|
Eschenmoser–Tanabe Fragmentation
The Eschenmoser fragmentation, first published in 1967, is the chemical reaction of α,β-epoxyketones (1) with aryl sulfonylhydrazines (2) to give alkynes (3) and carbonyl compounds (4). The reaction is named after the Swiss chemist Albert Eschenmoser, who devised it in collaboration with an industrial research group of Günther Ohloff, and applied it to the production of muscone and related macrocyclic musks. The reaction is also sometimes known as the Eschenmoser–Ohloff fragmentation or the Eschenmoser–Tanabe fragmentation as Masato Tanabe independently published an article on the reaction the same year. The general formula of the fragmentation using ''p''-toluenesulfonylhydrazide is: :: Several examples exist in the literature, and the reaction is also carried out on industrial scale. Reaction mechanism The mechanism of the Eschenmoser fragmentation begins with the condensation of an α,β-epoxyketone (1) with an aryl sulfonylhydrazine (2) to afford the intermediate hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.Rossberg, M. ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Occurrence Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions. Production DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron Lett
''Tetrahedron Letters'' is a weekly international journal for rapid publication of full original research papers in the field of organic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.415. Indexing ''Tetrahedron Letters'' is indexed in: References See also *''Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...'' *'' Tetrahedron: Asymmetry'' Chemistry journals Weekly journals Publications established in 1959 Elsevier academic journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapiro Reaction
The Shapiro reaction or tosylhydrazone decomposition is an organic reaction in which a ketone or aldehyde is converted to an alkene through an intermediate hydrazone in the presence of 2 equivalents of organolithium reagent. The reaction was discovered by Robert H. Shapiro in 1967. The Shapiro reaction was used in the Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis. This reaction is very similar to the Bamford–Stevens reaction, which also involves the basic decomposition of tosyl hydrazones. Reaction mechanism In a prelude to the actual Shapiro reaction, a ketone or an aldehyde (1) is reacted with p-toluenesulfonylhydrazide, ''p''-toluenesulfonylhydrazide(2) to form a ''p''-toluenesulfonylhydrazone (or tosylhydrazone) which is a hydrazone (3). Two equivalents of strong base (chemistry), base such as N-Butyllithium, ''n''-butyllithium abstract the Hydron (chemistry), proton from the hydrazone (4) followed by the less carbon acid, acidic proton α to the hydrazone carbon (5), forming a carbanion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wharton Reaction
The Wharton olefin synthesis or the Wharton reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the reduction of α,β-epoxy ketones using hydrazine to give allylic alcohols. This reaction, introduced in 1961 by P. S. Wharton, is an extension of the Wolff–Kishner reduction. The general features of this synthesis are: 1) the epoxidation of α,β-unsaturated ketones is achieved usually in basic conditions using hydrogen peroxide solution in high yield; 2) the epoxy ketone is treated with 2–3 equivalents of a hydrazine hydrate in presence of stochiometry, substoichiometric amounts of acetic acid. This reaction occurs rapidly at room temperature with the evolution of nitrogen and the formation of an allylic alcohol. It can be used to synthesize compounds. Wharton's initial procedure has been improved. Mechanism and scope The Reaction mechanism, mechanism of the Wharton reaction begins with reaction of the ketone (1) with hydrazine to form a hydrazone (2). Rearrangement of the hydraz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grob Fragmentation
In chemistry Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ..., a Grob fragmentation is an elimination reaction that breaks a neutral aliphatic chain into three fragments: a cation, positive ion spanning atoms 1 and 2 (the "electrofuge"), an unsaturated hydrocarbon, unsaturated neutral fragment spanning positions 3 and 4, and a anion, negative ion (the "nucleofuge") comprising the rest of the chain. For example, the positive ion may be a carbenium ion, carbenium, carbonium ion, carbonium or acylium ion; the neutral fragment could be an alkene, alkyne, or imine; and the negative fragment could be a tosyl or hydroxyl ion: The reaction is named for the Swiss chemist . Alternately, atom 1 could begin as an anion, in which case it becomes neutral rather than going from neutral to cation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxidation
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether () with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an '' epoxy'', but such materials do not contain epoxide groups (or contain only a few residual epoxy gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
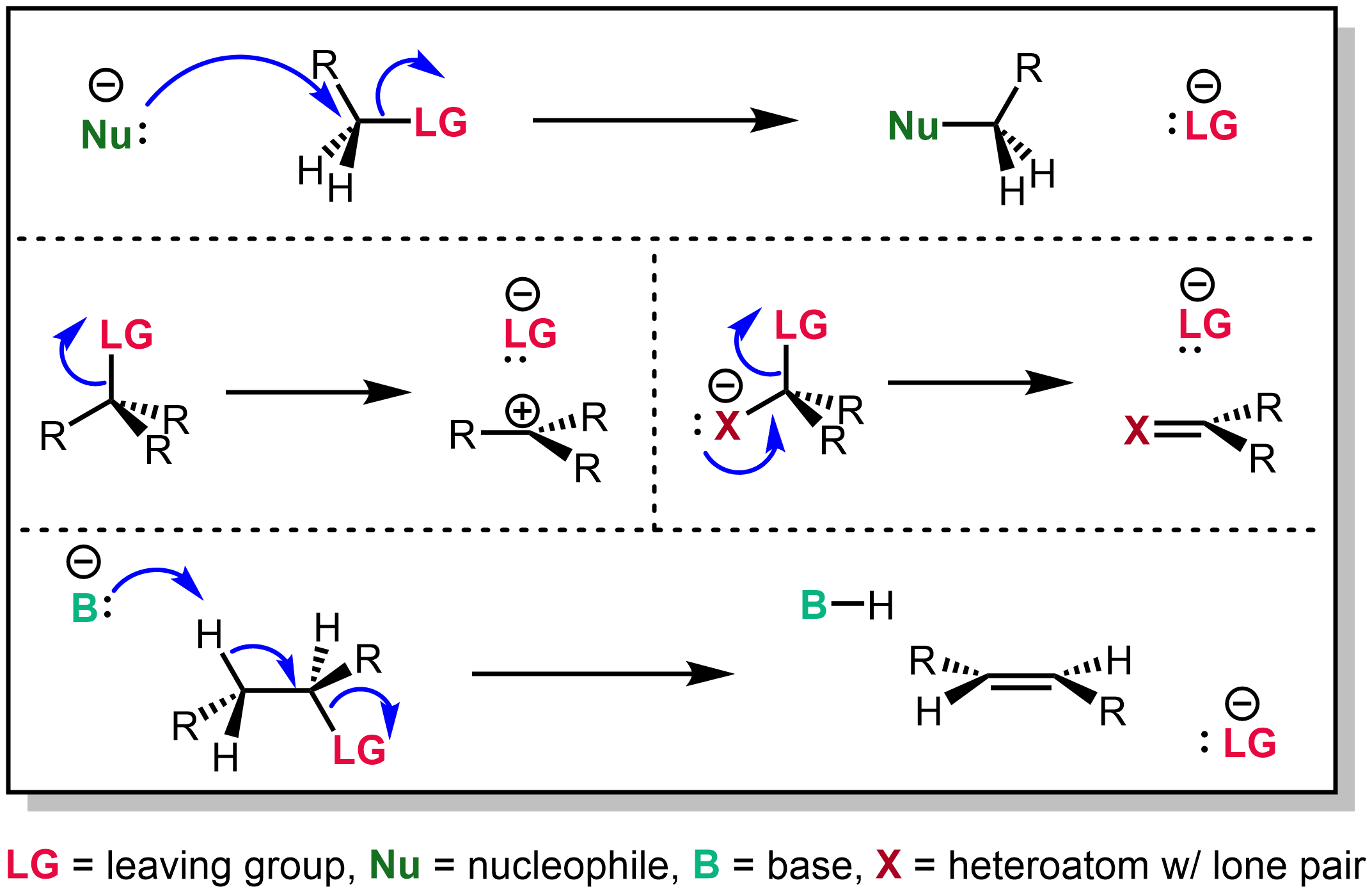
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term '' nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Analog
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sec-butanol
2-Butanol, or ''sec''-butanol, is an organic compound with formula C H3CH( OH)CH2CH3. Its structural isomers are 1-butanol. isobutanol, and ''tert''-butanol. 2-Butanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (''R'')-(−)-2-butanol and (''S'')-(+)-2-butanol. It is normally encountered as a 1:1 mixture of the two stereoisomers — a racemic mixture. This secondary alcohol is a flammable, colorless liquid that is soluble in three parts water and completely miscible with organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale, primarily as a precursor to the industrial solvent methyl ethyl ketone. Manufacture and applications 2-Butanol is manufactured industrially by the hydration of 1-butene or 2-butene: : Sulfuric acid is used as a catalyst for this conversion.. In the laboratory it can be prepared via Grignard reaction by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with acetaldehyde in dried diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran. Although some 2-butanol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-Dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin
DBDMH (also known as 1,3-Dibromo-5,5-Dimethylhydantoin) is an organic compound derived from the heterocycle called dimethylhydantoin. This white crystalline compound with a slight bromine odor is widely used as a disinfectant used for drinking water purification, recreational water treatment, as a bleaching agent in pulp and paper mills, and for treating industrial/commercial water cooling systems. David Ioffe, Arieh Kampf "Bromine, Organic Compounds" in ''Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology'', 2002, by John Wiley & Sons. {{doi, 10.1002/0471238961.0218151325150606.a01 Its action does not involve the use of hypochlorous acid. Mechanism of action 1,3-Dibromo-5,5-Dimethylhydantoin is a source of bromine, which is equivalent to hypobromous acid (HOBr). :Br2X + 2 H2O → 2 HOBr + H2X (Where H2X is 5,5-dimethylhydantoin) With a p''K''a of 8.6, hypobromous acid partially dissociates in water: :HOBr ⇌ H+ + BrO− Hypobromous acid serves as a source of "Br+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |