|
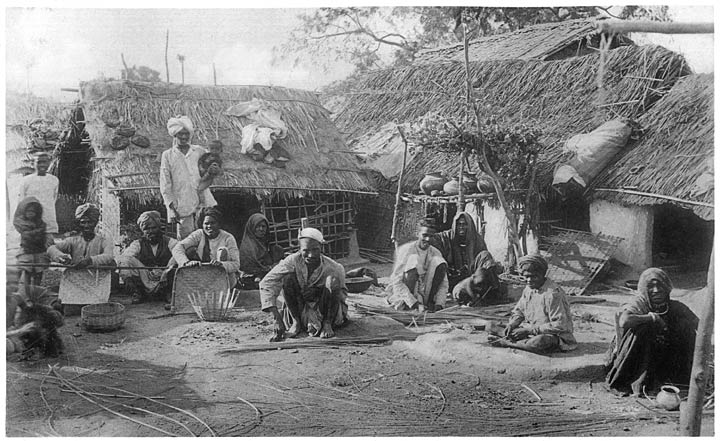
Dabgar
The Dabgar are a Hindu caste found in the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh in India. They are also known as Dhalgar and have scheduled caste status in Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh, while they have Other Backward Class status in Gujarat.In Rajasthan, the community prefer the self-designation is Dhalgar. Origin The word Dabgar is said to be derived from the Sanskrit word ''daravakarra'', which means the makers of any spoon shaped vessels. According to their own traditions, they were originally found in Rajasthan, and were soldiers. They took an oath to resist the Mughals, but were defeated. After this defeat, a section converted to Islam, from whom descend the Muslim Dabgar community. The rest of the community fled in the jungles of Bundelkhand, and slowly spread to the Doab region of Uttar Pradesh. They then took up the occupation of manufacturing of rawhide jars. The Rajasthan Dabgar are involved in the manufacture of a number of musical instruments such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Dabgar
The Muslim Dabgar are a Muslim community found in the state of Uttar Pradesh in India. They are also known as Dalgar and are converts to Islam from the Hindu Dabgar caste.People of India Uttar Pradesh Volume XLII Part One edited by A Hasan & J C Das pages 393 to 397 Manohar Publications Origin The word Dabgar is said to be derived from the Sanskrit word ''daravakarra'', which means the makers of any spoon-shaped vessels. They are said to be a sub-group within the Hindu community. According to their own traditions, they were originally found in Rajasthan, and were soldiers. They took an oath to resist the Mughals, but were defeated. A section converted to Islam, from whom descend the Muslim Dabgar community. Present times The Dabgar are strictly endogamous, and marry close kin. Like their Hindu counterparts, the Muslim Dabgar community is also divided into a number of clans. Their main clans are the Punjabi and Delhiwal, but unlike the Hindu Dabgar, there is no prohibition i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-identity within the local In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroda
Vadodara (), also known as Baroda, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Vadodara district and is situated on the banks of the Vishwamitri River, from the state capital of Gandhinagar. The railway line and National Highway 8, which connect Delhi with Mumbai, pass through Vadodara. The city is named for its abundance of the Banyan (''Vad'') tree. Vadodara is also locally referred to as the ''Sanskari Nagari'' () and ''Kala Nagari'' () of India. The city is prominent for landmarks such as the Laxmi Vilas Palace, which served as the residence of the Maratha royal Gaekwad dynasty that ruled over Baroda State. It is also the home of the Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda. Etymology The city in one period was called Chandanavati after the rule of Chanda of the Dodiya Rajputs. The capital was also known as Virakshetra or Viravati (Land of Warriors). Later on, it was known as Vadpatraka or Vadodará, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exogamy
Exogamy is the social norm of marrying outside one's social group. The group defines the scope and extent of exogamy, and the rules and enforcement mechanisms that ensure its continuity. One form of exogamy is dual exogamy, in which two groups continually intermarry with each other. In social science, exogamy is viewed as a combination of two related aspects: biological and cultural. Biological exogamy is marriage of nonblood-related beings, regulated by forms of incest law. Cultural exogamy is marrying outside a specific cultural group; the opposite being endogamy, marriage within a social group. Biology of exogamy Exogamy often results in two individuals that are not closely genetically related marrying each other; that is, outbreeding as opposed to inbreeding. In moderation, this benefits the offspring as it reduces the risk of the offspring inheriting two copies of a defective gene. Increasing the genetic diversity of the offspring improves the chances of offspring reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogamy
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific social group, religious denomination, caste, or ethnic group, rejecting those from others as unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships. Endogamy is common in many cultures and ethnic groups. Several religious and ethnic religious groups are traditionally more endogamous, although sometimes with the added dimension of requiring marital religious conversion. This permits an exogamous marriage, as the convert, by accepting the partner's religion, becomes accepted within the endogamous rules. Endogamy, as distinct from consanguinity, may result in transmission of genetic disorders, the so-called founder effect, within the relatively closed community. Adherence Endogamy can serve as a form of self-segregation; a community can use it to resist integrating and completely merging with surrounding populations. Minorities can use it to stay ethnically homogeneous over a long time as distinct communities withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castes
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultural notions of purity and pollution. * Quote: "caste ort., casta=basket ranked groups based on heredity within rigid systems of social stratification, especially those that constitute Hindu India. Some scholars, in fact, deny that true caste systems are found outside India. The caste is a closed group whose members are severely restricted in their choice of occupation and degree of social participation. Marriage outside the caste is prohibited. Social status is determined by the caste of one's birth and may only rarely be transcended." * Quote: "caste, any of the ranked, hereditary, endogamous social groups, often linked with occupation, that together constitute traditional societies in South Asia, particularly among Hindus in India. Althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salaat
(, plural , romanized: or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːh, ( or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːtʰin construct state) ), also known as ( fa, نماز) and also spelled , are prayers performed by Muslims. Facing the , the direction of the Kaaba with respect to those praying, Muslims pray first standing and later kneeling or sitting on the ground, reciting prescribed prayers and phrases from the Quran as they bow and prostrate themselves in between. is composed of prescribed repetitive cycles of bows and prostrations, called ( ). The number of s, also known as units of prayer, varies from prayer to prayer. Ritual purity and are prerequisites for performing the prayers. The daily obligatory prayers collectively form the second of the five pillars in Islam, observed three or five times (the latter being the majority) every day at prescribed times. These are usually (observed at dawn), (observed at noon), (observed late in the afternoon), (observed after sunset), and (observed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world. * * * * The city has a syncretic tradition of Muslim artisanship that underpins its religious tourism. * * * * * Located in the middle-Ganges valley in the southeastern part of the state of Uttar Pradesh, Varanasi lies on the left bank of the river. It is to the southeast of India's capital New Delhi and to the east of the state capital, Lucknow. It lies downstream of Allahabad (officially Prayagraj), where the confluence with the Yamuna river is another major Hindu pilgrimage site. Varanasi is one of the world's oldest continually inhabited cities. Kashi, its ancient name, was associated with a kingdom of the same name of 2,500 years ago. The Lion capital of Ashoka at nearby Sarnath has been interpreted to be a commemoration of the Buddha's first sermon there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad ('' sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of Southeast As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes from the Sanskrit root ' meaning "disciple", or ' meaning "instruction". Singh, Khushwant. 2006. ''The Illustrated History of the Sikhs''. Oxford University Press. . p. 15.Kosh, Gur Shabad Ratnakar Mahan. https://web.archive.org/web/20050318143533/http://www.ik13.com/online_library.htm is an Indian religion that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent,"Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikh originated in India." around the end of the 15th century CE. It is the most recently founded major organized faith and stands at fifth-largest worldwide, with about 25–30 million adherents (known as Sikhs) .McLeod, William Hewat. 2019 998 Sikhism developed from the spiritual teachings of Guru Nanak (1469–1539), the faith's first gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
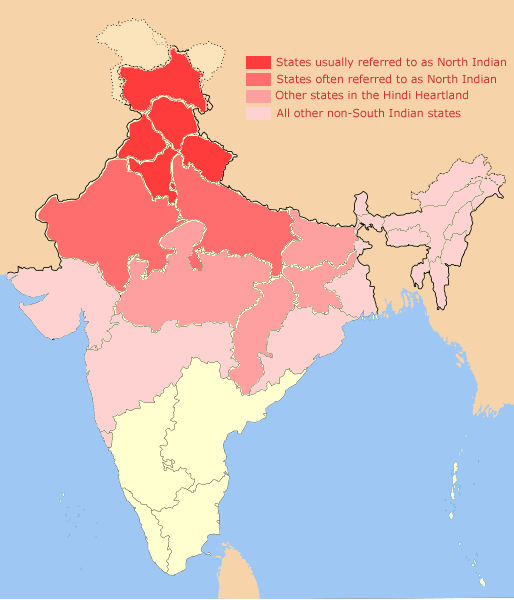
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindi Language
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India. Hindi is the '' lingua franca'' of the Hindi Belt. It is also spoken, to a lesser extent, in other parts of India (usually in a simplified or pidginised variety such as Bazaar Hindustani or Haflong Hindi). Outside India, several ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)