|
Diffuse Infrared Background Experiment
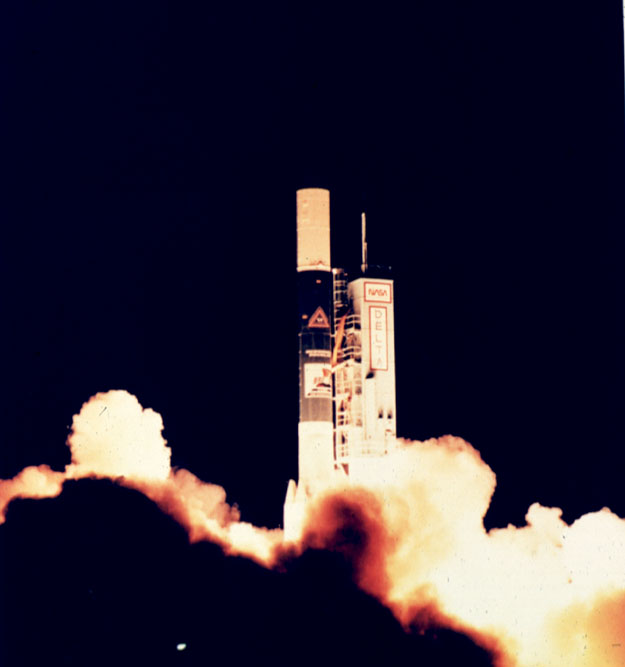
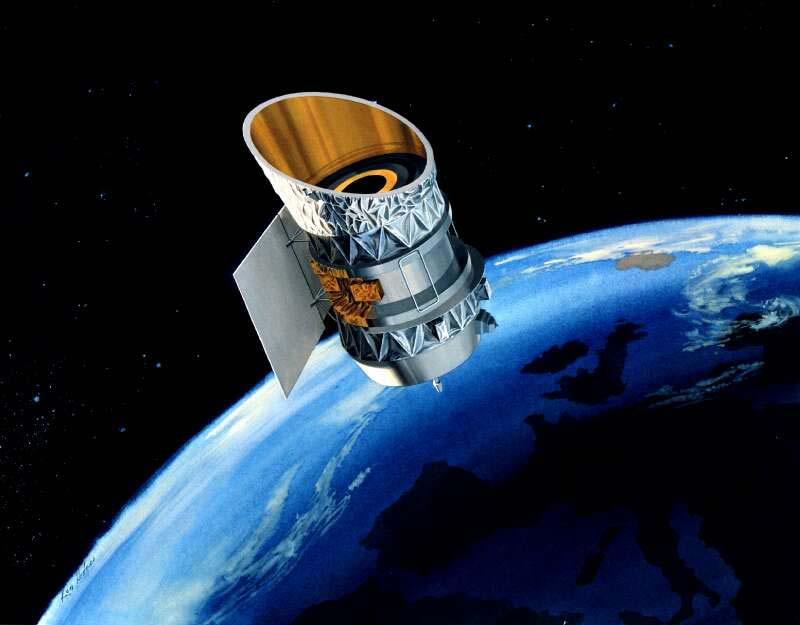
Diffuse Infrared Background Experiment (DIRBE) was an experiment on NASA's COBE mission, to survey the diffuse infrared sky. Measurements were made with a reflecting telescope with 19 cm diameter aperture.Riccardo Giacconi, Daniela Calzetti, Mario Livio, Piero Madau Space Telescope Science Institute (U.S.) - Extragalactic background radiation: a meeting in honor of Riccardo Giacconi : proceedings of the Extragalactic Background Radiation Meeting, Baltimore, 1993 May 18-20, Volume 1993 - Page 137 (Google Books accessed October 2010)/ref> The goal was to obtain brightness maps of the universe at ten frequency bands ranging from the near to far infrared (1.25 to 240 micrometer). Also, linear polarization was measured at 1.25, 2.2, and 3.5 micrometers. During the mission, the instrument could sample half the celestial sphere each day. Mission details The Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) mission was launched in November 1989. The spacecraft contained liquid helium that cooled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIRBE
Diffuse Infrared Background Experiment (DIRBE) was an experiment on NASA's COBE mission, to survey the diffuse infrared sky. Measurements were made with a reflecting telescope with 19 cm diameter aperture.Riccardo Giacconi, Daniela Calzetti, Mario Livio, Piero Madau Space Telescope Science Institute (U.S.) - Extragalactic background radiation: a meeting in honor of Riccardo Giacconi : proceedings of the Extragalactic Background Radiation Meeting, Baltimore, 1993 May 18-20, Volume 1993 - Page 137 (Google Books accessed October 2010)/ref> The goal was to obtain brightness maps of the universe at ten frequency bands ranging from the near to far infrared (1.25 to 240 micrometer). Also, linear polarization was measured at 1.25, 2.2, and 3.5 micrometers. During the mission, the instrument could sample half the celestial sphere each day. Mission details The Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) mission was launched in November 1989. The spacecraft contained liquid helium that cooled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Background Explorer
The Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE ), also referred to as Explorer 66, was a NASA satellite dedicated to cosmology, which operated from 1989 to 1993. Its goals were to investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB or CMBR) of the universe and provide measurements that would help shape our understanding of the cosmos. COBE's measurements provided two key pieces of evidence that supported the Big Bang theory of the universe: that the CMB has a near-perfect black-body spectrum, and that it has very faint anisotropies. Two of COBE's principal investigators, George F. Smoot and John C. Mather, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2006 for their work on the project. According to the Nobel Prize committee, "the COBE project can also be regarded as the starting point for cosmology as a precision science". COBE was the second cosmic microwave background satellite, following RELIKT-1, and was followed by two more advanced spacecraft: the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniela Calzetti
Daniela Calzetti is an Italian-American astronomer known for her research on cosmic dust, star formation, and galaxy formation and evolution, and in particular for the Calzetti dust extinction law, an estimate for how much information about distant galaxies has been obscured by cosmic dust. She is a professor of astronomy and head of the astronomy department at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, and principal investigator of the Legacy ExtraGalactic Ultraviolet Survey project of the Hubble Space Telescope. Education and career Calzetti is originally from Parma. She earned a laurea in physics from Sapienza University of Rome in 1987, where she completed her Ph.D. in 1992, with the dissertation ''Large-Scale Distribution of Galaxies and Clusters: The Scale of Inhomogeneity'' supervised by Remo Ruffini. She worked as a researcher for the Space Telescope Science Institute from 1990 to 2007, when she moved to the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Recognition Calzetti wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Polarization
In electrodynamics, linear polarization or plane polarization of electromagnetic radiation is a confinement of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector to a given plane along the direction of propagation. The term ''linear polarization'' (French: ''polarisation rectiligne'') was coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1822.A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), ''Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel'', vol. 1 (1866), pp.731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", , 2021 (open access); §9. See '' polarization'' and ''plane of polarization'' for more information. The orientation of a linearly polarized electromagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Introduction Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westward o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Astronomy
Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared (IR) radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 micrometers, and falls in between visible radiation, which ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers, and submillimeter waves. Infrared astronomy began in the 1830s, a few decades after the discovery of infrared light by William Herschel in 1800. Early progress was limited, and it was not until the early 20th century that conclusive detections of astronomical objects other than the Sun and Moon were made in infrared light. After a number of discoveries were made in the 1950s and 1960s in radio astronomy, astronomers realized the information available outside the visible wavelength range, and modern infrared astronomy was established. Infrared and optical astronomy are often practiced using the same telescopes, as the same mirrors or lenses are usually effective over a wavelengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Infrared Background
Cosmic infrared background is infrared radiation caused by stellar dust. History Recognizing the cosmological importance of the darkness of the night sky (Olbers' paradox) and the first speculations on an extragalactic background light dates back to the first half of the 19th century. Despite its importance, the first attempts were made only in the 1950-60s to derive the value of the visual background due to galaxies, at that time based on the integrated starlight of these stellar systems. In the 1960s the absorption of starlight by dust was already taken into account, but without considering the re-emission of this absorbed energy in the infrared. At that time Jim Peebles pointed out, that in a Big Bang-created Universe there must have been a cosmic infrared background (CIB) – different from the cosmic microwave background – that can account for the formation and evolution of stars and galaxies. In order to produce today's metallicity, early galaxies must have been signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Largest Infrared Telescopes
The largest infrared telescopes for infrared astronomy are listed in terms of diameter of primary mirror. The infrared spectrum with its longer wavelength than visible light has a number of challenges, especially for ground-based observatories but also in space. Notably infrared radiation is emitted by all physical objects above Absolute Zero temperature so telescopes are subject to local interference. Overall Infrared observations from Earth's surface are possible in a limited way but can be very dependent on location and atmospheric conditions. Water vapour in the Earth's atmosphere blocks much of the infrared band, although some limited observations are possible and there is a number of infrared observatories. Sometimes other optical telescopes can make infrared observations if they are equipped with the right detectors, even if they are not dedicated infrared observatories. For ground-based observatories, the location can make a big difference in how much observation is po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRAS
The Infrared Astronomical Satellite (Dutch: ''Infrarood Astronomische Satelliet'') (IRAS) was the first space telescope to perform a survey of the entire night sky at infrared wavelengths. Launched on 25 January 1983, its mission lasted ten months. The telescope was a joint project of the United States (NASA), the Netherlands ( NIVR), and the United Kingdom ( SERC). Over 250,000 infrared sources were observed at 12, 25, 60, and 100 micrometer wavelengths. Support for the processing and analysis of data from IRAS was contributed from the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center at the California Institute of Technology. Currently, the Infrared Science Archive at IPAC holds the IRAS archive. The success of IRAS led to interest in the 1985 Infrared Telescope (IRT) mission on the Space Shuttle, and the planned Shuttle Infrared Telescope Facility which eventually transformed into the Space Infrared Telescope Facility, SIRTF, which in turn was developed into the Spitzer Space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |