|
Erebiola Butleri
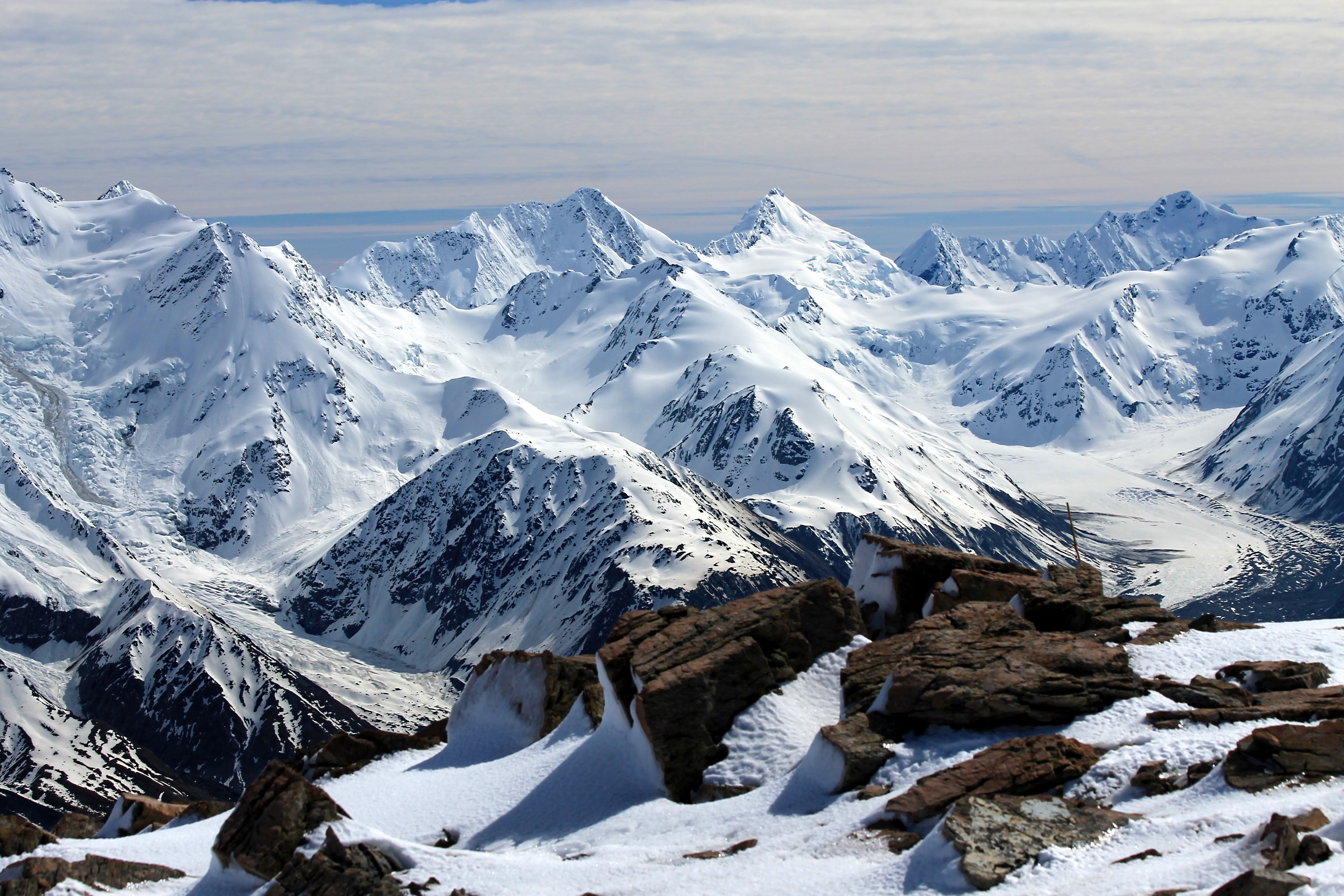
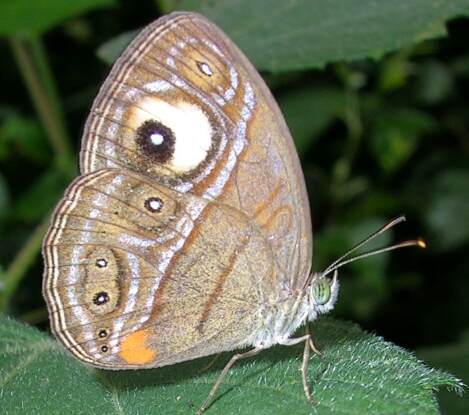
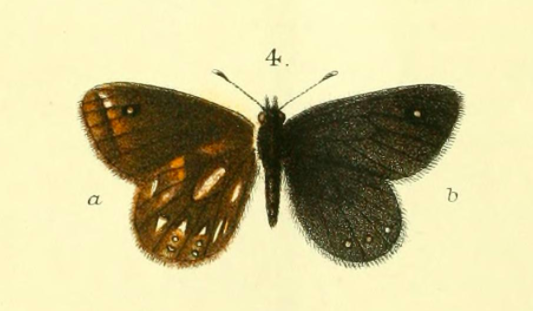
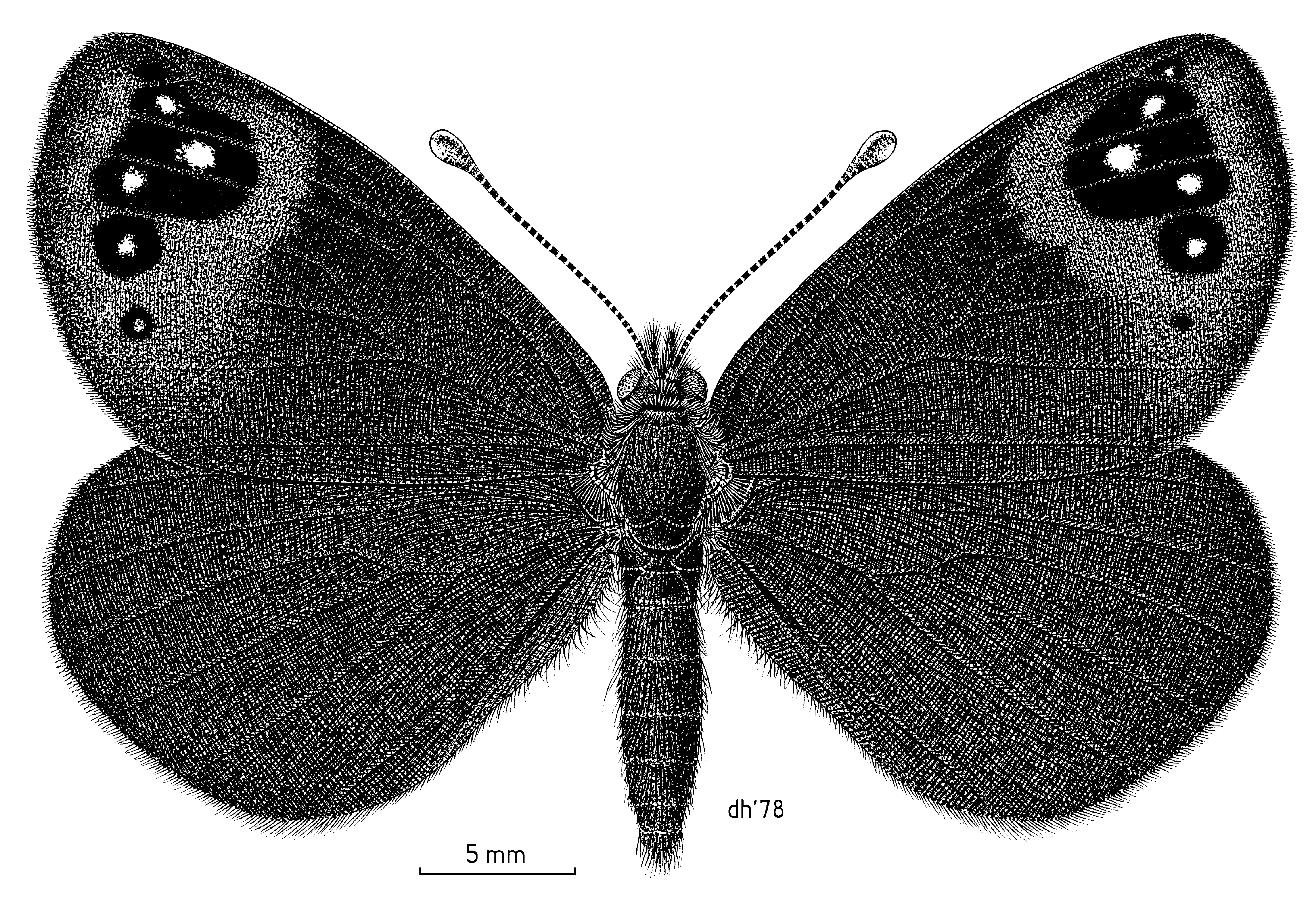
''Erebiola butleri'', or Butler's ringlet, is an elusive New Zealand endemic butterfly, discovered in 1879 by John Enys at the alpine pass at the head of the Rakaia River. It is the only member of the genus ''Erebiola''. ''Erebiola'' is derived from Erebus, the ancient Greek world of darkness between Earth and Hades, while the specific name, ''butleri'', was after Arthur Gardiner Butler of the British Museum who played a major role in early descriptions of New Zealand butterflies. Its Māori name is ''pepe pouri'', which means dark moth, and shares the name with the black mountain ringlet and the forest ringlet butterfly. Description Butler's ringlet has a wingspan of 35–43 mm, with a 40 mm average for males and a 37 mm average for females. Both males and females are smoky brown, though males tend towards the richer browns while the females tend towards the paler browns. The underside of the hindwing has wedge-shaped silvery-white marks. Both the under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard William Fereday
Richard William Fereday (c.1820–30 August 1899) was a New Zealand lawyer, entomologist and artist. He was born in Ettingshall, Staffordshire, England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ... on c.1820. References 1820 births 1899 deaths New Zealand artists 19th-century New Zealand lawyers People from Ettingshall New Zealand entomologists British emigrants to New Zealand {{NewZealand-law-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erebiola Butleri Cropped Fereday
''Erebiola butleri'', or Butler's ringlet, is an elusive New Zealand endemic butterfly, discovered in 1879 by John Enys at the alpine pass at the head of the Rakaia River. It is the only member of the genus ''Erebiola''. ''Erebiola'' is derived from Erebus, the ancient Greek world of darkness between Earth and Hades, while the specific name, ''butleri'', was after Arthur Gardiner Butler of the British Museum who played a major role in early descriptions of New Zealand butterflies. Its Māori name is ''pepe pouri'', which means dark moth, and shares the name with the black mountain ringlet and the forest ringlet butterfly. Description Butler's ringlet has a wingspan of 35–43 mm, with a 40 mm average for males and a 37 mm average for females. Both males and females are smoky brown, though males tend towards the richer browns while the females tend towards the paler browns. The underside of the hindwing has wedge-shaped silvery-white marks. Both the under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Described In 1879
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular Taxonomic rank, ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's Linnaean taxonomy, system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard de Jussieu, Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satyrini
The Satyrini is one of the tribes of the subfamily Satyrinae. It includes about 2200 species and is therefore the largest tribe in the subfamily which comprises 2500 species. Distribution Satyrini butterflies have a worldwide distribution, but the distribution pattern differs between subtribes. Some subtribes are almost restricted to a single biogeographic region, such as the Pronophilina, which is found only in Andean cloud forests from Venezuela to Bolivia. Biology The larval food plants of many species in this tribe are grasses, i.e. Poaceae. It is considered that the Satyrini diversified at about the same time as the grasses did, and that the radiation of the tribe is therefore closely related to the evolution of the grasses. In contrast, the tribe has a few genera which show uncommon feeding preferences. Three genera, '' Euptychia'', ''Ragadia'' and ''Acrophtalmia'', feed on Lycopsida, and moreover, some species of ''Euptychia'' have been reported to feed on mosses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterflies Of New Zealand
The butterflies of New Zealand include twelve endemism, endemic species, as well as several introduced and migrant species. Lepidoptera, which includes the butterflies and moths, is the third largest insect order (biology), order in New Zealand. Species list Conservation Very little is known about any butterfly extinctions since human settlement of New Zealand since they leave few remains. The majority of New Zealand invertebrates are found in forests, so it is possible that some butterflies became extinct due to the large scale forest clearance after human settlement. , Report Ref. ME612, Ministry for the Environment, Wellington, New Zealand. See also *List of Lepidoptera of New Zealand *Fauna of New Zealand *Environment of New Zealand |
Percnodaimon Pluto
''Percnodaimon merula'', the black mountain ringlet, is a satyrid butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is currently the only recognised species in the monotypic genus ''Percnodaimon,'' endemic to New Zealand, although there may be other undescribed species in the genus. The black mountain ringlet is notable for living exclusively in rocky areas of New Zealand's Southern Alps, usually above 1200 m. Its eggs are laid on rocks, its larvae feed on mountain ''Poa'' species, and it pupates under a stone. It has distinctive dark velvety wings and a zig-zag flight pattern over the scree slopes on which it lives. Taxonomy This species has had a complicated taxonomic history. It was originally described as ''Erebia pluto'' by Richard W. Fereday in 1872 from the Craigieburn Range in the South Island, and was moved to the new genus ''Percnodaimon'' by Butler in 1876. It was known as ''Percnodaimon pluto'' for many years, and Wise in 1967 regarded this as the correct name for the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erebia
''Erebia'' is a Holarctic genus of brush-footed butterflies, family Nymphalidae. Most of the about 90–100 species (see also below) are dark brown or black in color, with reddish-brown to orange or more rarely yellowish wing blotches or bands. These usually bear black spots within, which sometimes have white center spots. This genus has found it easy to adapt to arid and especially cold conditions. Most of its members are associated with high-altitude lands, forest clearings or high latitude and tundra. ''Erebia'' species are frequent in the Alps, Rocky Mountains, subarctic and even Arctic regions, and the cooler parts of Central Asia. In fact, the North American term for these butterflies is alpines. Palearctic species are collectively known as ringlets or arguses. However, none of these terms is used exclusively for this genus. Taxonomy and systematics The genus ''Erebia'' was erected by Johan Wilhelm Dalman in 1816. As type species, the Arran brown—described as ''Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dracophyllum
''Dracophyllum'' is a genus of plants belonging to the family Ericaceae, formerly Epacridaceae. There are 61 species in the genus, mostly shrubs, but also cushion plants and trees, found in New Zealand, Australia, Lord Howe Island and New Caledonia. The name ''Dracophyllum'', meaning dragon-leaf, refers to their strong outward similarity to the unrelated '' Dracaena'', sometimes known as dragon tree. Although dicotyledonous, they resemble primitive monocots with their slender leaves concentrated in clumps at the ends of the branches; they are sometimes called grass-trees. The height varies from one centimetre ('' D. minimum'') to about 12 metres ('' D. longifolium''). Species The following species are recognised by ''The Plant List'': *'' Dracophyllum acerosum'' Berggr. *''Dracophyllum adamsii'' Petrie *''Dracophyllum alticola'' Däniker *''Dracophyllum arboreum'' Cockayne * ''Dracophyllum'' × ''arcuatum'' W.R.B.Oliv. *''Dracophyllum balansae'' Virot *''Dracophyllum cosmelioi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebe (plant)
''Veronica'' sect. ''Hebe'' is a group of plants within the genus '' Veronica'', native to New Zealand, Rapa in French Polynesia, the Falkland Islands and South America. It was formerly treated as the separate genus ''Hebe'' (). It includes about 90 species. Almost all species occur in New Zealand, apart from ''Veronica rapensis'' (endemic to Rapa) and ''Veronica salicifolia'', found in South America. It is named after the Greek goddess of youth, Hebe. Informally, species in the section may be called shrubby veronicas or hebes. Hebes are widely grown as ornamental plants (see Cultivation below). Description Species in ''Veronica'' sect. ''Hebe'' have four perpendicular rows of leaves in opposite decussate pairs. The flowers are perfect, the corolla usually has four slightly unequal lobes, the flower has two stamens and a long style. Flowers are arranged in a spiked inflorescence. Identification of species is difficult, especially if they are not in flower. The plants range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern Alps" generally refers to the entire range, although separate names are given to many of the smaller ranges that form part of it. The range includes the South Island's Main Divide, which separates the water catchments of the more heavily populated eastern side of the island from those on the west coast. Politically, the Main Divide forms the boundary between the Marlborough, Canterbury and Otago regions to the southeast and the Tasman and West Coast regions to the northwest. Names The Māori name of the range is , meaning "the Mirage of the Ocean". The English explorer James Cook bestowed the name ''Southern Alps'' on 23 March 1770, admiring their "prodigious height". p. 384. They had previously been noted by Abel Tasman in 1642, whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, and to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers , making it the world's 12th-largest island. At low altitude, it has an oceanic climate. The South Island is shaped by the Southern Alps which run along it from north to south. They include New Zealand's highest peak, Aoraki / Mount Cook at . The high Kaikōura Ranges lie to the northeast. The east side of the island is home to the Canterbury Plains while the West Coast is famous for its rough coastlines such as Fiordland, a very high proportion of native bush and national parks, and the Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers. The main centres are Christchurch and Dunedin. The economy relies on agriculture and fishing, tourism, and general manufacturing and services. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyespot (mimicry)
An eyespot (sometimes ocellus) is an eye-like marking. They are found in butterflies, reptiles, cats, birds and fish. Eyespots could be explained in at least three different ways. They may be a form of mimicry in which a spot on the body of an animal resembles an eye of a different animal, to deceive potential predator or prey species. They may be a form of self-mimicry, to draw a predator's attention away from the prey's most vulnerable body parts. Or they may serve to make the prey appear inedible or dangerous. Eyespot markings may play a role in intraspecies communication or courtship; the best-known example is probably the eyespots on a peacock's display feathers. The pattern-forming biological process (morphogenesis) of eyespots in a wide variety of animals is controlled by a small number of genes active in embryonic development, including the genes called Engrailed, Distal-less, Hedgehog, Antennapedia, and the Notch signaling pathway. Artificial eyespots have been sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_male.jpg)

_male_Bulgaria.jpg)


