|
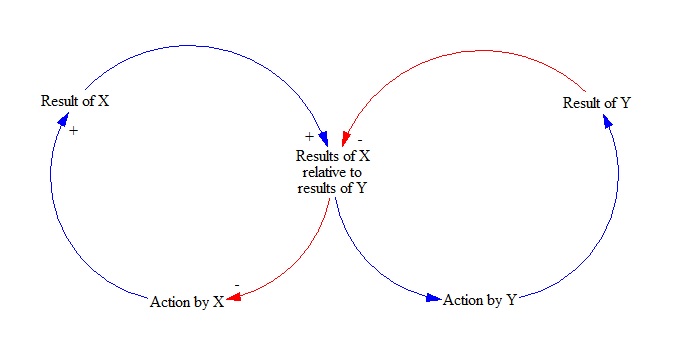
Escalation Archetype
The escalation archetype is one of possible types of system behaviour that are known as system archetypes. The escalation archetype is common for situations of non-cooperative games where each player can make own decisions and these decisions lead to the outcome for the player. However, when both player try to maximize their output (at the expense of the other one) they can get into a loop where each player will try harder and harder to surpass the opponent. While it can have favourable consequences it can also lead to self-destructive behaviour. Structure Elements of archetype Escalation archetype system can be described using causal loop diagrams which may consist of balancing and reinforcing loops. Balancing loop Balancing loop is a structure representing negative feedback process. In such a structure, a change in system leads to actions that usually eliminate the effect of that change which means that the system tends to remain stable in time. Reinforcing loop Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Archetypes
System archetypes are patterns of behavior of a system. Systems expressed by circles of causality have therefore similar structure. Identifying a system archetype and finding the leverage enables efficient changes in a system. The basic system archetypes and possible solutions of the problems are mentioned in the section '' Examples of system archetypes''. A fundamental property of nature is that no cause can affect the past. System archetypes do not imply that current causes affect past effects. Circles of causality The basic idea of system thinking is that every action triggers a reaction. In system dynamics this reaction is called feedback. There are two types of feedback – reinforcing feedback and balancing feedback. Sometimes a feedback (or a reaction) does not occur immediately – the process contains delays. Any system can be drawn as a diagram set up with circles of causality – including actions, feedbacks and delays. Reinforcing feedback (+) Reinforcing fee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of Geopolitics, geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term ''Cold war (term), cold war'' is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary Allies of World War II, alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the Nuclear arms race, nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, Cold War espionage, espionage, far-reaching Economic sanctions, embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be ''causal factors'' for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysically prior to notions of time and space. Causality is an abstraction that indicates how the world progresses. As such a basic concept, it is more apt as an explanation of other concepts of progression than as something to be explained by others more basic. The concept is like those of agency and efficacy. For this reason, a leap of intuition may be needed to grasp it. Acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limits To Growth
''The Limits to Growth'' (''LTG'') is a 1972 report that discussed the possibility of exponential economic and population growth with finite supply of resources, studied by computer simulation. The study used the World3 computer model to simulate the consequence of interactions between the earth and human systems. The model was based on the work of Jay Forrester of MIT, as described in his book ''World Dynamics''. Commissioned by the Club of Rome, the findings of the study were first presented at international gatherings in Moscow and Rio de Janeiro in the summer of 1971. The report's authors are Donella H. Meadows, Dennis L. Meadows, Jørgen Randers, and William W. Behrens III, representing a team of 17 researchers. The report concludes that, without substantial changes in resource consumption, "the most probable result will be a rather sudden and uncontrollable decline in both population and industrial capacity". Although its methods and premises were heavily challenged on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth And Underinvestment
The Growth and Underinvestment Archetype is one of the common system archetype patterns defined as part of the system dynamics discipline. System dynamics is an approach which strives to understand, describe and optimize nonlinear behaviors of complex systems over time, using tools such as feedback loops in order to find leverage pointof the system. As part of this discipline, several commonly found patterns of system behavior were found, named and described in detail. The Growth and Underinvestment Archetype is one of such patterns. Elements of Archetype The system described in the Growth and Underinvestment Archetype consists of three feedback loops. Each feedback loop can be one of two types: * Reinforcing loop – A reinforcing loop is a type of a feedback loop, where a positive increase of variable A causes an increase in variable B, which then in turn causes a positive increase in variable A. The behavior of such system in time is an exponential increase in both variables ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixes That Fail
Fixes that fail is a system archetype that in system dynamics is used to describe and analyze a situation, where a fix effective in the short-term creates side effects for the long-term behaviour of the system and may result in the need of even more fixes.Senge, Peter M., "The Fifth Discipline" (1990). . This archetype may be also known as fixes that backfireFixes that backfire Isee systems, 2006. Retrieved 2011-11-01 or corrective actions that fail.Flood, Robert L., "Rethinking The Fifth Discipline: learning within the unknowable" (1999). p. 19 It resembles the archetype. |
Attractiveness Principle
Attractiveness Principle is one of System Dynamics archetypes. System archetypes describe common patterns of behavior in dynamic complex systems. Attractiveness principle is a variation of Limits to Growth archetype, with restrictions caused by multiple limits. The limiting factors here are each of different character and usually cannot be dealt with the same way and/or (and very likely) they cannot be all addressed. Introduction to the problem Attractiveness principle is a concept that incorporates the fact that any product or kind of business cannot ever be ''“all things to all people”'' Attractiveness Principle at Systems-thinking.org. http://www.systems-thinking.org/theWay/sap/ap.htm though companies very often strive to follow this way.Powell, Bob (2001). The Attractiveness Principle. Continuous Improvement Associates. 1–2. http://www.exponentialimprovement.com/cms/uploads/flyer_attractiveness_principle2p.pdf One needs to make necessary decisions on the characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative Game Theory
In game theory, a cooperative game (or coalitional game) is a game with competition between groups of players ("coalitions") due to the possibility of external enforcement of cooperative behavior (e.g. through contract law). Those are opposed to non-cooperative games in which there is either no possibility to forge alliances or all agreements need to be self-enforcing (e.g. through credible threats). Cooperative games are often analysed through the framework of cooperative game theory, which focuses on predicting which coalitions will form, the joint actions that groups take and the resulting collective payoffs. It is opposed to the traditional non-cooperative game theory which focuses on predicting individual players' actions and payoffs and analyzing Nash equilibria. Cooperative game theory provides a high-level approach as it only describes the structure, strategies and payoffs of coalitions, whereas non-cooperative game theory also looks at how bargaining procedures wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is in a person's 20s, with females affected about twice as often as males. The course of the disorder varies widely, from one e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Performance Enhancing Drug
Performance-enhancing substances, also known as performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs), are substances that are used to improve any form of activity performance in humans. A well-known example of cheating in sports involves doping in sport, where banned physical performance-enhancing drugs are used by athletes and bodybuilders. Athletic performance-enhancing substances are sometimes referred to as ergogenic aids. Cognitive performance-enhancing drugs, commonly called nootropics, are sometimes used by students to improve academic performance. Performance-enhancing substances are also used by military personnel to enhance combat performance. The use of performance-enhancing drugs spans the categories of legitimate use and substance abuse. Definition The classifications of substances as performance-enhancing substances are not entirely clear-cut and objective. As in other types of categorization, certain prototype performance enhancers are universally classified as such (like anaboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallet
A pallet (also called a skid) is a flat transport structure, which supports goods in a stable fashion while being lifted by a forklift, a pallet jack, a front loader, a jacking device, or an erect crane. A pallet is the structural foundation of a unit load, which allows handling and storage efficiencies. Goods in shipping containers are often placed on a pallet secured with strapping, stretch wrap or shrink wrap and shipped. Since its invention in the twentieth century, its use has dramatically supplanted older forms of crating like the wooden box and the wooden barrel, as it works well with modern packaging like corrugated boxes and intermodal containers commonly used for bulk shipping. In addition, pallet collars can be used to support and protect items shipped and stored on pallets. While most pallets are wooden, pallets can also be made of plastic, metal, paper, and recycled materials. Overview Containerization for transport has spurred the use of pallet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)



