|
Dáire Cerbba
Dáire Cerbba (or Cerba, Cearba, Cearb; meaning "Silver Dáire" or "Dáire the Sharp/Cutting") was a 4th-century Irish dynast who was evidently a king of late prehistoric central northern Munster, called Medón Mairtíne at the time. A frequently believed grandson of his, Crimthann mac Fidaig, was High King of Ireland and some British territories, and another descendant Bressal mac Ailello may have been King of Munster, and whose sister Angias was Queen of Lóegaire mac Néill, High King of Ireland. Finally, another descendant, according to Geoffrey Keating, was a king of Munster named Cormac, son of Ailill, son of Eochaid, son of Dáire Cearb. Unlike many other individuals due to name or obvious descent sometimes considered Dáirine, neither Dáire Cerbba nor his family appear to have any certain associations with the Corcu Loígde and are instead considered, at least officially, relatively close relations of the Éoganachta. Origins and relations Outline Of uncertain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emly
Emly or Emlybeg () is a village in County Tipperary, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is a civil parish in the historical Barony (Ireland), barony of Clanwilliam (County Tipperary), Clanwilliam. It is also an Ecclesiastical parish in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly. The village is 14 km west of Tipperary town, on the R515 road (Ireland), R515 road which goes from Tipperary town to Abbeyfeale, County Limerick. Emly had a population of 302 in 2016. History Ancient times The Taxus baccata, yew tree references the pre-Christian history of Emly. Emly is one of the oldest centres of Christianity in Ireland and pre-dates the coming to Ireland of the National Apostle, St. Patrick. Up until the Early Medieval Ireland 800–1166, early Middle Ages, Emly was the premier diocese in the south of Ireland. Ailbe, St. Ailbe is the patron saint of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly, Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly. Tradition tells us that he preached Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
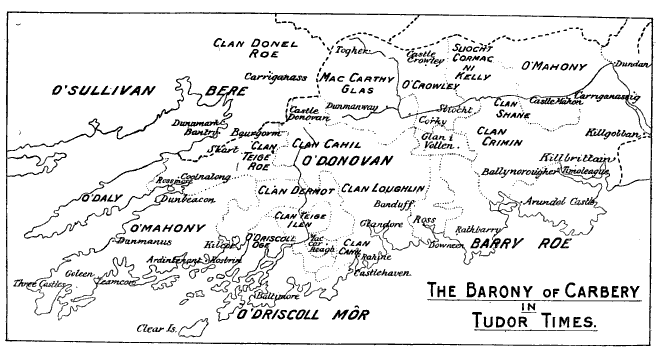
Corcu Loígde
The Corcu Loígde (Corcu Lóegde, Corco Luigde, Corca Laoighdhe, Laidhe), meaning Gens of the Calf Goddess, also called the Síl Lugdach meic Itha, were a kingdom centred in West County Cork who descended from the proto-historical rulers of Munster, the Dáirine, of whom they were the central royal sept. They took their name from Lugaid Loígde "Lugaid of the Calf Goddess", a King of Tara and High King of Ireland, son of the great Dáire Doimthech (a quo Dáirine). A descendant of Lugaid Loígde, and their most famous ancestor, is the legendary Lugaid Mac Con, who is listed in the Old Irish '' Baile Chuinn Chétchathaig''. Closest kin to the Corcu Loígde were the Dál Fiatach princes of the Ulaid. Overview The Corcu Loígde were the rulers of Munster, and likely of territories beyond the province, until the early 7th century AD, when their ancient alliance with the Kingdom of Osraige fell apart as the Eóganachta rose to power. Many peoples formerly subject to the Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Irish
Middle Irish, also called Middle Gaelic (, , ), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of Late Old English and Early Middle English. The modern Goidelic languages—Modern Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Manx Gaelic—are all descendants of Middle Irish. Grammar Middle Irish is a fusional, VSO, nominative-accusative language, and makes frequent use of lenition. Nouns decline for two genders: masculine and feminine, though traces of neuter declension persist; three numbers: singular, dual, plural; and five cases: nominative, accusative, genitive, prepositional, vocative. Adjectives agree with nouns in gender, number, and case. Verbs conjugate for three tenses: past, present, future; four moods: indicative, subjunctive, conditional, imperative; independent and dependent forms. Verbs conjugate for three persons and an impersonal, agentless form ( agent). There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic (, Ogham, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ; ; or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic languages, Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from 600 to 900. The main contemporary texts are dated 700–850; by 900 the language had already transitioned into early Middle Irish. Some Old Irish texts date from the 10th century, although these are presumably copies of texts written at an earlier time. Old Irish is forebear to Modern Irish, Manx language, Manx and Scottish Gaelic. Old Irish is known for having a particularly complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and especially of allomorphy (more or less unpredictable variations in stems and suffixes in differing circumstances), as well as a complex phonology, sound system involving grammatically significant Irish initial mutations, consonant mutations to the initial consonant of a word. Apparently,It is difficult to know for sure, giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarabaeidae
The family Scarabaeidae, as currently defined, consists of over 35,000 species of beetles worldwide; they are often called scarabs or scarab beetles. The classification of this family has undergone significant change. Several groups formerly treated as subfamilies have been elevated to family rank (e.g., Bolboceratidae, Geotrupidae, Glaresidae, Glaphyridae, Hybosoridae, Ochodaeidae, and Pleocomidae), and some reduced to lower ranks. The subfamilies listed in this article are in accordance with those in Catalog of Life (2023). Description Scarabs are stout-bodied beetles; most are brown or black in colour, but many, generally species that are diurnally active, have bright metallic colours, measuring between . The antenna (biology), antennae of most species superficially seem to be knobbed (capitate), but the several segments comprising the head of the antenna are, as a rule, lamellate: they extend laterally into plates called lamella (zoology), lamellae that they usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mug Ruith
Mug Ruith (or Mogh Roith, "slave of the wheel") is a figure in Irish mythology, a powerful blind druid of Munster who lived on Valentia Island, County Kerry. He could grow to enormous size, and his breath caused storms and turned men to stone. He wore a hornless bull-hide and a bird mask, and flew in a ship called the ''roth rámach'', the "oared wheel". He had a fiery ox-driven chariot with blazing jewels that made night seem as bright as day, a star-speckled black shield with a silver rim, and a stone which could turn into a poisonous eel when thrown in water. Legend Stories about Mug Ruith are set in various periods of Irish history. Some say he lived during the reign of 3rd century High King Cormac mac Airt, while others put him in Jerusalem during the time of Christ. In ''Lebor Gabála Érenn'' he is said to have died in the reign of Conmael, nearly two thousand years before Cormac's time. Perhaps due to this array of times and settings, poets attributed the druid with ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudonym
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true meaning ( orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individual's own. Many pseudonym holders use them because they wish to remain anonymous and maintain privacy, though this may be difficult to achieve as a result of legal issues. Scope Pseudonyms include stage names, user names, ring names, pen names, aliases, superhero or villain identities and code names, gamertags, and regnal names of emperors, popes, and other monarchs. In some cases, it may also include nicknames. Historically, they have sometimes taken the form of anagrams, Graecisms, and Latinisations. Pseudonyms should not be confused with new names that replace old ones and become the individual's full-time name. Pseudonyms are "part-time" names, used only in certain contexts: to provide a more clear-cut separation between one's privat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discussion 2
Conversation is interactive communication between two or more people. The development of conversational skills and etiquette is an important part of socialization. The development of conversational skills in a new language is a frequent focus of language teaching and learning. Conversation analysis is a branch of sociology which studies the structure and organization of human interaction, with a more specific focus on conversational interaction. Definition and characterization No generally accepted definition of conversation exists, beyond the fact that a conversation involves at least two people talking together. Consequently, the term is often defined by what it is not. A ritualized exchange such as a mutual greeting is not a conversation, and an interaction that includes a marked status differential (such as a boss giving orders) is also not a conversation. An interaction with a tightly focused topic or purpose is also generally not considered a conversation. Summarizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conall Corc
Corc mac Luigthig (340-379),Genealogy of the House of Mac-Carthy formerly Sovereign of the Two Momonies or Southern Ireland, P. Louis Lainé, pg. 26, https://celt.ucc.ie/published/F830000-001.html also called Conall Corc, Corc of Cashel, and Corc mac Láire, is the hero of Irish language tales which form part of the origin legend of the Eóganachta, a group of kindreds which traced their descent from Conall Corc and took their name from his ancestor Éogan Mór. The early kindred they belonged to are known as the Deirgtine. He was probably a grandson of Ailill Flann Bec, and possible cousins were Dáire Cerbba and the famous Crimthann mac Fidaig. The latter is his opponent in a celebrated cycle of stories. Biography The name and identity of Corc's actual father is something of a mystery, however. While certainly belonging to the kindred of the proto-Eóganachta, he is inconsistently named in the genealogies and tales as Lugaid or Láre. Further confusion is caused by the fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Meath
County Meath ( ; or simply , ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is bordered by County Dublin to the southeast, County Louth, Louth to the northeast, County Kildare, Kildare to the south, Offaly to the southwest, Westmeath to the west, County Cavan, Cavan to the northwest, and County Monaghan, Monaghan to the north. To the east, Meath also borders the Irish Sea along a narrow strip between the rivers River Boyne, Boyne and Delvin River, Delvin, giving it the List of Irish counties by coastline, second shortest coastline of any county. Meath County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. Meath is the List of Irish counties by area, 14th-largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties by land area, and the List of Irish counties by population, 8th-most populous, with a total population of 220,826 according to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mag Breg
The Kings of Brega were rulers of Brega, a petty kingdom north of Dublin in medieval Ireland. Overview Brega took its name from ' ('), meaning "fine plain", in modern County Meath, County Louth and County Dublin, Ireland. They formed part of the Uí Néill kindred, belonging to the Síl nÁedo Sláine branch of the southern Uí Néill. The kingdom of Brega included the Hill of Tara, the site where the High King of Ireland was proclaimed. Brega was bounded on the east by the Irish Sea and on the south by the River Liffey. It extended northwards across the River Boyne to include Sliabh Breagha the line of hills in southern County Louth. The western boundary, which separated it from the Kingdom of Mide, was probably quite fluid and is not accurately known. Brega was annexed in the 6th century by the Uí Néill. By the middle of the 8th century the Síl nÁedo Sláine had split into two hostile branches: Southern Brega, or the Kingdom of Loch Gabhair, which was ruled by the Uí Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |