|
Epilimnion
The epilimnion or surface layer is the top-most layer in a thermally stratified lake. It sits above the deeper metalimnion and hypolimnion. It is typically warmer and has a higher pH and higher dissolved oxygen concentration than the hypolimnion. Physical Structure Properties In the water column, the epilimnion sits above all other layers. The epilimnion is only present in stratified lakes. On the topside of the epilimnion it is in contact with air, which leaves it open to wind action, which allows the water to experience turbulence. Turbulence and convection work together to make waves which increases aeration. On the bottom side of the epilimnion is the metalimnion, which contains the thermocline. The thermocline is created because of the difference in temperature between the epilimnion and the metalimnion. This is due to the fact that since the epilimnion is in contact with air and is above everything, it interacts with the sun and heat more, making it warmer than the lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypolimnion
The hypolimnion or under lake is the dense, bottom layer of water in a thermally- stratified lake. The word hypolimnion is derived from the Greek "limnos" meaning "lake". It is the layer that lies below the thermocline. Typically the hypolimnion is the coldest layer of a lake in summer, and the warmest layer during winter. In deep, temperate lakes, the bottom-most waters of the hypolimnion are typically close to 4 °C throughout the year. The hypolimnion may be much warmer in lakes at warmer latitudes. Being at depth, it is isolated from surface wind-mixing during summer, and usually receives insufficient irradiance (light) for photosynthesis to occur. Oxygen dynamics The deepest portions of the hypolimnion have low oxygen concentrations. In eutrophic lakes, the hypolimnion is often anoxic. Deep mixing of lakes during the fall and early winter allows oxygen to be transported from the epilimnion to the hypolimnion. The cooling of the epilimnion during the fall reduces la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Stratification
Lake stratification is the tendency of lakes to form separate and distinct thermal layers during warm weather. Typically stratified lakes show three distinct layers, the Epilimnion comprising the top warm layer, the thermocline (or Metalimnion): the middle layer, which may change depth throughout the day, and the colder Hypolimnion extending to the floor of the lake. Definition The thermal stratification of lakes refers to a change in the temperature at different depths in the lake, and is due to the density of water varying with temperature. Cold water is denser than warm water and the epilimnion generally consists of water that is not as dense as the water in the hypolimnion. However, the temperature of maximum density for freshwater is 4 °C. In Temperate climate, temperate regions where lake water warms up and cools through the seasons, a cyclical pattern of overturn occurs that is repeated from year to year as the cold dense water at the top of the lake sinks (see stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Stratification (11)
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
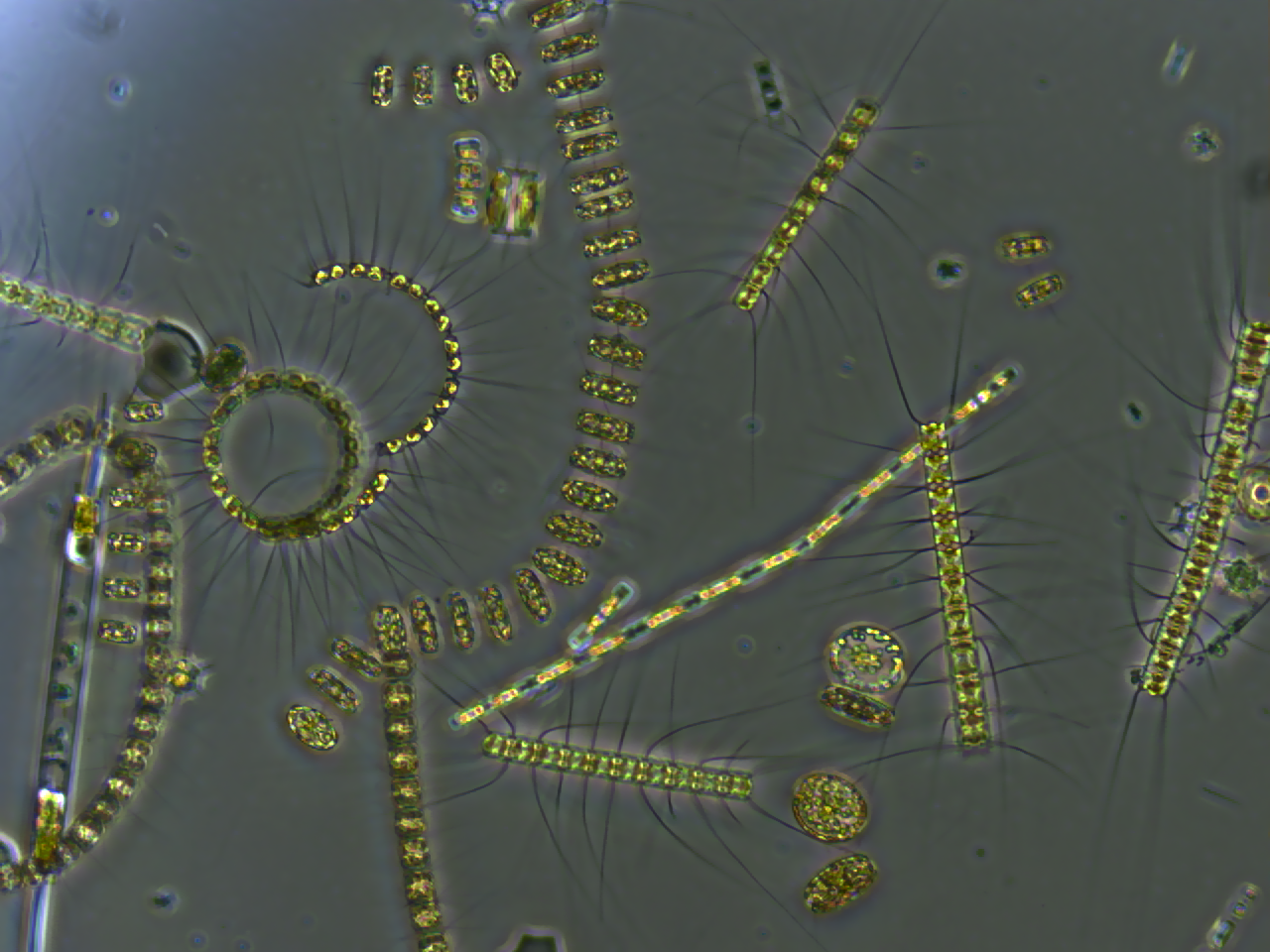
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolian Processes
Aeolian processes, also spelled eolian, pertain to wind activity in the study of geology and weather and specifically to the wind's ability to shape the surface of the Earth (or other planets). Winds may erode, transport, and deposit materials and are effective agents in regions with sparse vegetation, a lack of soil moisture and a large supply of unconsolidated sediments. Although water is a much more powerful eroding force than wind, aeolian processes are important in arid environments such as deserts. The term is derived from the name of the Greek god Aeolus, the keeper of the winds. Definition and setting ''Aeolian processes'' are those processes of erosion, transport, and deposition of sediments that are caused by wind at or near the surface of the earth. Sediment deposits produced by the action of wind and the sedimentary structures characteristic of these deposits are also described as ''aeolian''. Aeolian processes are most important in areas where there is little or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runoff Model (reservoir)
A runoff model is a mathematical model describing the rainfall–runoff relations of a rainfall ''catchment area'', drainage basin or ''watershed''. More precisely, it produces a surface runoff hydrograph in response to a rainfall event, represented by and input as a hyetograph. In other words, the model calculates the conversion of rainfall into runoff. A well known runoff model is the ''linear reservoir'', but in practice it has limited applicability. The runoff model with a ''non-linear reservoir'' is more universally applicable, but still it holds only for catchments whose surface area is limited by the condition that the rainfall can be considered more or less uniformly distributed over the area. The maximum size of the watershed then depends on the rainfall characteristics of the region. When the study area is too large, it can be divided into sub-catchments and the various runoff hydrographs may be combined using flood routing techniques. Rainfall-runoff models need to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
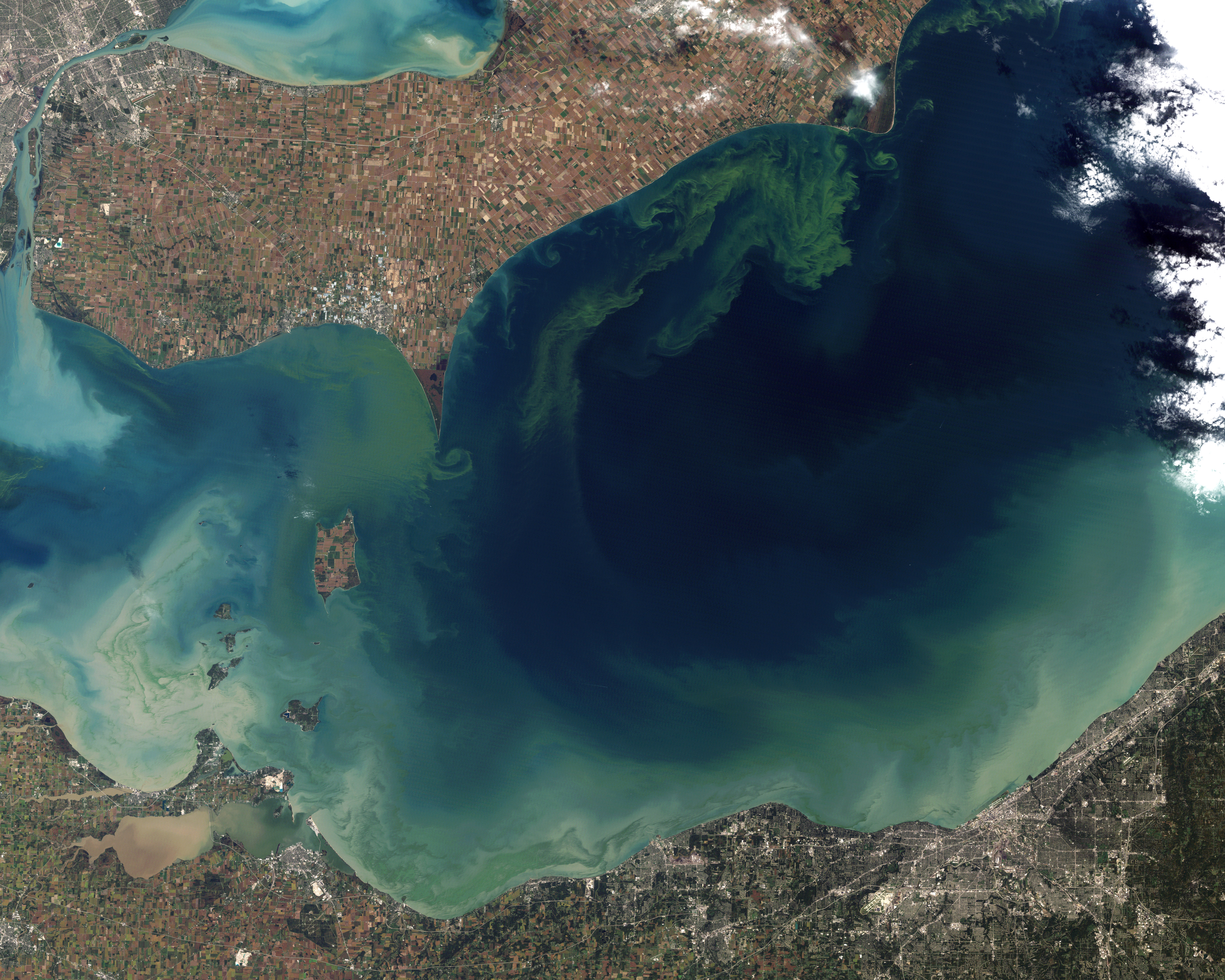
Algal Bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasses many types of aquatic photosynthetic organisms, both macroscopic multicellular organisms like seaweed and microscopic unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria. ''Algal bloom'' commonly refers to the rapid growth of microscopic unicellular algae, not macroscopic algae. An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest. Algal blooms are the result of a nutrient, like nitrogen or phosphorus from various sources (for example fertilizer runoff or other forms of nutrient pollution), entering the aquatic system and causing excessive growth of algae. An algal bloom affects the whole ecosystem. Consequences range from the benign feeding of higher trophic levels to more harmful effects like blocking sunlight from reaching other organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with depth than it does in the layers above or below. In the ocean, the thermocline divides the upper mixed layer from the calm deep water below. Depending largely on season, latitude, and turbulent mixing by wind, thermoclines may be a semi-permanent feature of the body of water in which they occur, or they may form temporarily in response to phenomena such as the radiative heating/cooling of surface water during the day/night. Factors that affect the depth and thickness of a thermocline include seasonal weather variations, latitude, and local environmental conditions, such as tides and currents. Oceans Most of the heat energy of the sunlight that strikes the Earth is absorbed in the first few centimeters at the ocean's surface, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeration
Aeration (also called aerification or aeriation) is the Systems engineering process, process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or solvation, dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid (such as soil). Aeration processes create additional surface area in the mixture, allowing greater chemical or suspension reactions. Aeration of liquids Methods Aeration of liquids (usually water) is achieved by: * passing air through the liquid by means of the Venturi tube, Aeration Turbine, aeration turbines or compressed air which can be combined with diffuser(s) air stone(s), as well as fine bubble diffusers, coarse bubble diffusers or linear aeration tubing. Ceramics are suitable for this purpose, often involving dispersion of fine air or gas bubbles through the porous ceramic into a liquid. The smaller the bubbles, the more gas is exposed to the liquid increasing the gas transfer efficiency. Diffusers or spargers can also be designed into the system to cause turbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |