|
Palaeoloxodon
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species of elephants, over four metres tall at the shoulders, including the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), and the southern Asian ''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'', the latter of which was possibly the Largest land mammal, largest known land mammal based on fragmentary remains, but this requires proper reexamination. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of Dwarf elephant, dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some only a metre in height, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long and complex taxonomic history, and at various times, it has been considered to belong to ''Loxodonta'' or ''Elephas'', but today is usually considered a valid and separate genus in its own right. Tax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Huaihoensis
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species of elephants, over four metres tall at the shoulders, including the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), and the southern Asian ''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'', the latter of which was possibly the largest known land mammal based on fragmentary remains, but this requires proper reexamination. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some only a metre in height, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long and complex taxonomic history, and at various times, it has been considered to belong to '' Loxodonta'' or ''Elephas'', but today is usually considered a valid and separate genus in its own right. Taxonomy In 1924, circumscribed ''Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Creutzburgi
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species of elephants, over four metres tall at the shoulders, including the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), and the southern Asian ''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'', the latter of which was possibly the largest known land mammal based on fragmentary remains, but this requires proper reexamination. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some only a metre in height, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long and complex taxonomic history, and at various times, it has been considered to belong to '' Loxodonta'' or ''Elephas'', but today is usually considered a valid and separate genus in its own right. Taxonomy In 1924, circumscribed ''Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Elephant
Dwarf elephants are prehistoric members of the order Proboscidea which, through the process of allopatric speciation on islands, evolved much smaller body sizes (around ) in comparison with their immediate ancestors. Dwarf elephants are an example of insular dwarfism, the phenomenon whereby large terrestrial vertebrates (usually mammals) that colonize islands evolve dwarf forms, a phenomenon attributed to adaptation to resource-poor environments and selection for early maturation and reproduction. Some modern populations of Asian elephants have also undergone size reduction on islands to a lesser degree, resulting in populations of pygmy elephants. Fossil remains of dwarf elephants have been found on the Mediterranean islands of Cyprus, Malta (at Għar Dalam), Crete (in Chania at Vamos, Stylos and in a now-underwater cave on the coast), Sicily, Sardinia, the Cyclades Islands and the Dodecanese Islands. Other islands where dwarf ''Stegodon'' have been found are Sulawesi, Flores, Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Elephant
Dwarf elephants are prehistoric members of the order Proboscidea which, through the process of allopatric speciation on islands, evolved much smaller body sizes (around ) in comparison with their immediate ancestors. Dwarf elephants are an example of insular dwarfism, the phenomenon whereby large terrestrial vertebrates (usually mammals) that colonize islands evolve dwarf forms, a phenomenon attributed to adaptation to resource-poor environments and selection for early maturation and reproduction. Some modern populations of Asian elephants have also undergone size reduction on islands to a lesser degree, resulting in populations of pygmy elephants. Fossil remains of dwarf elephants have been found on the Mediterranean islands of Cyprus, Malta (at Għar Dalam), Crete (in Chania at Vamos, Stylos and in a now-underwater cave on the coast), Sicily, Sardinia, the Cyclades Islands and the Dodecanese Islands. Other islands where dwarf ''Stegodon'' have been found are Sulawesi, Flores, Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
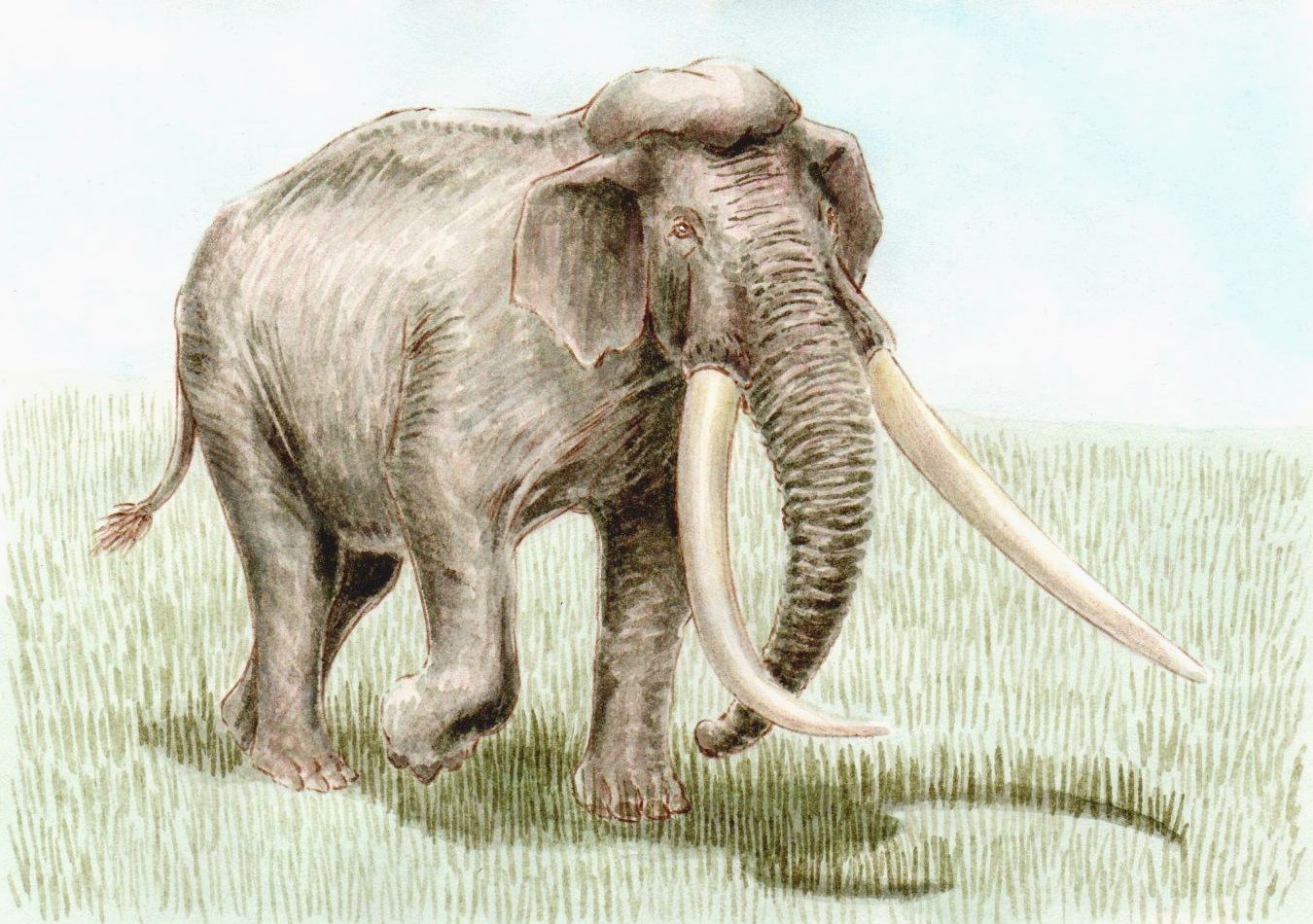
Palaeoloxodon Antiquus
The straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'') is an extinct species of elephant that inhabited Europe and Western Asia during the Middle and Late Pleistocene (781,000–30,000 years before present). Recovered individuals have reached up to in height, and an estimated in weight. The straight-tusked elephant probably lived in small herds, flourishing in interglacial periods, when its range would extend as far north as Great Britain. Isolated tusks are often found while partial or whole skeletons are rare, and there is evidence of predation by early humans. It is the ancestral species of most dwarf elephants that inhabited islands in the Mediterranean. Description ''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'' was quite large, with individuals reaching in height. Like other members of ''Palaeoloxodon'', ''P. antiquus'' possesses a well developed parieto-occipital crest at the top of the cranium that anchored the splenius as well as possibly the rhomboid muscles to support the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-tusked Elephant
The straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'') is an extinct species of elephant that inhabited Europe and Western Asia during the Middle and Late Pleistocene (781,000–30,000 years before present). Recovered individuals have reached up to in height, and an estimated in weight. The straight-tusked elephant probably lived in small herds, flourishing in interglacial periods, when its range would extend as far north as Great Britain. Isolated tusks are often found while partial or whole skeletons are rare, and there is evidence of predation by early humans. It is the ancestral species of most dwarf elephants that inhabited islands in the Mediterranean. Description ''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'' was quite large, with individuals reaching in height. Like other members of '' Palaeoloxodon'', ''P. antiquus'' possesses a well developed parieto-occipital crest at the top of the cranium that anchored the splenius as well as possibly the rhomboid muscles to support the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Naumanni
''Palaeoloxodon naumanni'', occasionally called Naumann's elephant, is an extinct species belonging to the genus ''Palaeoloxodon'' found in the Japanese archipelago during the Middle to Late Pleistocene around 430,000 to 24,000 years ago. It is named after Heinrich Edmund Naumann who discovered the first fossils at Yokosuka, Kanagawa, Japan. Fossils attributed to ''P. naumanni'' are also known from China and Korea, though the status of these specimens are unresolved, with some authors regarding these as belonging to separate species. Description ''Palaeoloxodon naumanni,'' like other members of the genus ''Palaeoloxodon'' had a pair of long straight tusks and a parietal-occipital crest on the top of the head. These tusks grew more than 2.4 m in length, 20 cm in diameter. It was a little smaller than Asian elephants averaging to . It lived in forest which mixed subarctic conifers and cool-temperate deciduous trees. The ancestor of ''Palaeoloxodon naumanni'' moved from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Namadicus
''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'' or the Asian straight-tusked elephant, is an extinct species of prehistoric elephant known from the early Middle to Late Pleistocene of the Indian subcontinent, and possibly also elsewhere in Asia. Some authorities regard it to be a subspecies of ''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'', the European straight-tusked elephant, due to extreme similarities of the tusks. Their skull structure was also different from that of a modern elephant. The grouping of this genus is supported by cranial synapomorphies with other species of ''Palaeoloxodon,'' which includes a large crest at the top of the skull that anchored the splenius muscles used to support the head. Later research suggested that ''P. namadicus'' can be distinguished from ''P. antiquus'' by its less robust limb bones and more stout cranium. Based on the stable isotope ratioes of carbon and oxygen and the morphology of their teeth, it is suggested that ''P. namadicus'' tended towards a grazing diet, as opposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Cypriotes
''Palaeoloxodon cypriotes'', the Cyprus dwarf elephant, is an extinct species that inhabited the island of Cyprus during the Late Pleistocene. Remains comprise 44 molars, found in the north of the island, seven molars discovered in the south-east, a single measurable femur and a single tusk among very sparse additional bone and tusk fragments. The molars support derivation from the large straight-tusked elephant ''(Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), that inhabited Europe since 780,000 years ago. The species is presumably derived from the older, larger ''P. xylophagou'' from the late Middle Pleistocene which reached the island presumably during a Pleistocene glacial maximum when low sea levels allowed a low probability sea crossing between Cyprus and Asia Minor. During subsequent periods of isolation the population adapted within the evolutionary mechanisms of insular dwarfism, which the available sequence of molar fossils confirms to a certain extent. The fully developed ''Palaeoloxodon c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon Xylophagou
''Palaeoloxodon cypriotes'', the Cyprus dwarf elephant, is an extinct species that inhabited the island of Cyprus during the Late Pleistocene. Remains comprise 44 molars, found in the north of the island, seven molars discovered in the south-east, a single measurable femur and a single tusk among very sparse additional bone and tusk fragments. The molars support derivation from the large straight-tusked elephant ''(Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), that inhabited Europe since 780,000 years ago. The species is presumably derived from the older, larger ''P. xylophagou'' from the late Middle Pleistocene which reached the island presumably during a Pleistocene glacial maximum when low sea levels allowed a low probability sea crossing between Cyprus and Asia Minor. During subsequent periods of isolation the population adapted within the evolutionary mechanisms of insular dwarfism, which the available sequence of molar fossils confirms to a certain extent. The fully developed ''Palaeoloxodon cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is distinct from the intentional creation of dwarf breeds, called dwarfing. This process has occurred many times throughout evolutionary history, with examples including dinosaurs, like '' Europasaurus'' and ''Magyarosaurus dacus'', and modern animals such as elephants and their relatives. This process, and other "island genetics" artifacts, can occur not only on islands, but also in other situations where an ecosystem is isolated from external resources and breeding. This can include caves, desert oases, isolated valleys and isolated mountains ("sky islands"). Insular dwarfism is one aspect of the more general "island effect" or "Foster's rule", which posits that when mainland animals colonize islands, small species tend to evolve larger bodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea. The order was formerly much more diverse during the Pleistocene, but most species became extinct during the Late Pleistocene epoch. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Elephants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_colourised.png)