|
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress In Beta Cells
Beta cells are heavily engaged in the synthesis and secretion of insulin. They are therefore particularly sensitive to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and the subsequent unfolded protein response (UPR). Severe or prolonged episodes of ER stress can lead to the death of beta cells,Eizirik DL, Cardozo AK, Cnop M (2008) The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr Rev 29:42-61 which can contribute to the development of both Type I and Type II diabetes. ER stress in beta cells links obesity to type 2 diabetes and inflammation to type 1 diabetes. ER stress in peripheral cells has also been linked to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Activation of ER stress ER stress can be activated by a variety of factors. In experimental conditions, excessive lipid (which can happen following obesity, a common condition preceding type 2 diabetes) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (which can occur following an inflammation, a common cause for type 1 dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
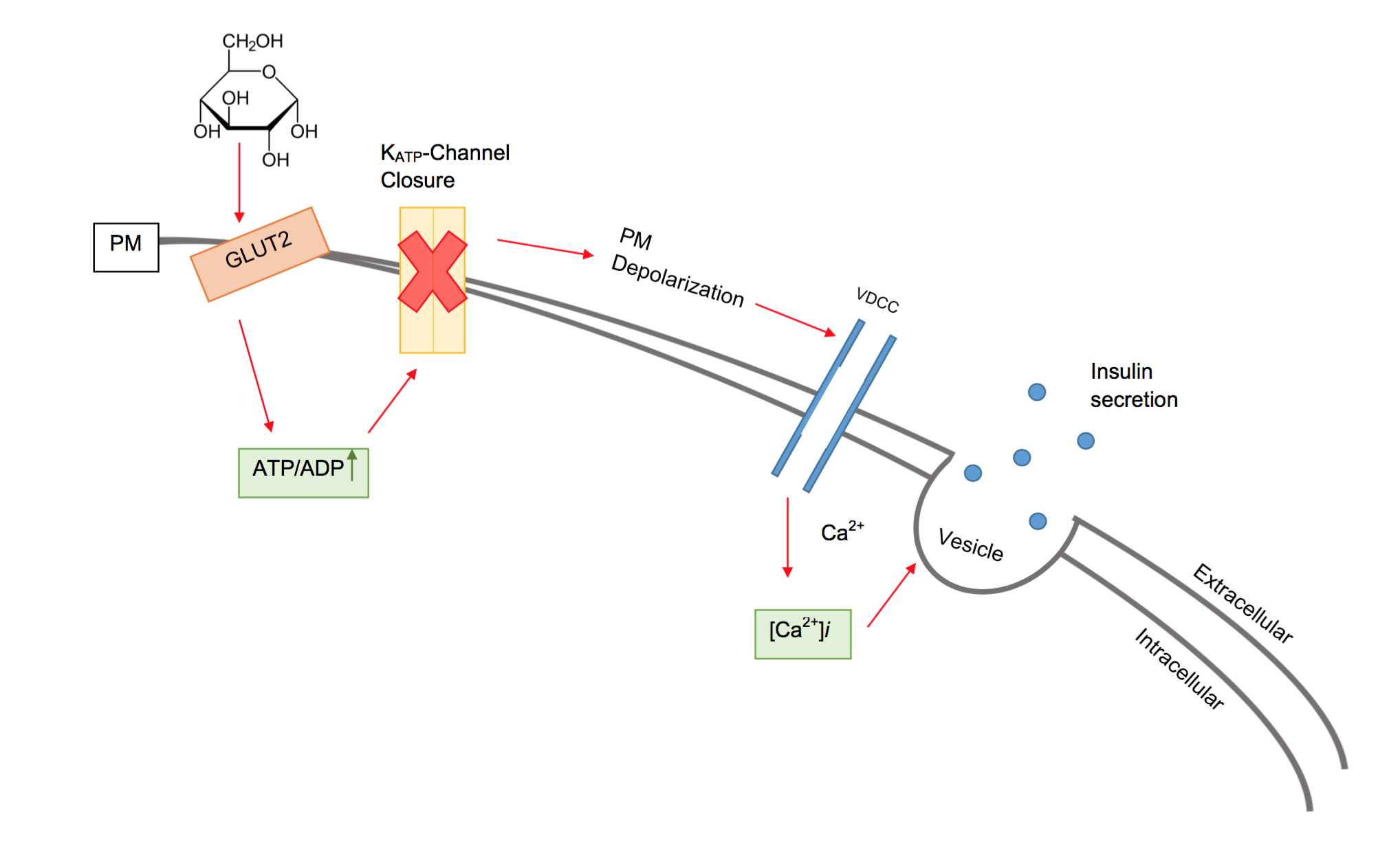
Beta Cells
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia. Function The primary function of a beta cell is to produce and release insulin and amylin. Both are hormones which reduce blood glucose levels by different mechanisms. Beta cells can respond quickly to spikes in blood glucose concentrations by secreting some of their stored insulin and amylin while simultaneously producing more. Primary cilia on beta cells regulate their function and energy metabolism. Cilia deletion can lead to islet dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, it simultaneously increases proinsulin biosynthesis, mainly through translational cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for energy and it helps regulate glucose levels in the bloodstream. Before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. The common symptoms of this elevated blood sugar are frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other serious complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing. Symptoms typically develop over a short period of time, often a matter of weeks. The cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves an autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Diabetes is diagnosed by testing the level of sugar or gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. This is achieved by monitoring the amplification reaction using fluorescence, a technique called real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Combined RT-PCR and qPCR are routinely used for analysis of gene expression and quantification of viral RNA in research and clinical settings. The close association between RT-PCR and qPCR has led to metonymic use of the term qPCR to mean RT-PCR. Such use may be confusing, as RT-PCR can be used without qPCR, for example to enable molecular cloning, sequencing or simple detection of RNA. Conversely, qPCR may be used without RT-PCR, for example to quantify the copy number of a specific piece of DNA. Nomenclature The combine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/EBP Homologous Protein
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3, also known as C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), is a pro-apoptotic transcription factor that is encoded by the ''DDIT3'' gene. It is a member of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family of DNA-binding transcription factors. The protein functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor by forming heterodimers with other C/EBP members, preventing their DNA binding activity. The protein is implicated in adipogenesis and erythropoiesis and has an important role in the cell's stress response. Structure C/EBP proteins are known to have a conserved C-terminal structure, basic leucine zipper domain(bZIP), that is necessary for the formation of DNA-binding capable homodimers or heterodimers with other proteins or members of the C/EBP protein family. CHOP is a relatively small (29kDa) protein that differs from most C/EBP proteins in several amino acid substitutions, which impacts its DNA-binding ability. Regulation and function Due to a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRE1
The serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease inositol-requiring enzyme 1 α (IRE1α) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ERN1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is the ER to nucleus signalling 1 protein, a human homologue of the yeast Ire1 gene product. This protein possesses intrinsic kinase activity and an endoribonuclease activity and it is important in altering gene expression as a response to endoplasmic reticulum-based stress signals (mainly the unfolded protein response). Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Signaling IRE1α possesses two functional enzymatic domains, an endonuclease and a trans-autophosphorylation kinase domain. Upon activation, IRE1α oligomerizes and carries out an unconventional RNA splicing activity, removing an intron from the X-box binding protein 1 ( XBP1) mRNA, and allowing it to become translated into a functional transcription factor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATF6
Activating transcription factor 6, also known as ATF6, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''ATF6'' gene and is involved in the unfolded protein response. Function ATF6 is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-regulated transmembrane transcription factor that activates the transcription of ER molecules. Accumulation of misfolded proteins in the Endoplasmic Reticulum results in the proteolytic cleavage of ATF6. The cytosolic portion of ATF6 will move to the nucleus and act as a transcription factor to cause the transcription of ER chaperones. See also * Activating transcription factor Interactions ATF6 has been shown to interact with YY1 and Serum response factor Serum response factor, also known as SRF, is a transcription factor protein. Function Serum response factor is a member of the MADS (MCM1, Agamous, Deficiens, and SRF) box superfamily of transcription factors. This protein binds to the serum .... References Further reading * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaperone (protein)
In molecular biology, molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding of large proteins or macromolecular protein complexes. There are a number of classes of molecular chaperones, all of which function to assist large proteins in proper protein folding during or after synthesis, and after partial denaturation. Chaperones are also involved in the translocation of proteins for proteolysis. The first molecular chaperones discovered were a type of assembly chaperones which assist in the assembly of nucleosomes from folded histones and DNA. One major function of molecular chaperones is to prevent the aggregation of misfolded proteins, thus many chaperone proteins are classified as heat shock proteins, as the tendency for protein aggregation is increased by heat stress. The majority of molecular chaperones do not convey any steric information for protein folding, and instead assist in protein folding by binding to and stabilizing folding interme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPR78
Probable G-protein coupled receptor 78 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPR78'' gene. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs, or GPRs) contain 7 transmembrane domains and transduce extracellular signals through heterotrimeric G protein G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their a ...s. upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> References Further reading * * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unfolded Protein Response
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is a cellular stress response related to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. It has been found to be conserved between all mammalian species, as well as yeast and worm organisms. The UPR is activated in response to an accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. In this scenario, the UPR has three aims: initially to restore normal function of the cell by halting protein translation, degrading misfolded proteins, and activating the signalling pathways that lead to increasing the production of molecular chaperones involved in protein folding. If these objectives are not achieved within a certain time span or the disruption is prolonged, the UPR aims towards apoptosis. Sustained overactivation of the UPR has been implicated in prion diseases as well as several other neurodegenerative diseases, and inhibiting the UPR could become a treatment for those diseases. Diseases amenable to UPR inhibition inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |