|
Elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus''). They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears and convex or level backs. Elephants are scatter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Elephant
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living ''Elephas'' species. It is the largest living land animal in Asia and the second largest living Elephantidae, elephantid in the world. It is characterised by its long Elephant trunk, trunk with a single finger-like processing; large tusks in males; laterally folded large ears and wrinkled grey skin that is partly depigmented on the trunk, ears or neck. Adult males average in weight and females . It has a large and well developed neocortex of the brain, is highly intelligent and self-aware being able to display behaviours associated with grief, learning and greeting. Three subspecies are recognised—''Sri Lankan elephant, E. m. maximus'', Indian elephant, ''E. m. indicus'' and ''Sumatran elephant, E. m. sumatranus''. The Asian elephant is distributed in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west to Borneo in the east, and Nepal in the north to Sumatra in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
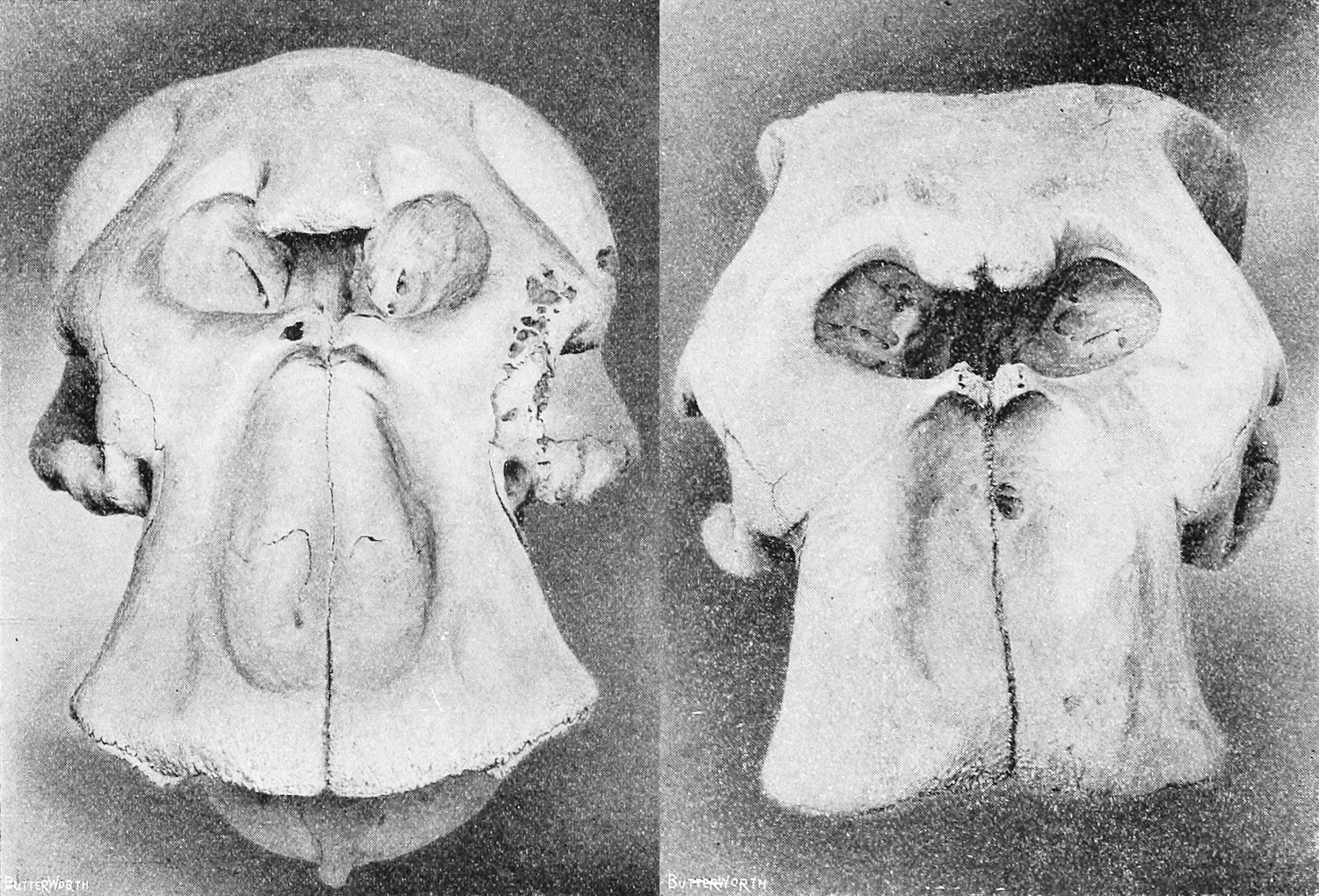
African Bush Elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), also known as the African savanna elephant, is a species of elephant native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of three extant elephant species and, along with the African forest elephant, one of two extant species of African elephant. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with fully grown bulls reaching an average shoulder height of and a body mass of ; the largest recorded specimen had a shoulder height of and an estimated body mass of . The African bush elephant is characterised by its long prehensile trunk with two finger-like processes; a convex back; large ears which help reduce body heat; and sturdy tusks that are noticeably curved. The skin is grey with scanty hairs, and bending cracks which support thermoregulation by retaining water. The African bush elephant inhabits a variety of habitats such as forests, grasslands, woodlands, wetlands and agricultural land. It is a mixed herbivore feeding mostly on grasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Elephant
African elephants are members of the genus ''Loxodonta'' comprising two living elephant species, the African bush elephant (''L. africana'') and the smaller African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''). Both are social herbivores with grey skin. However, they differ in the size and colour of their tusks as well as the shape and size of their ears and skulls. Both species are at a pertinent risk of extinction according to the IUCN Red List; as of 2021, the bush elephant is considered endangered while the forest elephant is considered critically endangered. They are threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation, along with poaching for the illegal ivory trade in several range countries. ''Loxodonta'' is one of two extant genera in the family Elephantidae. The name refers to the lozenge-shaped enamel of their molar teeth. Fossil remains of ''Loxodonta'' species have been found in Africa, spanning from the Late Miocene (from around 7–6 million years ago) onwards. Etymology T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Forest Elephant
The African forest elephant (''Loxodonta cyclotis'') is one of the two living species of African elephant, along with the African bush elephant. It is native to humid tropical forests in West Africa and the Congo Basin. It is the smallest of the three living elephant species, reaching a shoulder height of . As with other African elephants, both sexes have straight, down-pointing tusks, which begin to grow once the animals reach 1–3 years old. The forest elephant lives in highly sociable family groups of up to 20 individuals. Since they forage primarily on leaves, seeds, fruit, and tree bark, they have often been referred to as the 'megagardener of the forest'; the species is one of many that contributes significantly to maintaining the composition, diversity and structure of the Guinean Forests of West Africa and the Congolese rainforests. Seeds of various plants will go through the elephant's digestive tract and eventually pass through in the animal's droppings (likely in a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musth
Musth or must (from Persian, ) is a periodic condition in bull (male) elephants characterized by aggressive behavior in animals, aggressive behavior and accompanied by a large rise in reproductive hormones. It has been known in Asian elephants for 3 000 years but was only described in African elephants in 1981. Evidence indicates that similar behaviour occurred in extinct proboscideans like gomphotheres and mastodons. Elephants often discharge a thick, tar-like secretion called temporin from the temporal gland during musth. Behavioral management for captive bull elephants in musth includes physical restraint and a starvation diet for several days to a week. Etymology Musth comes from an Urdu term for intoxication; in Persian it means .''The Oxford Dictionary and Thesaurus: American edition'', published 1996 by Oxford University Press; p. 984 Biology Musth has been known in Asian elephants for 3000 years (described in the Rigveda 1500–1000 B.C.) but was recognized in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastodon
A mastodon, from Ancient Greek μαστός (''mastós''), meaning "breast", and ὀδούς (''odoús'') "tooth", is a member of the genus ''Mammut'' (German for 'mammoth'), which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to the early Holocene. Mastodons belong to the order Proboscidea, the same order as elephants and mammoths (which belong to the family Elephantidae). ''Mammut'' is the type genus of the extinct family Mammutidae, which diverged from the ancestors of modern elephants at least 27–25 million years ago, during the Oligocene. Like other members of Mammutidae, the molar (tooth), molar teeth of mastodons have zygodont morphology (where parallel pairs of cusp (anatomy), cusps are merged into sharp ridges), which strongly differ from those of elephantids. In comparison to its likely ancestor ''Zygolophodon'', ''Mammut'' is characterized by particularly long and upward curving upper tusks, reduced or absent tusks on the lower jaw, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Early Pleistocene, and expanded into Eurasia at the beginning of the Middle Pleistocene. The genus contains the largest known species of elephants, with mature bulls over tall at the shoulders and over in weight, representing among the largest land mammals ever, including the African '' Palaeoloxodon recki'', the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'') and the South Asian '' Palaeoloxodon namadicus. P. namadicus'' has been suggested to be the largest known land mammal by some authors based on extrapolation from fragmentary remains, though these estimates are highly speculative. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some like '' Palaeoloxodon falconeri'' less than in shoulder height as fully grown adults, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscidea
Proboscidea (; , ) is a taxonomic order of afrotherian mammals containing one living family (Elephantidae) and several extinct families. First described by J. Illiger in 1811, it encompasses the elephants and their close relatives. Three living species of elephant are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. Extinct members of Proboscidea include the deinotheres, mastodons, gomphotheres and stegodonts. The family Elephantidae also contains several extinct groups, including mammoths and '' Palaeoloxodon''. Proboscideans include some of the largest known land mammals, with the elephant '' Palaeoloxodon namadicus'' and mastodon ''"Mammut" borsoni'' suggested to have body masses surpassing , rivalling or exceeding paraceratheres (the otherwise largest known land mammals) in size. The largest extant proboscidean is the African bush elephant, with a world record of size of at the shoulder and . In addition to thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephas
''Elephas'' is a genus of elephants and one of two surviving genera in the Family (biology), family Elephantidae, comprising one extant species, the Asian elephant (''E. maximus''). Several extinct species have been identified as belonging to the genus, extending back to the Pliocene or possibly the late Miocene. Description Species of ''Elephas'' have distinct bossing of the parieto-occipital region of the skull. The premaxillae bones containing the tusks are tapered. Evolutionary history Relationships of living and extinct elephantids based on DNA, after Palkopoulou et al. 2018.Asian elephants share a closer common ancestry with mammoths (genus ''Mammuthus'') than they do with African elephants (''Loxodonta''). The oldest species attributed to the genus ''Elephas'' is ''E. nawataensis'' from the Late Miocene-Early Pliocene of Kenya, though the validity of this species and its relationship to ''Elephas'' has been doubted. The oldest species widely attributed to the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephantidae
Elephantidae is a family (biology), family of large, herbivorous proboscidean mammals which includes the living Elephant, elephants (belonging to the genera ''Elephas'' and ''Loxodonta''), as well as a number of extinct genera like ''Mammuthus'' (mammoths) and ''Palaeoloxodon''. They are large terrestrial animal, terrestrial mammals with a snout modified into a Elephant#Trunk, trunk and teeth modified into tusks. Most Genus, genera and species in the family are extinction, extinct. The family was first described by John Edward Gray in 1821, and later assigned to taxonomic ranks within the order Proboscidea. Elephantidae has been revised by various authors to include or exclude other extinct proboscidean genera. Description Elephantids are distinguished from more basal proboscideans like gomphotheres by their teeth, which have parallel lophs, formed from the merger of the cusps found in the teeth of more basal proboscideans, which are bound by cementum. In later elephantids, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabiting Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Mammoths are distinguished from living elephants by their (typically large) spirally twisted tusks and in some later species, the development of numerous adaptions to living in cold environments, including a thick layer of fur. Mammoths and Asian elephants are more closely related to each other than they are to African elephants. The oldest mammoth representative, '' Mammuthus subplanifrons'', appeared around 6 million years ago during the late Miocene in what is now southern and Eastern Africa.'''' Later in the Pliocene, by about three million years ago, mammoths dispersed into Eurasia, eventually covering most of Eurasia before migrating into North America around 1.5–1.3 million year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |