|
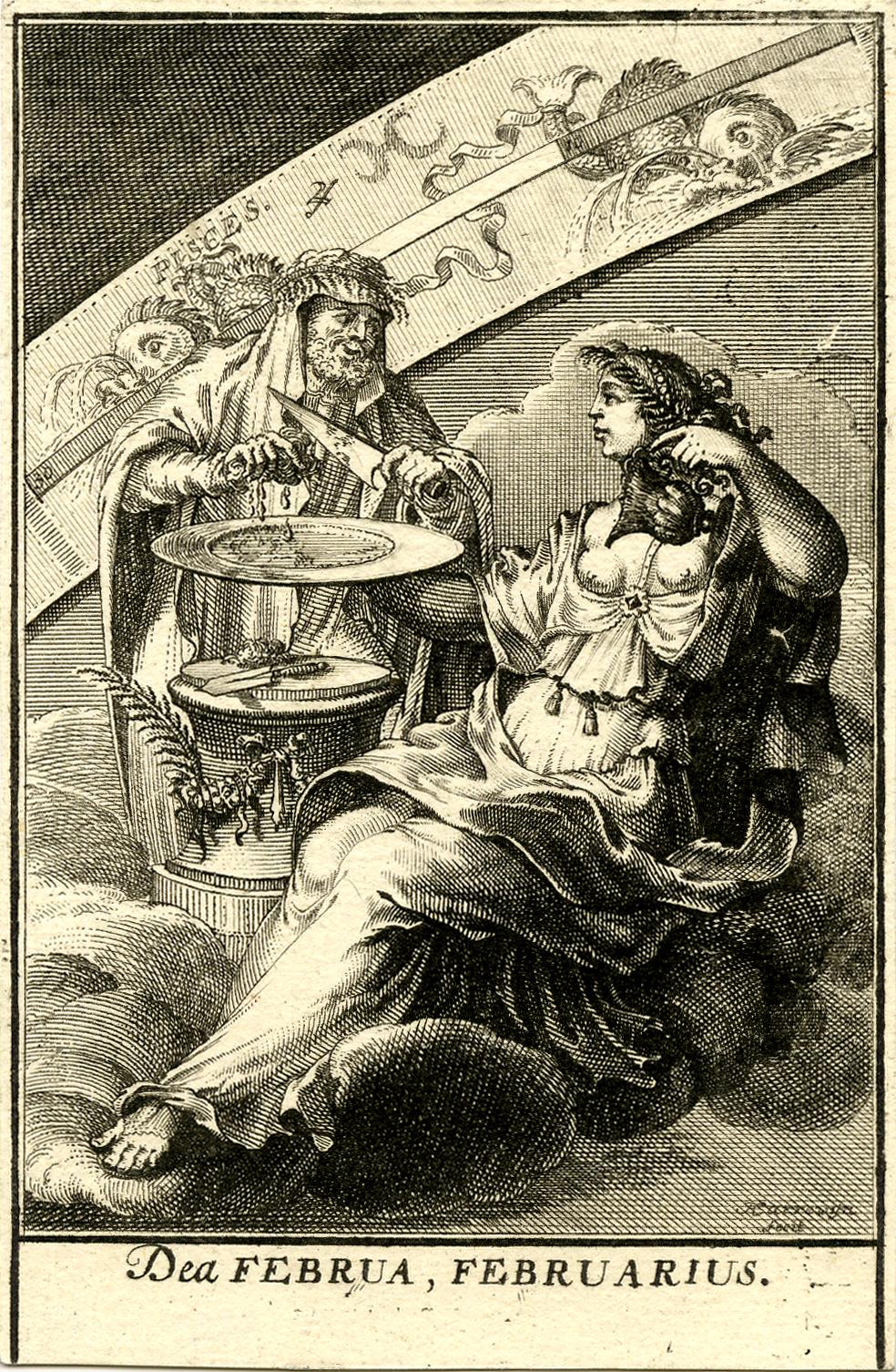
Dea Febris
Febris (), or Dea Febris (), is the Roman goddess of fevers, who embodied, but also protected people from fever and malaria. Because of this, Febris was a feared goddess whom people wanted the favour of. She does not have a myth of her own. Among her characteristic attributes are "shrewdness" and "honesty", according to Seneca the Younger's ''Apocolocyntosis''.Seneca the Younger, ''Apocolocyntosis'', 6 Febris was accompanied by two daughters or sisters of her named Dea Tertiana and Dea Quartana, the goddesses of tertian and quartan fever of malaria because the fever would come back in every three or four days. Theodorus Priscianus mentions Saturn as Tertiana and Quartana's father. The goddess Febris belongs to the apotropaic (turning away) deities (Lat. ''Dii averrunci'') who have power over a specific evil: to impose it or to get rid of it. Romans worshipped Febris so she would not do harm to them. She may have originated from the Etruscan-Roman god of purification, Februus. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fevers
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes flushed, and may begin to sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections—such as influenza, the common cold, meningitis, urinary tract infections, appendicitis, Lassa, COVID-19, and malaria. Non-infectious causes include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn (mythology)
Saturn ( la, Sāturnus ) was a god in ancient Roman religion, and a character in Roman mythology. He was described as a god of time, generation, dissolution, abundance, wealth, agriculture, periodic renewal and liberation. Saturn's mythological reign was depicted as a Golden Age of abundance and peace. After the Roman conquest of Greece, he was conflated with the Greek Titan Cronus. Saturn's consort was his sister Ops, with whom he fathered Jupiter, Neptune, Pluto, Juno, Ceres and Vesta. Saturn was especially celebrated during the festival of Saturnalia each December, perhaps the most famous of the Roman festivals, a time of feasting, role reversals, free speech, gift-giving and revelry. The Temple of Saturn in the Forum Romanum, Roman Forum housed the state treasury and archives (''aerarium'') of the Roman Republic and the early Roman Empire. The planet Saturn and the day of the week Saturday are both named after and were associated with him. Mythology The Roman land preserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics, and he is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. His influence on the Latin language was immense. He wrote more than three-quarters of extant Latin literature that is known to have existed in his lifetime, and it has been said that subsequent prose was either a reaction against or a return to his style, not only in Latin but in European languages up to the 19th century. Cicero introduced into Latin the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy and created a Latin philosophical vocabulary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factorum Ac Dictorum Memorabilium Libri IX
''Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX'' ("nine books of memorable deeds and sayings", also known as ''De factis dictisque memorabilibus'' or ''Facta et dicta memorabilia'') by Valerius Maximus (c. 20 BC – c. AD 50) was written around AD 30 or 31.Walker, p. xiii It is a collection of approximately a thousand short stories that Valerius wrote during the reign of Tiberius (42 BC – AD 37). The stories are a variety of anecdotes illustrating how the ancient Romans lived. While the majority of the stories are of Roman life, he does have some foreign stories at the end of some chapters. Most of these are of Greek life and most of those are about Greek philosophers or famous kings. Several of the stories relate to moral subjects that parallel those in the Old Testament and New Testament. Valerius refers to his moral stories as "examples" that were to be used as moral guidance. Valerius' work on the preservation of moral values of the Roman Republic of the past was w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerius Maximus
Valerius Maximus () was a 1st-century Latin writer and author of a collection of historical anecdotes: ''Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX'' ("Nine books of memorable deeds and sayings", also known as ''De factis dictisque memorabilibus'' or ''Facta et dicta memorabilia''). He worked during the reign of Tiberius (14 AD to 37 AD). During the Middle Ages, Valerius Maximus was one of the most copied Latin prose authors, second only to Priscian. More than 600 medieval manuscripts of his books have survived as a result.Briscoe, ''Valerius Maximus'', p. 15. Biography Nothing is known of his life except that his family was poor and undistinguished, and that he owed everything to Sextus Pompeius (consul AD 14), proconsul of Asia, whom he accompanied to the East in 27. Pompeius was the center of a literary circle to which Ovid belonged; he was also an intimate friend of the most literary prince of the imperial family, Germanicus. Although he shared the same name as a prestigious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
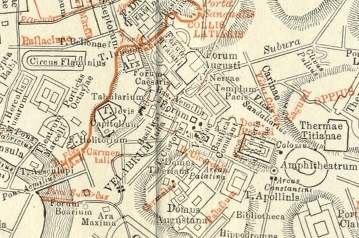
Velabrum
The Velabrum () is the low valley in the city of Rome that connects the Forum with the Forum Boarium, and the Capitoline Hill with the western slope of the Palatine Hill. The name Velabrum may translate to "place of mud." It was believed that before the construction of the Cloaca Maxima, which probably follows the course of an ancient stream, the area was a swamp, though this claim has been disproven by core samples taken from Velabrum in 1994. Ancient authorities state that in this marshy area the roots of a fig tree ''(Ficus Ruminalis)'' caught and stopped the basket carrying Romulus and Remus as it floated along on the Tiber current. The place therefore has a high symbolic significance. It was also used as a marketplace and a center of commerce. Even after the Cloaca was built, the area was still prone to flooding from the Tiber, until the ground level was raised after the Neronian fire. It is the site of the Arch of Janus, the Arcus Argentariorum and the church San Giorgio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; la, Collis Palatium or Mons Palatinus; it, Palatino ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city and has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire." The site is now mainly a large open-air museum while the Palatine Museum houses many finds from the excavations here and from other ancient Italian sites. Imperial palaces were built there, starting with Augustus. Before imperial times the hill was mostly occupied by the houses of the rich. The hill originally had two summits separated by a depression; the highest part was called Palatium and the other Germalus (or Cermalus). Using the Forma Urbis its perimeter enclosed ; while the Regionary Catalogues of the 4th century enclose . Etymology According to Livy (59 BC – AD 17) the Palatine hill got its name from the Arcadian settlers from Pallantium, named from its founder Pallas, son of Lycaon. More likely, it is derived from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juno (mythology)
Juno ( ; Latin ) was an ancient Roman goddess, the protector and special counsellor of the state. She was equated to Hera, queen of the gods in Greek mythology. A daughter of Saturn, she was the sister and wife of Jupiter and the mother of Mars, Vulcan, Bellona and Juventas. Like Hera, her sacred animal was the peacock.''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. Her Etruscan counterpart was Uni, and she was said to also watch over the women of Rome. As the patron goddess of Rome and the Roman Empire, Juno was called ("Queen") and was a member of the Capitoline Triad (''Juno Capitolina''), centered on the Capitoline Hill in Rome, and also including Jupiter, and Minerva, goddess of wisdom. Juno's own warlike aspect among the Romans is apparent in her attire. She was often shown armed and wearing a goatskin cloak. The traditional depiction of this warlike aspect was assimilated from the Greek goddess Athena, who bore a goatskin, or a goatsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Italic
The Proto-Italic language is the ancestor of the Italic languages, most notably Latin and its descendants, the Romance languages. It is not directly attested in writing, but has been reconstructed to some degree through the comparative method. Proto-Italic descended from the earlier Proto-Indo-European language. History Although an equation between archeological and linguistic evidence cannot be established with certainty, the Proto-Italic language is generally associated with the Terramare (1700–1150 BC) and Villanovan cultures (900–700 BC). On the other hand, work in glottochronology has argued that Proto-Italic split off from the western Proto-Indo-European dialects some time before 2500 BC. It was originally spoken by Italic tribes north of the Alps before they moved south into the Italian Peninsula during the second half of the 2nd millennium BC. Linguistic evidence also points to early contacts with Celtic tribes and Proto-Germanic speakers. Phonology Consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Febris
Febris (), or Dea Febris (), is the Roman goddess of fevers, who embodied, but also protected people from fever and malaria. Because of this, Febris was a feared goddess whom people wanted the favour of. She does not have a myth of her own. Among her characteristic attributes are "shrewdness" and "honesty", according to Seneca the Younger's ''Apocolocyntosis''.Seneca the Younger, ''Apocolocyntosis'', 6 Febris was accompanied by two daughters or sisters of her named Dea Tertiana and Dea Quartana, the goddesses of tertian and quartan fever of malaria because the fever would come back in every three or four days. Theodorus Priscianus mentions Saturn as Tertiana and Quartana's father. The goddess Febris belongs to the apotropaic (turning away) deities (Lat. ''Dii averrunci'') who have power over a specific evil: to impose it or to get rid of it. Romans worshipped Febris so she would not do harm to them. She may have originated from the Etruscan-Roman god of purification, Februus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |