|
Elbingian
Elbingian (german: Mundart der Elbinger Höhe, lit=dialect of the Elbingian upland) was a subdialect of Low Prussian spoken in East Prussia and West Prussia in the region of the , north of Elbląg. It had a border with Oberländisch, Mundart des Kürzungsgebiets, and Nehrungisch. It is related to Plautdietsch, which has far more speakers. The 1882 edition of dictionary of dialects Preußisches Wörterbuch includes ''Mundart der Elbinger Höhe'' using this wording. Phonology There was a border of ''/i'', ''e'' and ''ar/'' becoming ''/e'', ''a'' and ''or/'' respectively in its area. It has many features in common with Natangian Natangian was Low Prussian dialect of Low German. It is from East Prussia. The name is from the Natangians, a tribe of the Old Prussians. Geography It was spoken around Kornevo, Bartoszyce, Pravdinsk, Srokowo and Kętrzyn. Natangian has or ....Walther Ziesemer:'' Die ostpreußischen Mundarten''. Ferdinand Hirt, 1924, p. 132 References B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
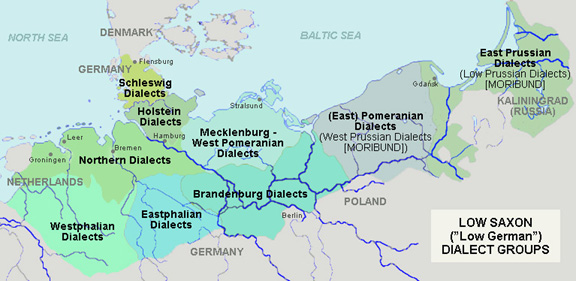
Low Prussian Dialect
Low Prussian (german: Niederpreußisch), sometimes known simply as Prussian (''Preußisch''), is a moribund dialect of East Low German that developed in East Prussia. Low Prussian was spoken in East and West Prussia and Danzig up to 1945. In Danzig it formed the particular city dialect of Danzig German. It developed on a Baltic substrate through the influx of Dutch- and Low German-speaking immigrants. It supplanted Old Prussian, which became extinct in the 18th century. Simon Dach's poem ''Anke van Tharaw'' was written in Low Prussian. Classification Low Prussian is a Low German dialect formally spoken in Prussia. It is separated from its only adjacent German dialect, High Prussian, by the Benrath line and the Uerdingen line, the latter dialect being Central German. This was once one of the, if not the hardest linguistic border within the German dialects. Plautdietsch, a Low German variety, is included within Low Prussian by some observers. Excluding Plautdietsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Prussian
Low Prussian (german: Niederpreußisch), sometimes known simply as Prussian (''Preußisch''), is a moribund dialect of East Low German that developed in East Prussia. Low Prussian was spoken in East and West Prussia and Danzig up to 1945. In Danzig it formed the particular city dialect of Danzig German. It developed on a Baltic substrate through the influx of Dutch- and Low German-speaking immigrants. It supplanted Old Prussian, which became extinct in the 18th century. Simon Dach's poem ''Anke van Tharaw'' was written in Low Prussian. Classification Low Prussian is a Low German dialect formally spoken in Prussia. It is separated from its only adjacent German dialect, High Prussian, by the Benrath line and the Uerdingen line, the latter dialect being Central German. This was once one of the, if not the hardest linguistic border within the German dialects. Plautdietsch, a Low German variety, is included within Low Prussian by some observers. Excluding Plautdietsch, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth annexed in the First Partition of Poland. West Prussia was dissolved in 1829 and merged with East Prussia to form the Province of Prussia, but was re-established in 1878 when the merger was reversed and became part of the German Empire. From 1918, West Prussia was a province of the Free State of Prussia within Weimar Germany, losing most of its territory to the Second Polish Republic and the Free City of Danzig in the Treaty of Versailles. West Prussia was dissolved in 1920, and its remaining western territory was merged with Posen to form Posen-West Prussia, and its eastern territory merged with East Prussia as the Region of West Prussia district. West Prussia's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbląg
Elbląg (; german: Elbing, Old Prussian: ''Elbings'') is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 117,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg County. Elbląg is one of the oldest cities in the province. Its history dates back to 1237, when the Teutonic Order constructed their fortified stronghold on the banks of a nearby river. The castle subsequently served as the official seat of the Teutonic Order Masters. Elbląg became part of the Hanseatic League, which contributed much to the city's wealth. Through the Hansa agreement, the city was linked to other major ports like Gdańsk, Lübeck and Amsterdam. Elbląg joined Poland in 1454 and after the defeat of the Teutonic Knights in the Thirteen Years’ War was recognized as part of Poland in the Second Peace of Thorn in 1466. It then flourished and turned into a significant trading point, but its growth was eventually hindered by the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natangian
Natangian was Low Prussian dialect of Low German. It is from East Prussia. The name is from the Natangians, a tribe of the Old Prussians. Geography It was spoken around Kornevo, Bartoszyce, Pravdinsk, Srokowo and Kętrzyn. Natangian has or used to have a border with Standard German, Mundart des Kürzungsgebiets, Westkäslausch, Ostsamländisch, Mundart des Ostgebietes, Ostkäslausch and Breslausch. There was a border of Prince-Bishopric of Warmia to the state of the Teutonic Order, which also was the border of Natangian to Ostkäslausch. Phonology In difference to Samländisch, vowel breaking of every long e to ei and every o to ou and the word ''dirch'' are characteristic. It has significant features shared with Mundart der Elbinger Höhe Elbingian (german: Mundart der Elbinger Höhe, lit=dialect of the Elbingian upland) was a subdialect of Low Prussian spoken in East Prussia and West Prussia in the region of the , north of Elbląg. It had a border with Oberländ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nehrungisch
Nehrungisch is a dialect (''Mundart'') of Low Prussian, belonging to the Low German language variety. It was spoken in East Prussia and West Prussia, in the region around the Vistula Spit (''Frische Nehrung'') near Gdansk. The easternmost locality where this variety was spoken was Narmeln, and it was spoken from Narmeln to Krakau ( Krakowiec). The dialect survives in Chortitza- Plautdietsch, a dialect of Low Prussian brought to Ukraine by migrants from the Vistula region. Nehrungisch shares features with Eastern Low Prussian. History Those of the Mennonites from the Vistula lowlands, that originated from the lower part of the Rhine belonged together with those from Gdańsk (Danzig), Elbląg (Elbing), and the Żuławy Gdańskie (Danziger Werder) and entered the larger area in the second half of the 1540s. The Chortitza Colony Plautdietsch language had no major linguistic difference from the original Nehrungisch, which had changed by 1880. By then, the most conspicuous feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundart Des Kürzungsgebiets
The Mundart des Kürzungsgebiets is a subdialect of Low Prussian, part of Low German, spoken in today's Poland. In 1918, it was spoken in East Prussia and West Prussia in their respective then borders. Mundart des Kürzungsgebiets was spoken around Braniewo and Frombork and had a border to Natangian, Westkäslausch, Mundart der Elbinger Höhe and Oberländisch. There was influence of Salzburgers. The Western border to Elbląg Upland was a border of denominations. Part of its Southern border was undetermined by political or religious borders. Long e before p, t and k is shortened to short i, long o before t and k is shortened to u. Between Plasswich and Borchertsdorf, its only border to High Prussian High Prussian (german: Hochpreußisch) is a group of East Central German dialects in former East Prussia, in present-day Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (Poland) and Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia). High Prussian developed in the 13th–15th centuries, ... ran. Shortening of û t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberländisch
High Prussian (german: Hochpreußisch) is a group of East Central German dialects in former East Prussia, in present-day Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (Poland) and Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia). High Prussian developed in the 13th–15th centuries, brought in by German settlers mainly from Silesia and Thuringia, and was influenced by the Baltic Old Prussian language. Classification High Prussian is a Central German dialect formally spoken in Prussia. It is separated from its only adjacent German dialect, Low Prussian, by the Benrath line and the Uerdingen line, the latter dialect being Low German. This was once one of the, if not the hardest linguistic border within the German dialects. It shares some features with Low Prussian, differentiating it from other Central German dialects east of the . Those Borussisms are: * Loss of ''/-n/'' in infinitives (''mache'' for Standard German , "to make"); * retention of the prefix ''//ge-//'' in the participe perfect passive (compare Meckel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdialect
Subdialect (from Latin , "under", and Ancient Greek , "discourse") is a linguistic term designating a dialectological category between the levels of dialect and idiolect. Subdialects are basic subdivisions of a dialect. Subdialects can be divided further, ultimately down to idiolects. Normally subdialects of one dialect are quite close to each other, differing mainly in pronunciation and certain local words. See also * Accent (dialect) * Variety (linguistics) * Language cluster * Dubrovnik subdialect * Laško subdialect * Lwów subdialect * Supradialect Supradialect (from Latin , "above", and Ancient Greek , "discourse") is a linguistic term designating a dialectological category between the levels of language and dialect. It is used in two distinctive contexts, describing structural or funct ... Reference Literature * Joseph R. Applegate, "Phonological Rules of a Subdialect of English", Word, vol. 17/2 (1961), p. 186-193. * Asta Leskauskaite, "The Perip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's Free State of Prussia, until 1945. Its capital city was Königsberg (present-day Kaliningrad). East Prussia was the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast. The bulk of the ancestral lands of the Baltic Old Prussians were enclosed within East Prussia. During the 13th century, the native Prussians were conquered by the crusading Teutonic Knights. After the conquest the indigenous Balts were gradually converted to Christianity. Because of Germanization and colonisation over the following centuries, Germans became the dominant ethnic group, while Masurians and Lithuanians formed minorities. From the 13th century, East Prussia was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |