|
Eclipta Alba
''Eclipta prostrata'', commonly known as false daisy, ''yerba de tago'', ''Gunta kalagaraku/Gunta galagaraku'', ''Karisalankanni'', and ''bhringraj'', is a species of plant in the family Asteraceae. It is widespread across much of the world. This plant has cylindrical, grayish roots. Solid, circular, purplish stems with white fine hairs 0.8m. Leaves arranged in opposite pairs, hairy in two-sided, lanceolate, serrated 2–12.5 cm long, 5-35 mm wide. The solitary flower heads are in diameter, with white florets. The bumpy achenes are compressed and narrowly winged. Steenis, CGGJ van (1981). ''Flora, untuk sekolah di Indonesia''. PT Pradnya Paramita, Jakarta. pp. 423-424 This species grows commonly in moist places in warm temperate to tropical areas worldwide. It is widely distributed throughout India, Nepal, China, Thailand, and Brazil. Traditional uses The plant has traditional uses in Ayurveda. In India, it is known as ''bhangra'' or ''bhringaraj''. ''Wedelia calendulac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedelia Calendulacea
''Wedelia calendulacea'' may refer to: *''Wedelia calendulacea'' (L.) Less., an illegitimate name that is a synonym of ''Sphagneticola calendulacea'' *''Wedelia calendulacea'' Rich, an unresolved name in the genus ''Wedelia ''Wedelia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. They are one of the genera commonly called "creeping-oxeyes". The genus is named in honor of German botanist and physician Georg Wolfgang Wedel, 1645–1721. Taxonomy There ...'' References {{SIA, plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol ( opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
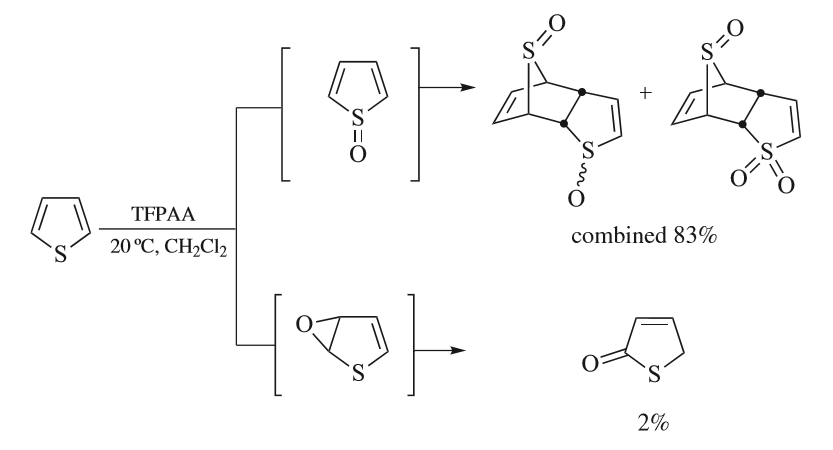
Thiophene
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring. Isolation and occurrence Thiophene was discovered as a contaminant in benzene. It was observed that isatin (an indole) forms a blue dye if it is mixed with sulfuric acid and crude benzene. The formation of the blue indophenin had long been believed to be a reaction of benzene itself. Viktor Meyer was able to isolate thiophene as the actual substance responsible for this reaction. Thiophene and especially its derivatives occur in petroleum, sometimes in concentrations up to 1–3%. The thiophenic content of oil and coal is removed via the hydrodesulfurization (HDS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyyne
In organic chemistry, a polyyne () is any organic compound with alternating single and triple bonds; that is, a series of consecutive alkynes, with ''n'' greater than 1. These compounds are also called polyacetylenes, especially in the natural products and chemical ecology literature, even though this nomenclature more properly refers to acetylene polymers composed of alternating single and double bonds with ''n'' greater than 1. They are also sometimes referred to as oligoynes, or carbinoids after " carbyne" , the hypothetical allotrope of carbon that would be the ultimate member of the series. In ''Avancés récentes en chimie des acétylènes – Recent advances in acetylene chemistry'' The synthesis of this substance has been claimed several times since the 1960s, but those reports have been disputed. Indeed, the substances identified as short chains of "carbyne" in many early organic synthesis attempts would be called polyynes today. The simplest polyyne is diacetylene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coumestan
Coumestan is a heterocyclic organic compound. Coumestan forms the central core of a variety of natural compounds known collectively as coumestans. Coumestans are oxidation products of pterocarpan that are similar to coumarin. Coumestans, including coumestrol, a phytoestrogen, are found in a variety of plants. Food sources high in coumestans include split peas, pinto beans, lima beans, and especially alfalfa and clover sprouts. Coumestrol has about the same binding affinity for the ER-β estrogen receptor as 17β-estradiol, but much less affinity than 17α-estradiol, although the estrogenic potency of coumestrol at both receptors is much less than that of 17β-estradiol. Because of the estrogenic activity of some coumestans, a variety of syntheses have been developed that allow the preparation of coumestans so that their pharmacological effects can be explored. Coumestans Image:coumestrol.png, Coumestrol Coumestrol is a natural organic compound in the class of phytoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytochemical
Phytochemicals are chemical compounds produced by plants, generally to help them resist fungi, bacteria and plant virus infections, and also consumption by insects and other animals. The name comes . Some phytochemicals have been used as poisons and others as traditional medicine. As a term, ''phytochemicals'' is generally used to describe plant compounds that are under research with unestablished effects on health, and are not scientifically defined as essential nutrients. Regulatory agencies governing food labeling in Europe and the United States have provided guidance for industry to limit or prevent health claims about phytochemicals on food product or nutrition labels. Definition Phytochemicals are chemicals of plant origin. Phytochemicals (from Greek ''phyto'', meaning "plant") are chemicals produced by plants through primary or secondary metabolism. They generally have biological activity in the plant host and play a role in plant growth or defense against competitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karel Heyne
Karel Heyne (1877–1947) was a Dutch botanist, known for his comprehensive handbook on the useful plants of the Dutch East Indies (''The useful plants of the Dutch East Indies''); this was the first such handbook and became a standard reference. (in Dutch) Towards the end of the 19th century he settled on Java in the former Dutch East Indies. In 1900, at the age of 23, he started working for the Koninklijke Paketvaart Maatschappij (KPM). He married Wilhelmina Louise Visser (1871–1913) in 1903 and they had two sons, the first in 1905 and the second in 1906. In January 1906, Heyne was appointed chief curator of the ''Museum voor Economische Botanie'' (Museum of Economic Botany) in Buitenzorg by Melchior Treub, the then director of 's Lands Plantentuin in Buitenzorg. In January 1920 he married Ida van Oorschot (1875–1957). In 1926, Heyne resigned as curator and in April 1927 he repatriated to the Netherlands. He and his wife went to live in Bennekom, where he bought a large h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
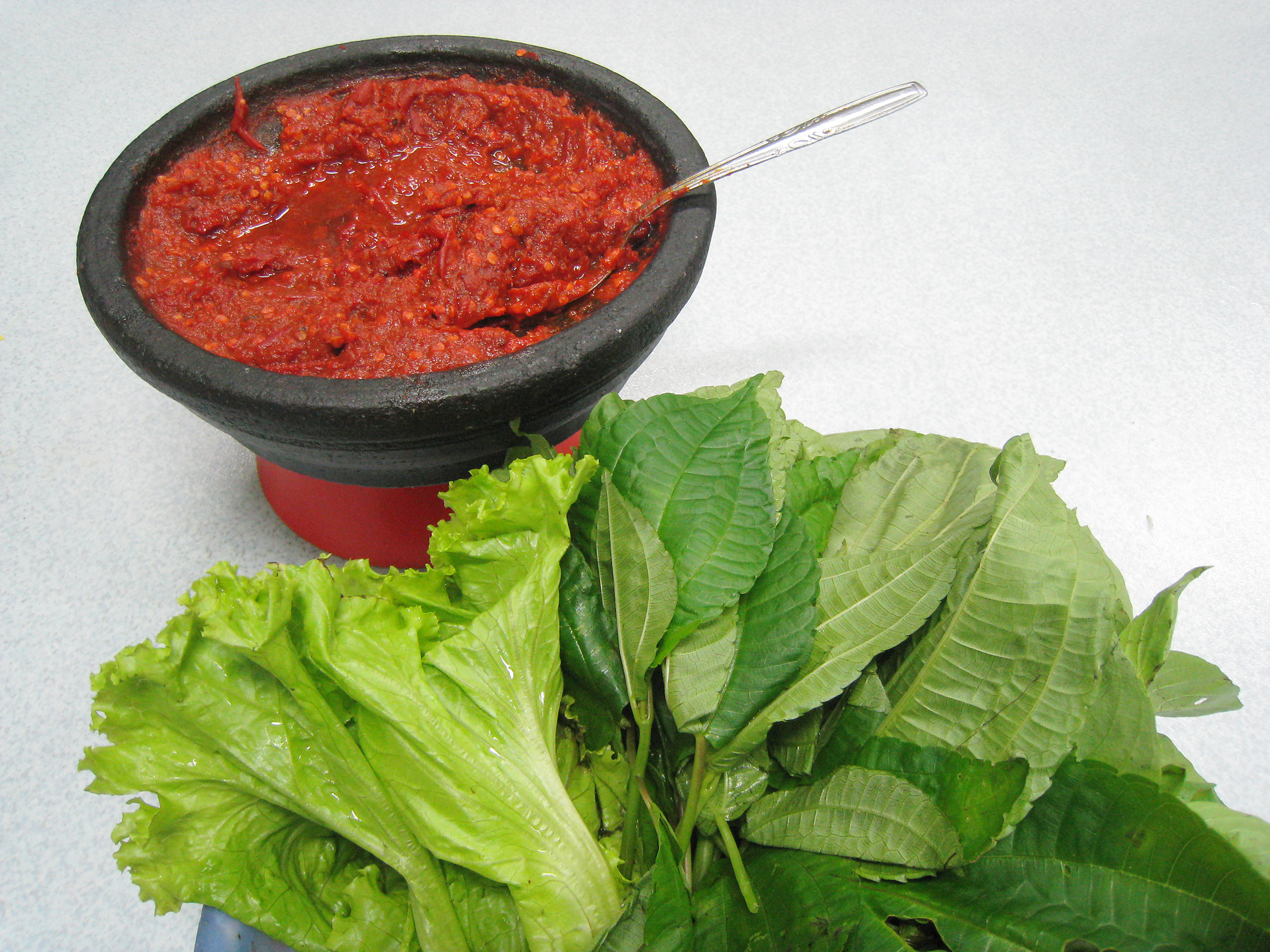
Lalap
''Lalab'' (Sundanese: , ''Lalab'') or ''lalap/lalapan'' (Indonesian) is a Sundanese raw vegetable salad served with ''sambal terasi''. It is a popular Sundanese vegetable dish originated from West Java & Banten, Indonesia. There are no set rules on what vegetables make into lalab, in practice all edible vegetables can be made as lalab. However, the most common raw vegetables are cucumber, tomato, cabbage, lettuce, lemon basil, ''leunca'' and long beans. While blanched or boiled vegetables include spinach, papaya leaves and chayote. The dressing for this salad usually is ''sambal terasi'' served directly from the stone mortar as a spicy dipping sauce for these assorted raw vegetables. Today, ''lalab'' is popular throughout Indonesia. It is usually served as vegetable side dish next to the main course, such as ''ayam goreng'' (fried chicken), '' ayam bakar'' (grilled chicken), '' pepes'', ''pecel lele'' (fried catfish), fried gourami, and many other '' ikan goreng'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javanese People
The Javanese ( id, Orang Jawa; jv, ꦮꦺꦴꦁꦗꦮ, ''Wong Jawa'' ; , ''Tiyang Jawi'' ) are an ethnic group native to the central and eastern part of the Indonesian island of Java. With approximately 100 million people, Javanese people are the largest ethnic group in Indonesia and the whole Southeast Asia in general. Their native language is Javanese, it is the largest of the Austronesian languages in number of native speakers and also the largest regional language in Southeast Asia. The Javanese as the largest ethnic group in the region have dominated the historical, social, and political landscape in the past as well as in modern Indonesia and Southeast Asia. There are significant numbers of Javanese diaspora outside of central and eastern Java regions, including the other provinces of Indonesia, and also in another countries such as Suriname, Singapore, Malaysia, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Yemen and the Netherlands. The Javanese ethnic group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |