|
Endometritis
Endometritis is inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus ( endometrium). Symptoms may include fever, lower abdominal pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. It is the most common cause of infection after childbirth. It is also part of spectrum of diseases that make up pelvic inflammatory disease. Endometritis is divided into acute and chronic forms. The acute form is usually from an infection that passes through the cervix as a result of an abortion, during menstruation, following childbirth, or as a result of douching or placement of an IUD. Risk factors for endometritis following delivery include Caesarean section and prolonged rupture of membranes. Chronic endometritis is more common after menopause. The diagnosis may be confirmed by endometrial biopsy. Ultrasound may be useful to verify that there is no retained tissue within the uterus. Treatment is usually with antibiotics. Recommendations for treatment of endometritis following delivery includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Infections
Postpartum infections, also known as childbed fever and puerperal fever, are any bacterial infections of the female reproductive tract following childbirth or miscarriage. Signs and symptoms usually include a fever greater than , chills, lower abdominal pain, and possibly bad-smelling vaginal discharge. It usually occurs after the first 24 hours and within the first ten days following delivery. The most common infection is that of the uterus and surrounding tissues known as puerperal sepsis, postpartum metritis, or postpartum endometritis. Risk factors include Caesarean section (C-section), the presence of certain bacteria such as group B streptococcus in the vagina, premature rupture of membranes, multiple vaginal exams, manual removal of the placenta, and prolonged labour among others. Most infections involve a number of types of bacteria. Diagnosis is rarely helped by culturing of the vagina or blood. In those who do not improve, medical imaging may be required. Other causes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
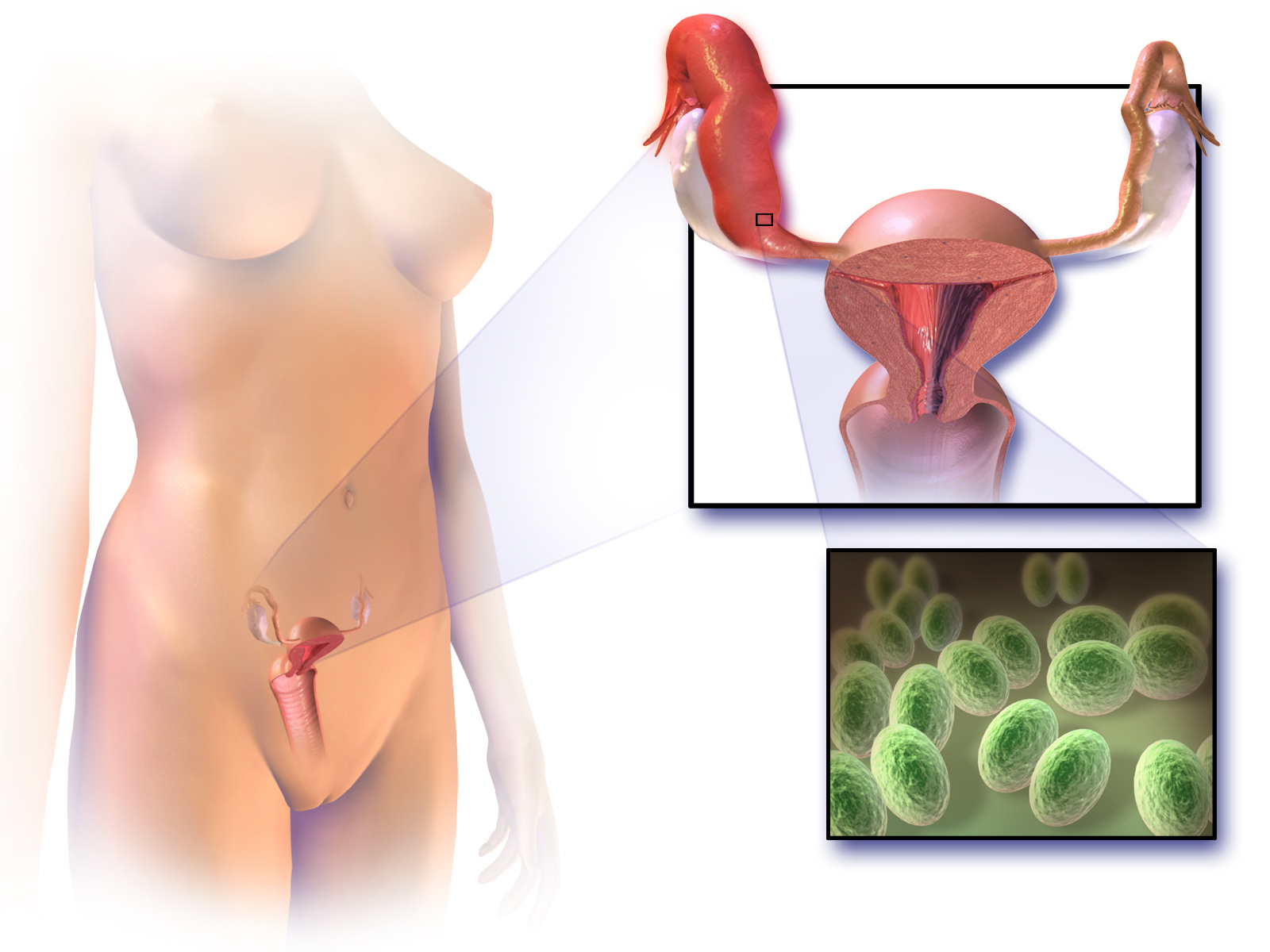
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with urination, pain with sex, bleeding after sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer. The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' or ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases. Often, multiple different bacteria are involved. Without treatment, about 10 percent of those with a chlamydial infection and 40 percent of those with a gonorrhea infection will develop PID. Risk factors are generally similar to those of sexua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesarean Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. Reasons for the operation include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. Most C-sections are performed without a medical reason, upon request by someone, usually the mother. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake, or under general anesthesia. A urinary catheter is used to drain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douching
A douche is a device used to introduce a stream of water into the body for medical or hygienic reasons, or the stream of water itself. Douche usually refers to vaginal irrigation, the rinsing of the vagina, but it can also refer to the rinsing of any body cavity. A douche bag is a piece of equipment for douching—a bag for holding the fluid used in douching. To avoid transferring intestinal bacteria into the vagina, the same bag must not be used for an enema and a vaginal douche. Douching after sexual intercourse is not an effective form of birth control. Additionally, douching is associated with a number of health problems, including cervical cancer, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometritis, and increased risk of sexually transmitted infections. Thus, its use is not recommended. Etymology The word's first known use is in 1766. ''Douche'' came into English via French, from it, doccia "conduit pipe" and ''docciare'' "pour by drops" to douche, from ''doccia'' water pip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolonged Rupture Of Membranes
Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labor. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis. Risk factors include infection of the amniotic fluid, prior PROM, bleeding in the later parts of pregnancy, smoking, and a mother who is underweight. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms and speculum exam and may be supported by testing the vaginal fluid or by ultrasound. If it occurs before 37 weeks it is known as PPROM (preterm prelabor rupture of membranes) otherwise it is known as term PROM. Treatment is based on how far along a woman is in pregnancy and whether complications are present. In those at or near term without any complications, induction of labor is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductive system, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can be normal, especially in early pregnancy. However, bleeding may also indicate a pregnancy complication that needs to be medically addressed. During pregnancy bleeding is usually, but not always, related to the pregnancy itself. Regular monthly vaginal bleeding during the reproductive years, menstruation, is a normal physiologic process. During the reproductive years, bleeding that is excessively heavy (menorrhagia or heavy menstrual bleeding), occurs between monthly menstrual periods (intermenstrual bleeding), occurs more frequently than every 21 days (abnormal uterine bleeding), occurs too infrequently (oligomenorrhea), or occurs after vaginal intercours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregnancies. When deliberate steps are taken to end a pregnancy, it is called an induced abortion, or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word ''abortion'' generally refers to an induced abortion. The reasons why women have abortions are diverse and vary across the world. Reasons include maternal health, an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, wishing to complete education or advance a career, and not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest. When properly done, induced abortion is one of the safest procedures in medicine. In the United States, the risk of maternal mortality is 14 times lower after induced abortion than after chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregnancies. When deliberate steps are taken to end a pregnancy, it is called an induced abortion, or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word ''abortion'' generally refers to an induced abortion. The reasons why women have abortions are diverse and vary across the world. Reasons include maternal health, an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, wishing to complete education or advance a career, and not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest. When properly done, induced abortion is one of the safest procedures in medicine. In the United States, the risk of maternal mortality is 14 times lower after induced abortion than after chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrial Biopsy
The endometrial biopsy is a medical procedure that involves taking a tissue sample of the lining of the uterus. The tissue subsequently undergoes a histologic evaluation which aids the physician in forming a diagnosis. Medical uses There are a number of indications for obtaining an endometrial biopsy from a non-pregnant woman: * Women with chronic anovulation such as the polycystic ovary syndrome are at increased risk for endometrial problems and an endometrial biopsy may be useful to assess their lining specifically to rule out endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. * In women with abnormal vaginal bleeding the biopsy may indicate the presence of abnormal lining such as endometrial hyperplasia or cancer. * In patients with suspected uterine cancer, the biopsy may discover the presence of cancer cells in the endometrium or cervix. * In female infertility the assessment of the lining can determine, if properly timed, that the patient ovulated, however, the same information can be obt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often define menopause as having occurred when a woman has not had any menstrual bleeding for a year. It may also be defined by a decrease in hormone production by the ovaries. In those who have had surgery to remove their uterus but still have functioning ovaries, menopause is not considered to have yet occurred. Following the removal of the uterus, symptoms typically occur earlier. In the years before menopause, a woman's periods typically become irregular, which means that periods may be longer or shorter in duration or be lighter or heavier in the amount of flow. During this time, women often experience hot flashes; these typically last from 30 seconds to ten minutes and may be associated with shivering, sweating, and reddening of the skin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle tone, muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes Flushing (physiology), flushed, and may begin to Perspiration, sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral infection, viral, bacterial infection, bacterial, and parasitic infect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 Hertz, kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating Predation, prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pyth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |