|
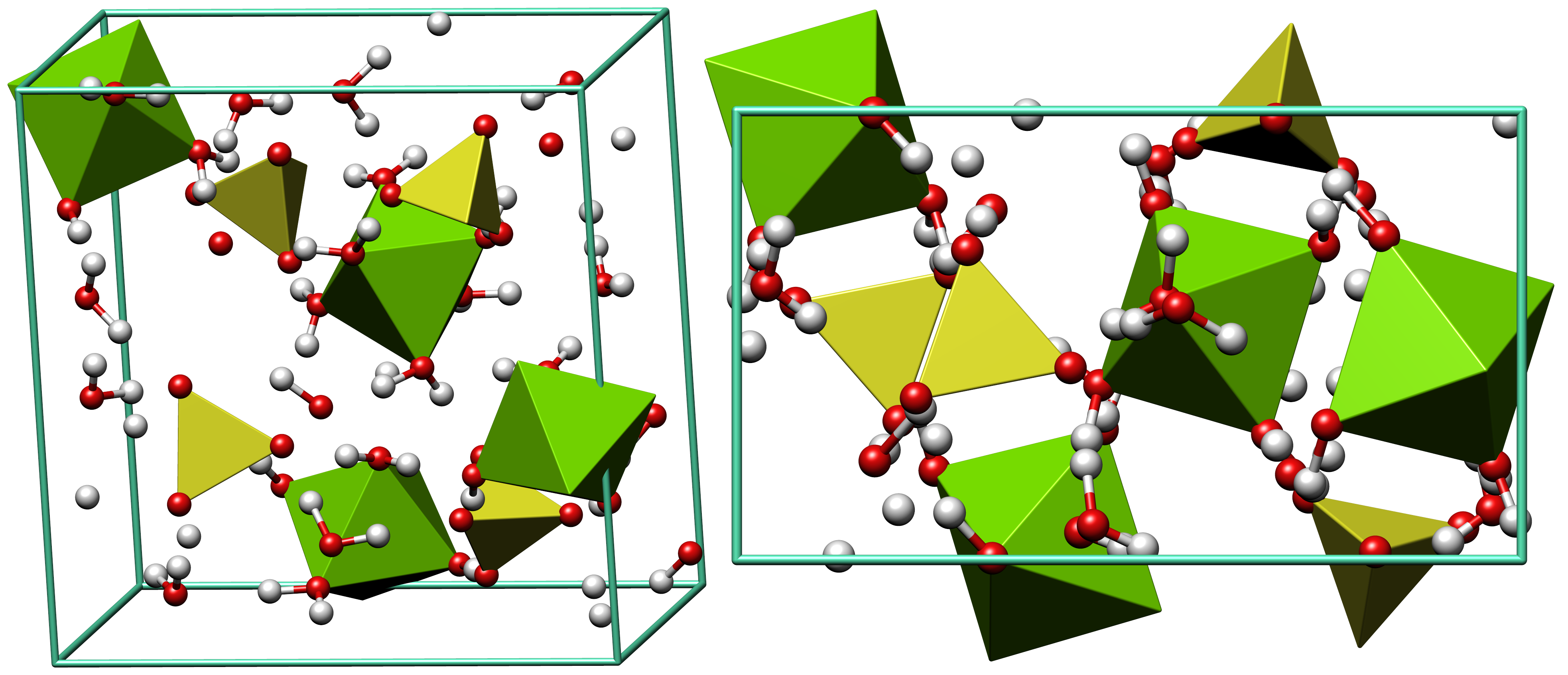
Epsomite
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O. Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massive encrustations. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. The Mohs hardness is 2 to 2.5 and it has a low specific gravity of 1.67. It is readily soluble in water. It absorbs water from the air and converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure. Etymology It was first systematically described in 1806 for an occurrence near Epsom, Surrey, England, after which it was named. Discovery and occurrence Epsomite forms as encrustations or efflorescences on limestone cavern walls and mine timbers and walls, rarely as volcanic fumarole deposits, and as rare beds in evaporite layers such as those found in certain bodies of salt water. It occurs in association with melanterite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate (in English-speaking countries other than the US) is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula , consisting of magnesium cations (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions . It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water but not in ethanol. Magnesium sulfate is usually encountered in the form of a hydrate , for various values of ''n'' between 1 and 11. The most common is the heptahydrate , known as Epsom salt, which is a household chemical with many traditional uses, including bath salts. The main use of magnesium sulfate is in agriculture, to correct soils deficient in magnesium (an essential plant nutrient because of the role of magnesium in chlorophyll and photosynthesis). The monohydrate is favored for this use; by the mid 1970s, its production was 2.3 million tons per year. The anhydrous form and several hydrates occur in nature as minerals, and the salt is a significant component of the water from some springs. Hydrates Magnesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Mineral
The sulfate minerals are a class of minerals that include the sulfate ion () within their structure. The sulfate minerals occur commonly in primary evaporite depositional environments, as gangue minerals in hydrothermal veins and as secondary minerals in the oxidizing zone of sulfide mineral deposits. The chromate and manganate minerals have a similar structure and are often included with the sulfates in mineral classification systems.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 347–354 . Sulfate minerals include: *Anhydrous sulfates **Barite BaSO4 ** Celestite SrSO4 **Anglesite PbSO4 **Anhydrite CaSO4 **Hanksite Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl *Hydroxide and hydrous sulfates **Gypsum CaSO4·2H2O **Chalcanthite CuSO4·5H2O **Kieserite MgSO4·H2O ** Starkeyite MgSO4·4H2O **Hexahydrite MgSO4·6H2O **Epsomite MgSO4·7H2O **Meridianiite MgSO4·11H2O **Melanterite FeSO4·7H2O **Antlerite Cu3SO4(OH)4 **Brochantite Cu4SO4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components. Two terms are mainly associated with solid solutions - ''solvents'' and ''solutes,'' depending on the relative abundance of the atomic species. In general if two compounds are isostructural then a solid solution will exist between the end members (also known as parents). For example sodium chloride and potassium chloride have the same cubic crystal structure so it is possible to make a pure compound with any ratio of sodium to potassium (Na1-xKx)Cl by dissolving that ratio of NaCl and KCl in water and then evaporating the solution. A member of this family is sold under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirabilite
Mirabilite, also known as Glauber's salt, is a hydrous sodium sulfate mineral with the chemical formula Na2SO4·10H2O. It is a vitreous, colorless to white monoclinic mineral that forms as an evaporite from sodium sulfate-bearing brines. It is found around saline springs and along saline playa lakes. Associated minerals include gypsum, halite, thenardite, trona, glauberite, and epsomite. Mirabilite is unstable and quickly dehydrates in dry air, the prismatic crystals turning into a white powder, thenardite (Na2SO4). In turn, thenardite can also absorb water and converts to mirabilite. Mirabilite is used as a purgative and anti-inflammatory remedy in the Traditional Chinese medicine; in Mandarin, it is called máng xiāo. The name 'mirabilite' is based on the phrase ''"Sal mirabilis"'' (Latin for "wonderful salt") used by Johann Rudolph Glauber when he inadvertently synthesized mirabilite. Mirabilite is found in several areas within the Mammoth Cave system, where it appears to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goslarite
Goslarite is a hydrated zinc sulfate mineral () which was first found in the Rammelsberg mine, Goslar, Harz, Germany. It was described in 1847. Goslarite belongs to the epsomite Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O. Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massi ... group which also includes epsomite () and morenosite (). Goslarite is an unstable mineral at the surface and will dehydrate to other minerals like bianchite (), boyleite () and gunningite (). Physical properties The composition of goslarite was determined by the US National Bureau of Standards (now the National Institute of Standards and Technology) in 1959 as follows: SO3 27.84 wt%, ZnO 28.30 wt% and 43.86 wt%. Goslarite's cleavage is perfect in , as for epsomite and morenosite. The color of goslarite ranges from brownish to pinkish, blue, brown, colorl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rozenite
Rozenite is a hydrous iron sulfate mineral, Fe2+SO4•4(H2O). It occurs as a secondary mineral, formed under low humidity at less than as an alteration of copper-free melanterite, which is a post mine alteration product of pyrite or marcasite. It also occurs in lacustrine sediments and coal seams. Associated minerals include melanterite, epsomite, jarosite, gypsum, sulfur, pyrite, marcasite and limonite. It was first described in 1960 for an occurrence on Ornak Mountain, Western Tatra Mountains, Małopolskie, Poland. It was named for Polish mineralogist Zygmunt Rozen (1874–1936). The thermal expansion of rozenite was studied from to using neutron diffraction. Rozenite exhibits negative linear thermal expansion Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic ..., meaning that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alunogen
Alunogen (from French ''alun'', “alum”), also called feather alum and hair salt is a colourless to white (although often coloured by impurities, such as iron substituting for aluminium) fibrous to needle-like aluminium sulfate mineral. It has the chemical formula Al2(SO4)3·17H2O. It is often found on the walls of mines and quarries as a secondary mineral. It can be found in the oxidation zones of some ore deposits as well as on burning coal dumps (i.e., as the product of millosevichite hydration). It also forms as a low temperature deposit in fumaroles. It occurs associated with pyrite, marcasite, halotrichite, pickeringite, epsomite, potash alum, melanterite and gypsum Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. .... The crystallochemical formula, can be written as: l(H2O) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pickeringite
Pickeringite is a magnesium aluminium sulfate mineral with formula MgAl2(SO4)4·22(H2O). It forms a series with halotrichite. It forms as an alteration product of pyrite in aluminium rich rocks and in coal seams. It also occurs in pyrite rich hydrothermal ore deposits in arid regions. It forms in fumaroles and in caves. It occurs with kalinite Kalinite is a mineral composed of hydrated potassium aluminium sulfate (a type of alum). It is a fibrous monoclinic alum, distinct from isometric potassium alum,American Mineralogist (1923) 8:15 named in 1868. Its name comes from ''kalium'' ..., alunogen, epsomite, melanterite, copiapite and gypsum. It was first described in 1844 for an occurrence in Cerros Pintados, Pampa del Tamarugal, Iquique Province, Tarapacá Region, Chile. It was named for American linguist and philologist John Pickering (linguist), John Pickering (1777–1846). References Sulfate minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14 {{sulfate-miner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |