|
Ehrenfest–Tolman Effect
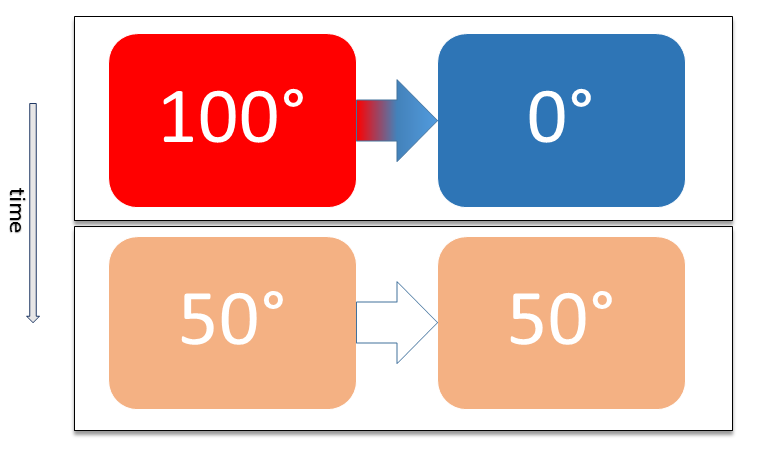
In general relativity, the Ehrenfest–Tolman effect (also known as the Tolman–Ehrenfest effect), created by Richard C. Tolman and Paul Ehrenfest, argues that temperature is not constant in space at thermal equilibrium, but varies with the spacetime curvature. Specifically, it depends on the spacetime metric. In a stationary spacetime with timelike Killing vector field \xi, the temperature T satisfies instead the Tolman-Ehrenfest relation: T\,, , \xi, , =\mathrm, where , , \xi, , =\sqrt is the norm of the timelike Killing vector field. This relationship leads to the concept of ''thermal time'' which has been considered as a possible basis for a fully general-relativistic thermodynamics. It has been shown that the Tolman–Ehrenfest effect can be derived by applying the equivalence principle In the theory of general relativity, the equivalence principle is the equivalence of gravitational and inertial mass, and Albert Einstein's observation that the gravitational "force" as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gravitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Chase Tolman
Richard Chace Tolman (March 4, 1881 – September 5, 1948) was an American Mathematical physics, mathematical physicist and physical chemist who made many contributions to statistical mechanics. He also made important contributions to Physical cosmology, theoretical cosmology in the years soon after Einstein's discovery of general relativity. He was a professor of physical chemistry and mathematical physics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). Biography Tolman was born in West Newton, Massachusetts and studied chemical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, receiving his bachelor's degree in 1903 and PhD in 1910 under Arthur Amos Noyes, A. A. Noyes. He married Ruth Sherman Tolman in 1924. In 1912, he conceived of the concept of relativistic mass, writing that "the expression m_0 \left(1 - \frac \right)^ is best suited for the mass of a moving body." In a 1916 experiment with Thomas Dale Stewart, Tolman demonstrated that electricity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Ehrenfest
Paul Ehrenfest (18 January 1880 – 25 September 1933) was an Austrian theoretical physicist, who made major contributions to the field of statistical mechanics and its relations with quantum mechanics, including the theory of phase transition and the Ehrenfest theorem. He bonded with Albert Einstein on a visit to Prague in 1912 and became a professor in Leiden, where he frequently hosted Einstein. Biography Paul Ehrenfest was born and grew up in Vienna to Jewish parents from Loštice in Moravia (now part of the Czech Republic). His parents, Sigmund Ehrenfest and Johanna Jellinek, ran a grocery store. Although the family was not overly religious, Paul studied Hebrew and the history of the Jewish people. Later, he always emphasized his Jewish roots. Ehrenfest excelled in grade school but did not do well at the Akademisches Gymnasium, his best subject being mathematics. After transferring to the Franz Josef Gymnasium, his marks improved. In 1899, he passed the final exams. He m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium with itself if the temperature within the system is spatially uniform and temporally constant. Systems in thermodynamic equilibrium are always in thermal equilibrium, but the converse is not always true. If the connection between the systems allows transfer of energy as 'change in internal energy' but does not allow transfer of matter or transfer of energy as work, the two systems may reach thermal equilibrium without reaching thermodynamic equilibrium. Two varieties of thermal equilibrium Relation of thermal equilibrium between two thermally connected bodies The relation of thermal equilibrium is an instance of equilibrium between two bodies, which means that it refers to transfer through a selectively permeable p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of spacetime as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates: * The laws of physics are invariant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killing Vector Field
In mathematics, a Killing vector field (often called a Killing field), named after Wilhelm Killing, is a vector field on a Riemannian manifold (or pseudo-Riemannian manifold) that preserves the metric. Killing fields are the infinitesimal generators of isometries; that is, flows generated by Killing fields are continuous isometries of the manifold. More simply, the flow generates a symmetry, in the sense that moving each point of an object the same distance in the direction of the Killing vector will not distort distances on the object. Definition Specifically, a vector field ''X'' is a Killing field if the Lie derivative with respect to ''X'' of the metric ''g'' vanishes: :\mathcal_ g = 0 \,. In terms of the Levi-Civita connection, this is :g\left(\nabla_Y X, Z\right) + g\left(Y, \nabla_Z X\right) = 0 \, for all vectors ''Y'' and ''Z''. In local coordinates, this amounts to the Killing equation :\nabla_\mu X_\nu + \nabla_ X_\mu = 0 \,. This condition is expressed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalence Principle
In the theory of general relativity, the equivalence principle is the equivalence of gravitational and inertial mass, and Albert Einstein's observation that the gravitational "force" as experienced locally while standing on a massive body (such as the Earth) is the same as the ''pseudo-force'' experienced by an observer in a non-inertial (accelerated) frame of reference. Einstein's statement of the equality of inertial and gravitational mass Development of gravitational theory Something like the equivalence principle emerged in the early 17th century, when Galileo expressed experimentally that the acceleration of a test mass due to gravitation is independent of the amount of mass being accelerated. Johannes Kepler, using Galileo's discoveries, showed knowledge of the equivalence principle by accurately describing what would occur if the Moon were stopped in its orbit and dropped towards Earth. This can be deduced without knowing if or in what manner gravity decreases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gravitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |