|
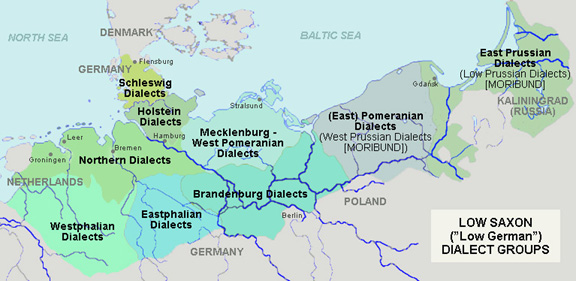
Low Prussian
Low Prussian (german: Niederpreußisch), sometimes known simply as Prussian (''Preußisch''), is a moribund dialect of East Low German that developed in East Prussia. Low Prussian was spoken in East and West Prussia and Danzig up to 1945. In Danzig it formed the particular city dialect of Danzig German. It developed on a Baltic substrate through the influx of Dutch- and Low German-speaking immigrants. It supplanted Old Prussian, which became extinct in the 18th century. Simon Dach's poem ''Anke van Tharaw'' was written in Low Prussian. Classification Low Prussian is a Low German dialect formally spoken in Prussia. It is separated from its only adjacent German dialect, High Prussian, by the Benrath line and the Uerdingen line, the latter dialect being Central German. This was once one of the, if not the hardest linguistic border within the German dialects. Plautdietsch, a Low German variety, is included within Low Prussian by some observers. Excluding Plautdietsch, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth annexed in the First Partition of Poland. West Prussia was dissolved in 1829 and merged with East Prussia to form the Province of Prussia, but was re-established in 1878 when the merger was reversed and became part of the German Empire. From 1918, West Prussia was a province of the Free State of Prussia within Weimar Germany, losing most of its territory to the Second Polish Republic and the Free City of Danzig in the Treaty of Versailles. West Prussia was dissolved in 1920, and its remaining western territory was merged with Posen to form Posen-West Prussia, and its eastern territory merged with East Prussia as the Region of West Prussia district. West Prussia's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Prussian
Old Prussian was a Western Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European languages, which was once spoken by the Old Prussians, the Baltic peoples of the Prussian region. The language is called Old Prussian to avoid confusion with the German dialects of Low Prussian and High Prussian and with the adjective ''Prussian'' as it relates to the later German state. Old Prussian began to be written down in the Latin alphabet in about the 13th century, and a small amount of literature in the language survives. Classification and relation to other languages Old Prussian is an Indo-European language belonging to the Baltic branch. It is considered to be a Western Baltic language. Old Prussian was closely related to the other extinct Western Baltic languages, namely Sudovian, West Galindian and possibly Skalvian and Old Curonian. Other linguists consider Western Galindian and Skalvian to be Prussian dialects. It is related to the Eastern Baltic languages su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evacuation Of East Prussia
The evacuation of East Prussia was the movement of German civilian population and military personnel from East Prussia between 20 January and March 1945, that was initially organized and carried out by state authorities but quickly turned into a chaotic flight from the Red Army. A part of the evacuation of German civilians towards the end of World War II, these events are not to be confused with the expulsion from East Prussia that followed after the war had ended. The area that was evacuated was not the Gau East Prussia, but the inter-war East Prussia where most people already held German citizenship. German citizens in Memel and other regions with proximity to East Prussia also took part in the evacuation, wishing to escape by sea, even though in their regions there was no official evacuation announced. The evacuation, which had been delayed for months, was initiated due to fear of the Red Army advances during the East Prussian Offensive. Some parts of the evacuation wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Death
In linguistics, language death occurs when a language loses its terminal speaker, last First language, native speaker. By extension, language extinction is when the language is no longer known, including by Second language, second-language speakers. Other similar terms include linguicide, the death of a language from natural or political causes, and rarely wiktionary:glottophagy, glottophagy, the absorption or replacement of a minor language by a major language. Language death is a process in which the level of a Speech community, speech community's linguistic competence in their Variety (linguistics), language variety decreases, eventually resulting in no native or fluent speakers of the variety. Language death can affect any language form, including dialects. Language death should not be confused with language attrition (also called language loss), which describes the loss of proficiency in a first language of an individual.Crystal, David (2000) ''Language Death''. Cambridge, UK: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Dialects
German dialects are the various traditional local varieties of the German language. Though varied by region, those of the southern half of Germany beneath the Benrath line are dominated by the geographical spread of the High German consonant shift, and the dialect continuum that connects German to the neighboring varieties of Low Franconian ( Dutch) and Frisian. The varieties of German are conventionally grouped into Upper German, Central German and Low German; Upper and Central German form the High German subgroup. Standard German is a standardized form of High German, developed in the early modern period based on a combination of Central German and Upper German varieties. Etymology and nomenclature Traditionally, all of the major dialect groupings of German dialects are typically named after so-called " stem duchies" or "tribal duchies" (German: ''Stammesherzogtümer'') by early German linguists, among whom the Brothers Grimm were especially influential. These tribal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
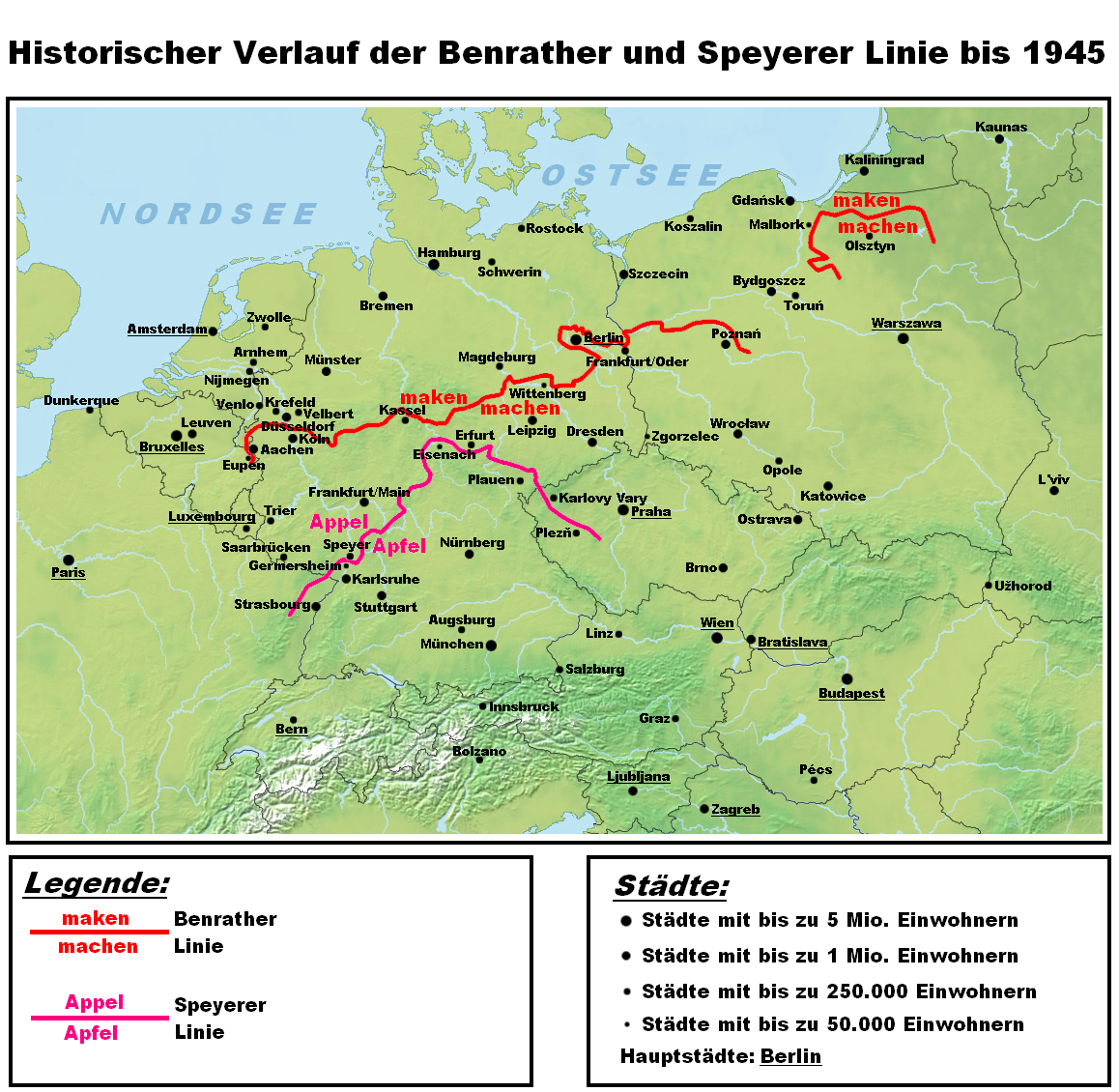
Central German
Central German or Middle German (german: mitteldeutsche Dialekte, mitteldeutsche Mundarten, Mitteldeutsch) is a group of High German dialects spoken from the Rhineland in the west to the former eastern territories of Germany. Central German divides into two subgroups, West Central German and East Central German. Central German is distinguished by having experienced the High German consonant shift to a lesser degree than Upper German. It is spoken in the linguistic transition region separated from Northern Germany (Low German/ Low Franconian) by the Benrath line isogloss and separated from Southern Germany (Upper German) by the Speyer line. Central German is spoken in large and influential German cities like the capital Berlin, the former West German capital Bonn, Cologne, Düsseldorf, Leipzig, Dresden and the main German financial center Frankfurt. The area corresponds to the geological region of the hilly Central Uplands that stretches from the North German plain to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uerdingen Line
The Uerdingen Line (german: Ürdinger Linie, Uerdinger Linie, nl, Uerdinger linie; named after Uerdingen by Georg Wenker) is the isogloss within West Germanic languages that separates dialects which preserve the ''-k'' sound in the first person singular pronoun word "ik" (north of the line) from dialects in which the word-final ''-k'' has changed to word final ''-ch'' in the word "ich" (IPA ) (south of the line). This sound shift is the one that progressed the farthest north among the consonant shifts that characterize High German and Middle German dialects. The line passes through Belgium, the Netherlands, and Germany. North of the line Low German and Dutch are spoken. South of the line Central German is spoken. In the area between the Uerdingen line and the Benrath line to its south, which includes parts of Belgium and the Netherlands, the Germanic dialect Limburgish is spoken. Especially in eastern Germany, the regional languages have been largely replaced by standard Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benrath Line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line (german: Benrather Linie) is the ''maken–machen'' isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in ''maken'' (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (''machen''). The Line runs from Aachen in the west via Benrath (south of Düsseldorf) to eastern Germany near Frankfurt an der Oder in the area of Berlin and Dessau and through former East Prussia dividing Low Prussian dialect and High Prussian dialect. It is called Benrath line because Benrath is the place where it crosses the Rhine. The High German consonant shift (3rd to 9th centuries AD), in which the (northern) Low German dialects for the most part did not participate, affected the southern varieties of the West Germanic dialect continuum. This shift is traditionally seen to distinguish the High German varieties from the other West Germanic languages The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Prussian
High Prussian (german: Hochpreußisch) is a group of East Central German dialects in former East Prussia, in present-day Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (Poland) and Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia). High Prussian developed in the 13th–15th centuries, brought in by German settlers mainly from Silesia and Thuringia, and was influenced by the Baltic Old Prussian language. Classification High Prussian is a Central German dialect formally spoken in Prussia. It is separated from its only adjacent German dialect, Low Prussian, by the Benrath line and the Uerdingen line, the latter dialect being Low German. This was once one of the, if not the hardest linguistic border within the German dialects. It shares some features with Low Prussian, differentiating it from other Central German dialects east of the . Those Borussisms are: * Loss of ''/-n/'' in infinitives (''mache'' for Standard German , "to make"); * retention of the prefix ''//ge-//'' in the participe perfect passive (compare Meckel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia (region)
Prussia ( Old Prussian: ''Prūsa''; german: Preußen; lt, Prūsija; pl, Prusy; russian: Пруссия, tr=Prussiya, ''/Prussia/Borussia'') is a historical region in Europe on the south-eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, that ranges from the Vistula delta in the west to the end of the Curonian Spit in the east and extends inland as far as Masuria. Tacitus's ''Germania'' (98 AD) is the oldest known record of an eyewitness account on the territory and its inhabitants. Pliny the Elder had already confirmed that the Romans had navigated into the waters beyond the ''Cimbric peninsula'' (Jutland). Suiones, Sitones, Goths and other Germanic people had temporarily settled to the east and west of the Vistula River during the Migration Period, adjacent to the Aesti, who lived further to the east. Overview The region's inhabitants of the Middle Ages have first been called ''Bruzi'' in the brief text of the Bavarian Geographer and since been referred to as Old Prussians, who, beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Dialekte 1910
Deutsch or Deutsche may refer to: *''Deutsch'' or ''(das) Deutsche'': the German language, in Germany and other places *''Deutsche'': Germans, as a weak masculine, feminine or plural demonym *Deutsch (word), originally referring to the Germanic vernaculars of the Early Middle Ages Businesses and organisations * André Deutsch, an imprint of Carlton Publishing Group * Deutsch Inc., a former American advertising agency that split in 2020 into: ** Deutsch NY, a New York City-based advertising agency * Deutsche Aerospace AG * Deutsche Akademie, a cultural organisation, superseded by the Goethe-Institut *Deutsche Bahn, the German railway service *Deutsche Bank *Deutsche Börse, a German stock exchange * Deutsche Geophysikalische Gesellschaft, the German Geophysical Society *Deutsche Grammophon, a German classical music record label *Deutsch Group, an international connector manufacturer *Deutsche Luft Hansa (1926–1945) * Deutsche Lufthansa (since 1953), an airline * Deutsche Marin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |