|
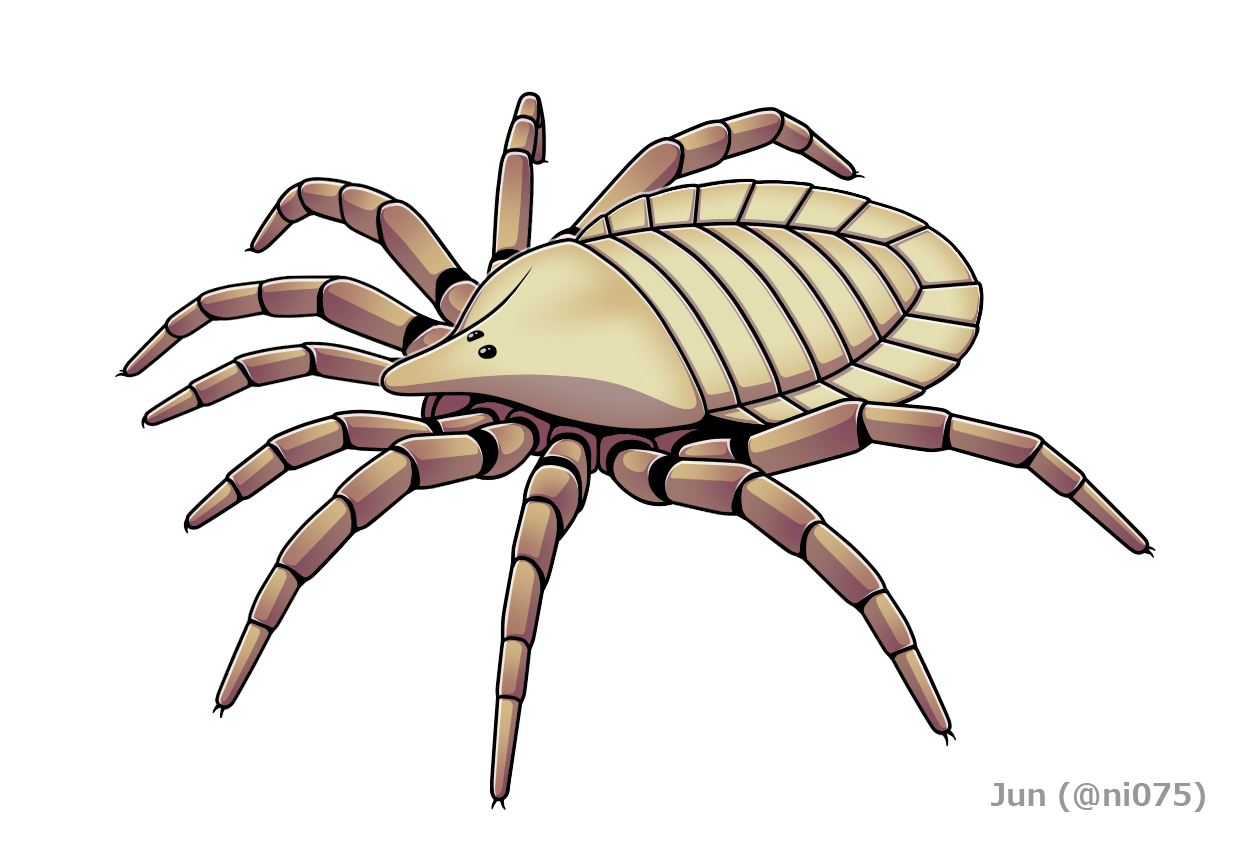
Eophrynus
''Eophrynus'' is an extinct genus of arachnids from the extinct order Trigonotarbida, which lived during the Late Carboniferous period in Europe. The genus was first described in 1871 by Henry Woodward (geologist). The name comes from ''Eo'', meaning 'dawn', and ''Phrynus'', an extant genus of whip spider (order Amblypygi). Two species have been recognised: * ''Eophrynus prestvicii'' in England * ''Eophrynus udus'' in Germany Species of ''Eophrynus'', as with other tribonotarbids, were similar to modern spiders but could not produce silk and the back-half of their body was made up of small plates. The English species, ''E. prestvici'', is known from a handful of good quality fossils preserved inside siderite concretions. Recent X-ray An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonotarbida
The order Trigonotarbida is a group of extinct arachnids whose fossil record extends from the late Silurian to the early Permian ( Pridoli to Sakmarian).Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2020A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 20.5 These animals are known from several localities in Europe and North America, as well as a single record from Argentina. Trigonotarbids can be envisaged as spider-like arachnids, but without silk-producing spinnerets. They ranged in size from a few millimetres to a few centimetres in body length and had segmented abdomens (opisthosoma), with the dorsal exoskeleton (tergites) across the backs of the animals' abdomens, which were characteristically divided into three or five separate plates. Probably living as predators on other arthropods, some later trigonotarbid species were quite heavily armoured and protected themselves with spines and tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonotarbids
The Order (biology), order Trigonotarbida is a group of extinct arachnids whose fossil record extends from the late Silurian to the early Permian (Pridoli epoch, Pridoli to Sakmarian).Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2020A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 20.5 These animals are known from several localities in Europe and North America, as well as a single record from Argentina. Trigonotarbids can be envisaged as spider-like arachnids, but without silk-producing spinnerets. They ranged in size from a few millimetres to a few centimetres in body length and had segmented abdomens (opisthosoma), with the dorsal exoskeleton (Tergum, tergites) across the backs of the animals' abdomens, which were characteristically divided into three or five separate plates. Probably living as predators on other arthropods, some later trigonotarbid species were quite heavily armoured and prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eophrynus Prestvicii
''Eophrynus prestvicii'' is an extinct species of arachnid belonging to the order Trigonotarbida. Historical background The first trigonotarbid was described in 1837 from the Coal Measures of Coalbrookdale in England by the famous English geologist Dean William Buckland. He believed it to be a fossil beetle and named it ''Curculoides prestvicii''. A much better preserved example was later discovered from Coseley near Dudley; also in the English West Midlands conurbation. Described in 1871 by Henry Woodward, he correctly identified it as an arachnid and renamed it ''Eophrynus prestvicii'' – whereby the genus name comes from (', meaning 'dawn'), and ''Phrynus'', a genus of living whip spider (Amblypygi). Description ''Eophrynus prestvicii'' can reach a length of about . These arachnids were similar to modern spiders, but they could not produce silk. Recent x-ray imaging revealed that ''Eophrynus prestvicii'' were covered by protective spikes on the back-half of its body. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eophrynidae
Eophrynidae is a family of the extinct arachnid order Trigonotarbida The order Trigonotarbida is a group of extinct arachnids whose fossil record extends from the late Silurian to the early Permian ( Pridoli to Sakmarian).Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2020A summary list of fossil spiders and their relative .... Eophrynids lived during the Carboniferous period in what is now modern Europe and North America. The family is probably found within the "eophrynid assemblage" clade: (''Aphantomartus'' (''Alkenia'' (''Pseudokreischeria'' (''Kreischeria'' (''Eophrynus'' + ''Pleophrynus''))))). Genera *'' Areomartus'' Petrunkevitch, 1913 *'' Eophrynus'' Woodward, 1871 *'' Nyranytarbus'' Harvey & Selden, 1995 *'' Petrovicia'' Frič, 1904 *'' Planomartus'' Petrunkevitch, 1953 *'' Pleophrynus'' Petrunkevitch, 1945 *'' Pocononia'' Petrunkevitch, 1953 *'' Somaspidion'' Jux, 1982 *'' Stenotrogulus'' Frič, 1904 *'' Vratislavia'' Frič, 1904 References Trigonotarbid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapworth Museum Of Geology
The Lapworth Museum of Geology is a geological museum run by the University of Birmingham and located on the university's campus in Edgbaston, south Birmingham, England. The museum is named after the geologist Charles Lapworth, its origins dating back to 1880. It reopened in 2016 following a £2.7 million redevelopment project that created new galleries and displays, as well as modern visitor and educational facilities. The Lapworth Museum is free to visit; its galleries are aimed at a broad range of audiences, from families and children to undergraduate students and specialist geology groups. The galleries use the Lapworth's collections to tell the story of the evolution of life and the planet over 4.5 billion years of Earth's history, with a particular focus on how the environment, climate, plants, and animals of the English Midlands have changed over time. The Lapworth's collection includes more than 250,000 specimens of fossils, rocks and minerals that are of inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Carboniferous
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian First Appearances
Mississippian may refer to: *Mississippian (geology), a subperiod of the Carboniferous period in the geologic timescale, roughly 360 to 325 million years ago *Mississippian culture, a culture of Native American mound-builders from 900 to 1500 AD *Mississippian Railway, a short line railroad *A native of Mississippi Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ... See also * Mississippi (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Arthropods Of Europe
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Arachnids
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian lineages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology Letters
''Biology Letters'' is a peer-reviewed, biological, scientific journal published by the Royal Society. It focuses on the rapid publication of short high quality research articles, reviews and opinion pieces across the biological sciences. ''Biology Letters'' has an average turnaround time of twenty four days from submission to a first decision. The editor-in-chief is Professor David Beerling FRS (University of Sheffield) who is supported by an international Editorial Board of practising scientists. Contents and themes As well as the conventional, short research articles, ''Biology Letters'' has recently published Special Features and Mini Series. While Special Features are a collection of up to 20 articles on a specific theme and published across multiple issues, Mini Series include up to six articles that are published in one issue. Examples of topics in these formats include ocean acidification, fossils, extinction, enhanced rock weathering and the evolutionary ecology of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |