|
Epipaleolithic
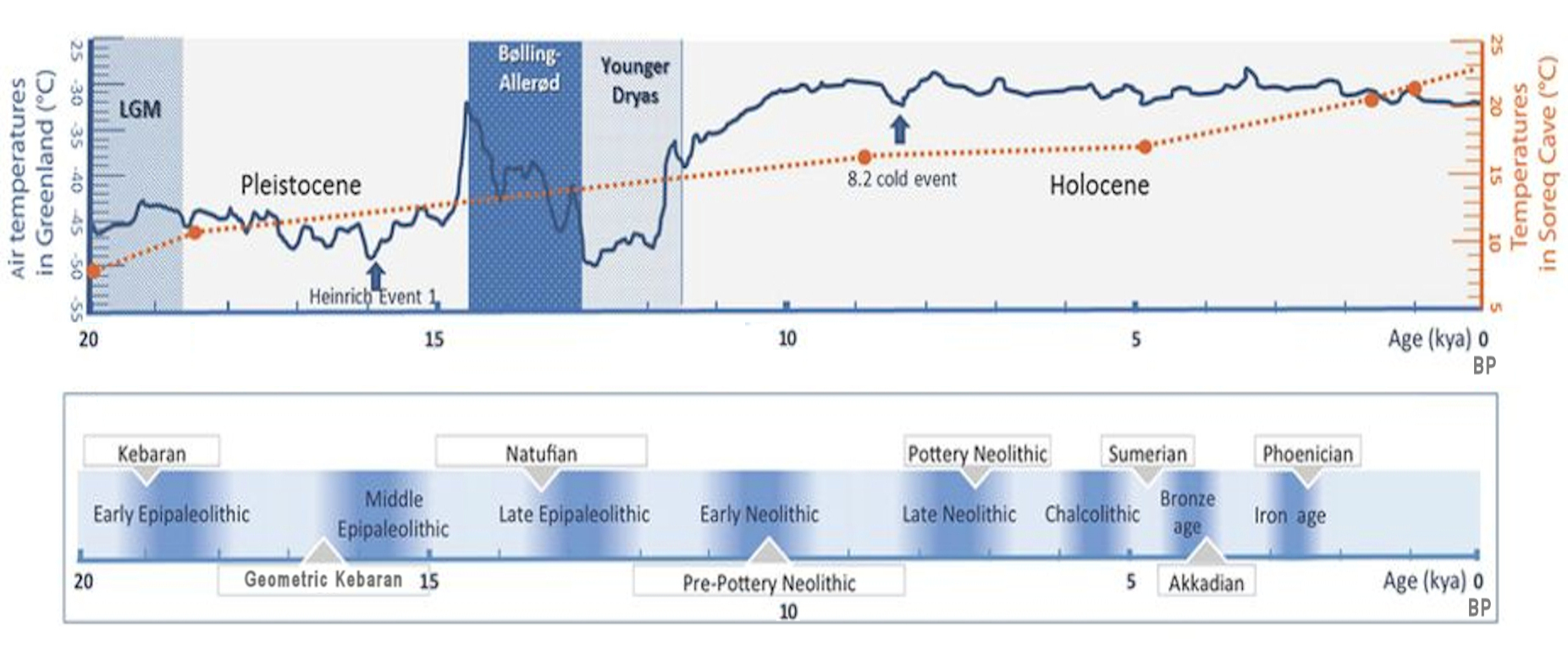
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are sometimes confused or used as synonyms. More often, they are distinct, referring to approximately the same period of time in different geographic areas. Epipaleolithic always includes this period in the Levant and, often, the rest of the Near East. It sometimes includes parts of Southeast Europe, where Mesolithic is much more commonly used. Mesolithic very rarely includes the Levant or the Near East; in Europe, Epipalaeolithic is used, though not very often, to refer to the early Mesolithic. The Epipalaeolithic has been defined as the "final Upper Palaeolithic industries occurring at the end of the final glaciation which appear to merge technologically into the Mesolithic". The period is generally dated from BP to 10,000 BP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
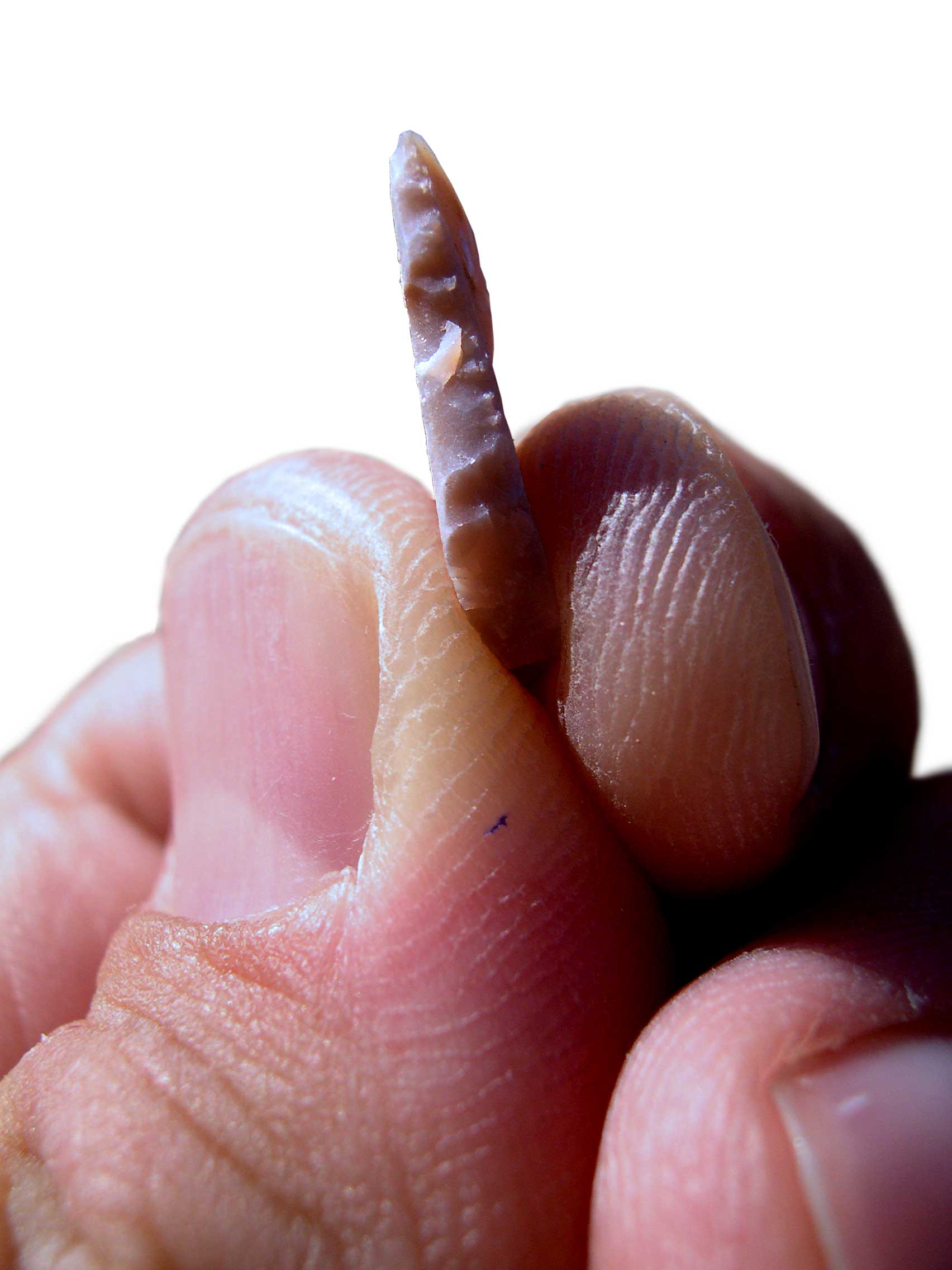
Microlith
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade ( microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic of the Mesolithic and the Neolithic. Geometric microlit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
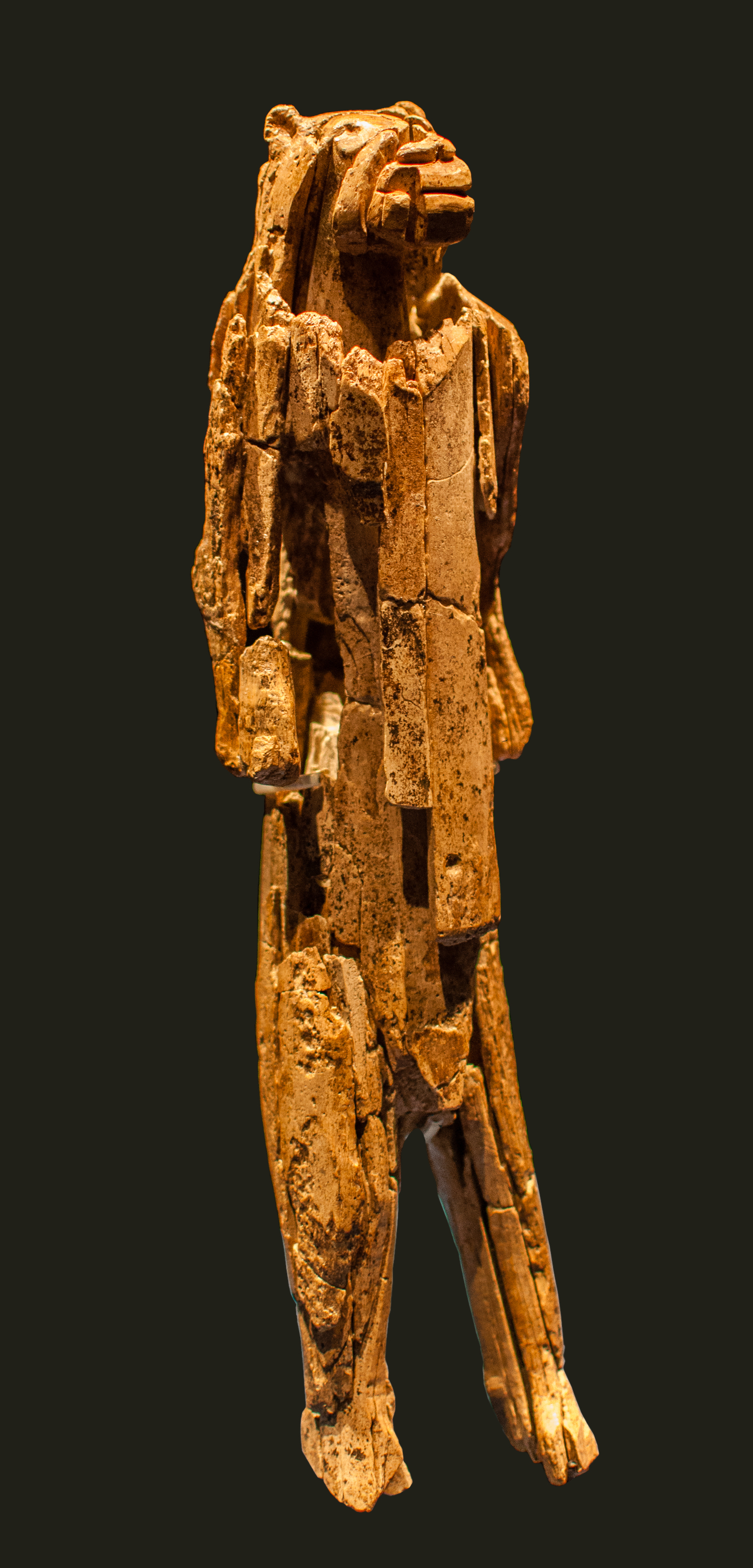
Natufian Culture
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction of agriculture. The Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the first Neolithic settlements of the region, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture, at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of earliest evidence of agriculture in the world. The world's oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan's northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia In addition, the oldest known evidence of possible beer-brewing, dating to approximately 13,000 BP, was found at the Raqefet Cave in Mount Carmel near Haifa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and Western Asia, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in Southwest Asia (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, but it is associated with a decline in the group hunting of large animals in favour of a broader hunt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3,000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys (bronze: originally copper and arsenic, later copper and tin) into tools, supplanting stone in many uses. Stone Age artifacts that have been discovered include tools used by modern humans, by their predecessor species in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipaleolithic Near East
The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic ("Final Old Stone Age", also known as Mesolithic) in the prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Palaeolithic and before the Neolithic, between approximately 20,000 and 10,000 years Before Present (BP). The people of the Epipalaeolithic were nomadic hunter-gatherers who generally lived in small, seasonal camps rather than permanent villages. They made sophisticated stone tools using microliths—small, finely-produced blades that were hafted in wooden implements. These are the primary artifacts by which archaeologists recognise and classify Epipalaeolithic sites. The start of the Epipalaeolithic is defined by the appearance of microliths. Although this is an arbitrary boundary, the Epipalaeolithic does differ significantly from the preceding Upper Palaeolithic. Epipalaeolithic sites are more numerous, better preserved, and can be accurately radiocarbon dated. The period coincides with the gradual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Palaeolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans, until the advent of the Neolithic Revolution and agriculture. Anatomically modern humans (i.e. ''Homo sapiens'') are believed to have emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago, it has been argued by some that their ways of life changed relatively little from that of archaic humans of the Middle Paleolithic, until about 50,000 years ago, when there was a marked increase in the diversity of artefacts found associated with modern human remains. This period coincides with the most common date assigned to expansion of modern humans from Africa throughout Asia and Eurasia, which contributed to the extinction of the Neanderthals. The Upper Paleolithic has the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kebaran
The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an archaeological culture in the Eastern Mediterranean area (c. 23,000 to 15,000 BP), named after its type site, Kebara Cave south of Haifa. The Kebaran were a highly mobile nomadic population, composed of hunters and gatherers in the Levant and Sinai areas who used microlithic tools. Overview The Kebaran is the last Upper Paleolithic phase of the Levant. Kebaran stone tool assemblages are characterized by small, geometric microliths, and are thought to have lacked the specialized grinders and pounders found in later Near Eastern cultures. Small stone tools called microliths and retouched bladelets can be found for the first time. The microliths of this culture period differ greatly from the Aurignacian artifacts. The Kebaran is preceded by the Athlitian phase of the Upper Paleolithic Levantine Aurignacian (formerly called Antelian) and followed by the proto-agrarian Natufian culture of the Ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans, until the advent of the Neolithic Revolution and agriculture. Anatomically modern humans (i.e. ''Homo sapiens'') are believed to have emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago, it has been argued by some that their ways of life changed relatively little from that of archaic humans of the Middle Paleolithic, until about 50,000 years ago, when there was a marked increase in the diversity of artefacts found associated with modern human remains. This period coincides with the most common date assigned to expansion of modern humans from Africa throughout Asia and Eurasia, which contributed to the extinction of the Neanderthals. The Upper Paleolithic has the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kebaran Culture
The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an archaeological culture in the Eastern Mediterranean area (c. 23,000 to 15,000 BP), named after its type site, Kebara Cave south of Haifa. The Kebaran were a highly mobile nomadic population, composed of hunters and gatherers in the Levant and Sinai areas who used microlithic tools. Overview The Kebaran is the last Upper Paleolithic phase of the Levant. Kebaran stone tool assemblages are characterized by small, geometric microliths, and are thought to have lacked the specialized grinders and pounders found in later Near Eastern cultures. Small stone tools called microliths and retouched bladelets can be found for the first time. The microliths of this culture period differ greatly from the Aurignacian artifacts. The Kebaran is preceded by the Athlitian phase of the Upper Paleolithic Levantine Aurignacian (formerly called Antelian) and followed by the proto-agrarian Natufian culture of the Epip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azilian
The Azilian is a Mesolithic industry of the Franco-Cantabrian region of northern Spain and Southern France. It dates approximately 10,000–12,500 years ago. Diagnostic artifacts from the culture include projectile points (microliths with rounded retouched backs), crude flat bone harpoons and pebbles with abstract decoration. The latter were first found in the River Arize at the type-site for the culture, the ''Grotte du Mas d'Azil'' at Le Mas-d'Azil in the French Pyrenees (illustrated, now with a modern road running through it). These are the main type of Azilian art, showing a great reduction in scale and complexity from the Magdalenian Art of the Upper Palaeolithic. The industry can be classified as part of the Epipaleolithic or the Mesolithic periods, or of both. Archaeologists think the Azilian represents the tail end of the Magdalenian as the warming climate brought about changes in human behaviour in the area. The effects of melting ice sheets would have diminished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1928_Natufian_culture_discovery.jpg)





