjiang, China. It is well known as the home of sweet Hami melons. In early 2016, the former Hami county-level city was merged with Hami Prefecture to form the Hami prefecture-level city with the county-level city becoming Yizhou District. Since the Han dynasty, Hami has been known for its production of agricultural products and raw resources. Origins and names Cumuḍa (sometimes ''Cimuda'' or ''Cunuda'') is the oldest known endonym of Hami, when it was founded by a people known in Han Chinese sources as the '' Xiao Yuezhi'' ("Lesser Yuezhi"), during the 1st millennium BCE. The oldest attested Chinese names is "" (; by the time of the Han dynasty it was referred to in Chinese as "" () or "" (), in the Tang dynasty as , . By the 10th century CE, the city and its residents were known to the Han as "" (). A monk named Gao Juhui, who had traveled to the Tarim Basin, wrote that the ''Zhongyun'' were descendants of the ''Xiao Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |