|
Dufek Coast
The Dufek Coast is that portion of the coast along the southwest margin of the Ross Ice Shelf between Airdrop Peak on the east side of the Beardmore Glacier and Morris Peak on the east side of Liv Glacier. It was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961 after Rear Admiral George J. Dufek, United States Navy, who served under Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd with the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and as commander of the Eastern Task Force of U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. He was Commander of U.S. Naval Support Force Antarctica, 1954–59, a period in which the following American science stations were established: McMurdo Station, Little America V, Byrd Station, South Pole Station, Wilkes Station, Hallett Station Cape Hallett is a snow-free area (Antarctic oasis) on the northern tip of the Hallett Peninsula on the Ross Sea coast of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Cape Adare lies to the north. History In 1956, during Operation Deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dufek Coast Map
Dufek may refer to: * 3781 Dufek, a minor planet named after George Dufek * Dufek Coast in Antarctica, named after U.S. Rear Admiral George J. Dufek * Dufek Head, a headland in Antarctica * Dufek Massif in the Pensacola Mountains of Antarctica * Dufek Mountain in Antarctica People * Don Dufek (born 1954), an American football player * Don Dufek, Sr. (1929–2014), an American football player * George J. Dufek (1903–1977), a U.S. Rear Admiral * Jan Dufek (born 1997), a Czech ice hockey player * Joe Dufek (born 1961), an American football quarterback * Karel Dufek Karel Dufek (24 January 1916 – 16 December 2009) was a Czechoslovak diplomat and a Spanish Civil War veteran who served in the International Brigades. Youth Dufek was born in Dolní Heřmanice, in the Austro-Hungarian Margraviate of Moravi ... (1916–2009), a Czechoslovak diplomat * Milan Dufek (1944–2005), a Czech singer and musician {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byrd Station
The Byrd Station is a former research station established by the United States during the International Geophysical Year by U.S. Navy Seabees during Operation Deep Freeze II in West Antarctica. History A joint Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marines operation supported an overland tractor train traverse that left out of Little America V in late 1956 to establish the station. The train was led by Army Major Merle Dawson and completed a traverse of over unexplored country in Marie Byrd Land to blaze a trail to a spot selected beforehand. The station consisted of a set of four prefabricated buildings and was erected in less than one month by U.S. Navy Seabees. It was commissioned on January 1, 1957. The original station ("Old Byrd") lasted about four years before it began to collapse under the snow. Construction of a second underground station in a nearby location began in 1960, and it was used until 1972. The Operation Deep Freeze activities were succeeded by "Operation Deep Freez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dufek Mountain
Dufek may refer to: * 3781 Dufek, a minor planet named after George Dufek * Dufek Coast in Antarctica, named after U.S. Rear Admiral George J. Dufek * Dufek Head, a headland in Antarctica * Dufek Massif in the Pensacola Mountains of Antarctica * Dufek Mountain in Antarctica People * Don Dufek (born 1954), an American football player * Don Dufek, Sr. (1929–2014), an American football player * George J. Dufek (1903–1977), a U.S. Rear Admiral * Jan Dufek (born 1997), a Czech ice hockey player * Joe Dufek (born 1961), an American football quarterback * Karel Dufek Karel Dufek (24 January 1916 – 16 December 2009) was a Czechoslovak diplomat and a Spanish Civil War veteran who served in the International Brigades. Youth Dufek was born in Dolní Heřmanice, in the Austro-Hungarian Margraviate of Moravi ... (1916–2009), a Czechoslovak diplomat * Milan Dufek (1944–2005), a Czech singer and musician {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dufek Massif
Dufek Massif, Augusto Pinochet Massif or Santa Teresita Massif is a rugged, largely snow-covered massif long, standing west of the Forrestal Range in the northern part of the Pensacola Mountains. It was discovered and photographed on January 13, 1956, on a transcontinental patrol plane flight of U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze from McMurdo Sound to the vicinity of the Weddell Sea and return, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Rear Admiral George J. Dufek,Dufek Coast, Dufek Head, and Dufek Mountain are also named for Dufek. U.S. Navy, who was in direct operational command of U.S. Navy Task Force 43 during that operation. The entire Pensacola Mountains were mapped by the U.S. Geological Survey in 1967 and 1968 from ground surveys and U.S. Navy tricamera aerial photographs taken in 1964. The range covers and its highest point is England Peak, at . Other notable local terrain features include Kelley Spur, a rock spur east of Spear Spur on the south side of Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dufek Head
Dufek Head () is an ice-covered headland northeast of Tyree Head in southern Ross Island. The headland rises to at the east side of the terminus of Aurora Glacier. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (2000) in association with Tyree Head, after Rear Admiral George J. Dufek, U.S. Navy, Commander of the U.S. Naval Support Force Antarctica, 1954–1959. Dufek Coast, Dufek Massif, and Dufek Mountain Dufek may refer to: * 3781 Dufek, a minor planet named after George Dufek * Dufek Coast in Antarctica, named after U.S. Rear Admiral George J. Dufek * Dufek Head, a headland in Antarctica * Dufek Massif in the Pensacola Mountains of Antarctica * Du ... are also named for Dufek. References Headlands of Ross Island {{RossIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
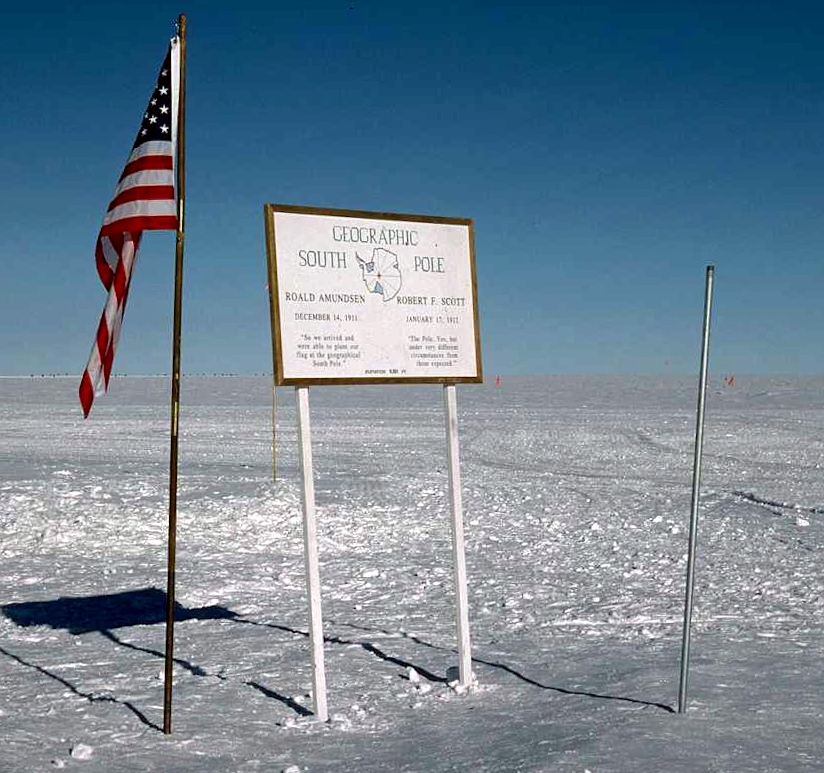
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipodally on the opposite side of Earth from the North Pole, at a distance of 12,430 miles (20,004 km) in all directions. Situated on the continent of Antarctica, it is the site of the United States Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, which was established in 1956 and has been permanently staffed since that year. The Geographic South Pole is distinct from the South Magnetic Pole, the position of which is defined based on Earth's magnetic field. The South Pole is at the centre of the Southern Hemisphere. Geography For most purposes, the Geographic South Pole is defined as the southern point of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface (the other being the Geographic North Pole). However, Earth's axis of rotat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Sound
McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica. It is the southernmost navigable body of water in the world, and is about from the South Pole. Captain James Clark Ross discovered the sound in February 1841, and named it after Lt. Archibald McMurdo of HMS ''Terror''. The sound today serves as a resupply route for cargo ships and for airplanes that land on the floating ice airstrips near McMurdo Station. Physical characteristics Wildlife in the sound include killer whales, seals, Adélie penguins, and emperor penguins. Boundary and Extents The sound extends approximately 55 kilometers (34 mi) in length and width, and opens into the larger Ross Sea to the north. To the south, the sound is bounded by the Ross Ice Shelf cavity, to the west lies the Royal Society Range, and to the east is Ross Island. McMurdo Sound is separated from the McMurdo Ice Shelf (itself part of the Ross Ice Shelf) by the Haskell Strait. Winter Quarters Bay lies at the south end of the Sound, and is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conrad Shinn
Conrad may refer to: People * Conrad (name) Places United States * Conrad, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Conrad, Indiana, an unincorporated community * Conrad, Iowa, a city * Conrad, Montana, a city * Conrad Glacier, Washington Elsewhere * Conrad, Alberta, Canada, a former unincorporated community * Conrad Mountains, Queen Maud Land, Antarctica * Mount Conrad, Oates Land, Antarctica Businesses * Conrad Editora, a Brazilian publisher * Conrad Electronic, a German retailer * Conrad Hotels, the global luxury brand of Hilton Hotels * Conrad Models, a German manufacturer of diecast toys and promotional models Other uses * ''Conrad'' (comic strip) * CONRAD (organization), an American organization which promotes reproductive health in the developing world * ORP ''Conrad'', name of the cruiser HMS ''Danae'' (D44) while loaned to the Polish Navy (1944-1946) See also * Conradi * Conradin * Conradines * Conrads (other) * Corrado (other) * Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R4D Skytrain
The Douglas C-47 Skytrain or Dakota (RAF, RAAF, RCAF, RNZAF, and SAAF designation) is a military transport aircraft developed from the civilian Douglas DC-3 airliner. It was used extensively by the Allies during World War II and remained in front-line service with various military operators for many years.Parker 2013, pp. 13, 35, 37, 39, 45-47. Design and development The C-47 differed from the civilian DC-3 by way of numerous modifications, including being fitted with a cargo door, hoist attachment and strengthened floor - along with a shortened tail cone for glider-towing shackles, and an astrodome in the cabin roof.Wilson, Stewart. ''Aircraft of WWII''. Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd., 1998. . During World War II, the armed forces of many countries used the C-47 and modified DC-3s for the transport of troops, cargo, and wounded. The U.S. naval designation was R4D. More than 10,000 aircraft were produced in Long Beach and Santa Monica, California, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellsworth Station
Ellsworth Scientific Station ( es, Estación Científica Ellsworth, or simply ''Estación Ellsworth'' or ''Base Ellsworth'') was a permanent, all year-round originally American, then Argentine Antarctic scientific research station named after American polar explorer Lincoln Ellsworth. It was located on Gould Bay, on the Filchner Ice Shelf. It was shut down in 1962 over safety concerns due to it being built on increasingly unstable ice, which produced fast deterioration of its superstructures and endangered both personnel and equipment. History Ellsworth Station was built by United States Navy Seabees under the command of Captain Finn Ronne, with the support of the icebreakers USS ''Staten Island'' and USS ''Wyandot'', captained by Francis Gambacorta. The originally planned site for the station was Cape Adams, but when the terrain proved impractical due to huge ice cliffs, an alternate location on Gould Bay was selected, on the western coast of the Weddell Sea over the Filchner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallett Station
Cape Hallett is a snow-free area (Antarctic oasis) on the northern tip of the Hallett Peninsula on the Ross Sea coast of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Cape Adare lies to the north. History In 1956, during Operation Deep Freeze II, was damaged by an ice floe at Cape Hallett. Hallett Station The cape was the location of a joint scientific base, Hallett Station, between the United States and New Zealand during the International Geophysical Year of 1957, and was manned permanently until 1964, when there was a major fire. It was then used as a summer only base until 1973. The site is currently being remediated by removing hazardous materials: fuel, and oil stored in several large tanks. This is an ongoing project which will take several years to complete. Antarctic Specially Protected Area An area of 74 ha is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.106 because it contains habitats with a rich and diverse range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilkes Station
Wilkes Station was an Antarctic research station established 29 January 1957 by the United States as one of seven U.S. stations established for the International Geophysical Year (IGY) program in Antarctica. It was taken over by Australia on 7 February 1959. History Navy personnel from the United States constructed the main part of Wilkes in a period of 16 days in January and February 1957, unloading 11,000 tons of material and supplies. It took a crew of over 100 to erect the station which housed 24 naval personnel and scientists for the next 18 months. As this was the time of the Cold War, there was considerable concern by the United States and Australia about Russian activity in Antarctica. Wilkes was seen to be strategically located because of its proximity to the south magnetic pole. Australia assumed custody of Wilkes, which remained the property of the U.S. State Department, in February 1959. Although Australia officially took over the operational command, the remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


