|
Dryopithecini
Dryopithecini is an extinct tribe of Eurasian and African great apes that are believed to be close to the ancestry of gorillas, chimpanzees and humans. Members of this tribe are known as dryopithecines. Taxonomy * Tribe Dryopithecini † ** ''Kenyapithecus'' *** ''Kenyapithecus wickeri'' **'' Danuvius'' *** ''Danuvius guggenmosi'' ** ''Ouranopithecus'' *** ''Ouranopithecus macedoniensis'' *** ''Ouranopithecus turkae'' ** ''Otavipithecus'' *** ''Otavipithecus namibiensis'' ** ''Oreopithecus'' *** ''Oreopithecus bambolii'' ** ''Nakalipithecus'' *** ''Nakalipithecus nakayamai'' ** ''Anoiapithecus'' *** ''Anoiapithecus brevirostris'' ** ''Dryopithecus'' *** ''Dryopithecus wuduensis'' *** ''Dryopithecus fontani'' ** ''Hispanopithecus'' *** ''Hispanopithecus laietanus'' *** ''Hispanopithecus crusafonti'' ** '' Neopithecus'' *** ''Neopithecus brancoi'' ** ''Pierolapithecus'' *** ''Pierolapithecus catalaunicus'' ** ''Rudapithecus'' *** ''Rudapithecus hungaricus'' ** ''Samburupithecus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryopithecus
''Dryopithecus'' is a genus of extinct great apes from the middle–late Miocene boundary of Europe 12.5 to 11.1 million years ago (mya). Since its discovery in 1856, the genus has been subject to taxonomic turmoil, with numerous new species being described from single remains based on minute differences amongst each other, and the fragmentary nature of the holotype specimen makes differentiating remains difficult. There is currently only one uncontested species, the type species ''D. fontani'', though there may be more. The genus is placed into the tribe Dryopithecini, which is either an offshoot of orangutans, African apes, or is its own separate branch. A male specimen was estimated to have weighed in life. ''Dryopithecus'' likely predominantly ate ripe fruit from trees, suggesting a degree of suspensory behaviour to reach them, though the anatomy of a humerus and femur suggest a greater reliance on walking on all fours (quadrupedalism). The face was similar to gorillas, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouranopithecus
''Ouranopithecus'' ("celestial ape" from Ancient Greek οὐρανός (ouranós), "sky, heaven" + πίθηκος (píthēkos),"ape") is a genus of extinct Eurasian great ape represented by two species, ''Ouranopithecus macedoniensis'', a late Miocene (9.6–8.7 mya) hominoid from Greece and ''Ouranopithecus turkae'', also from the late Miocene (8.7–7.4 mya) of Turkey. The first specimen ''O. macedoniensis'' was discovered by French palaeontologists Louis de Bonis and Jean Melentis in 1977, and ''O. turkae'' by Turkish team led by Erksin Savaş Güleç in 2007. For a long time it was considered as similar (synonymous) to ''Graecopithecus'' and member of the genus ''Sivapithecus,'' which more discoveries proved otherwise. Description and systematics Based on ''O. macedoniensis dental and facial anatomy, it has been suggested that ''Ouranopithecus'' was actually a dryopithecine. However, it is probably more closely related to the Ponginae. Some researchers consider ''O. macedon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
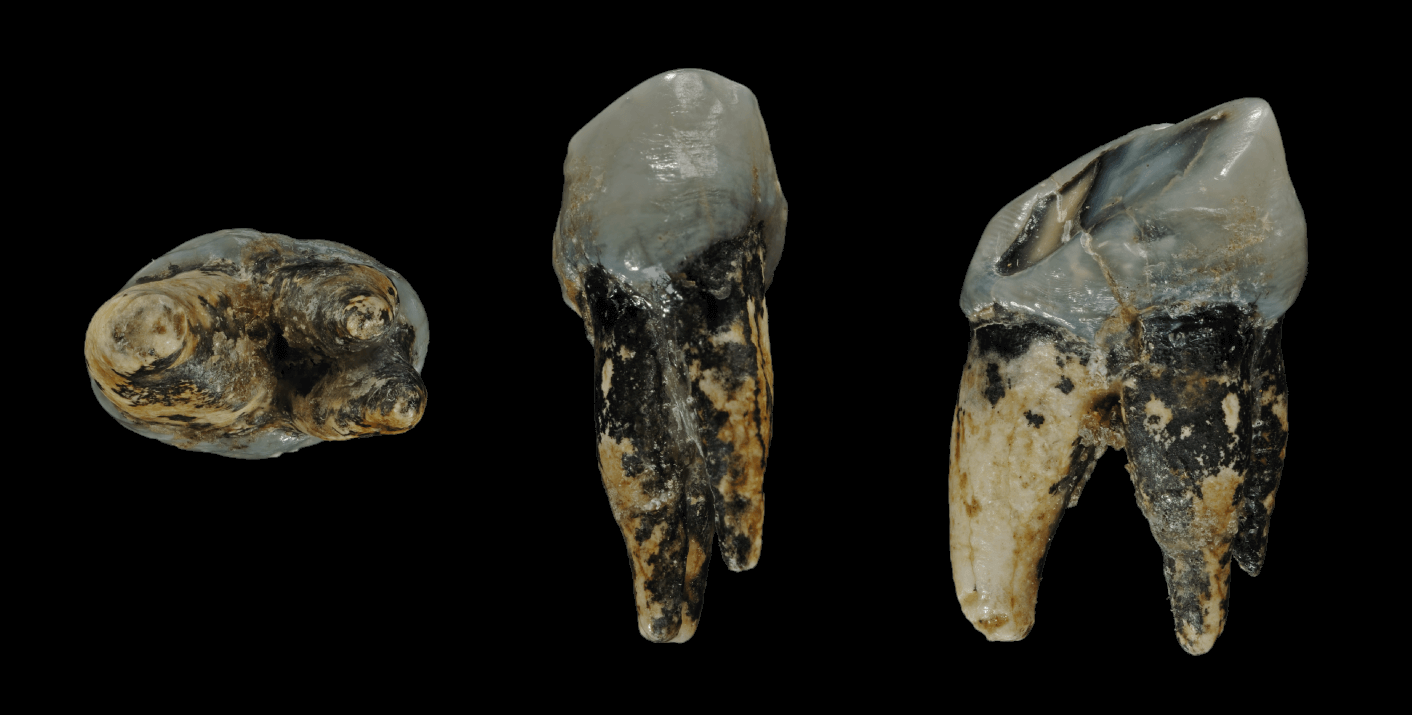
Graecopithecus
''Graecopithecus'' is an extinct species of hominid that lived in southeast Europe during the late Miocene around 7.2 million years ago. Originally identified by a single lower jaw bone bearing a molar tooth found in Pyrgos Vasilissis, Athens, Greece, in 1944, other tooth specimens were discovered from Azmaka quarry in Bulgaria in 2012. With only little and badly preserved materials to reveal its nature, it is considered as "the most poorly known European Miocene hominoids." The creature was popularly nicknamed 'El Graeco' (word play on the Spanish painter El Greco) by scientists. In 2017, an international team of palaeontologists led by Madelaine Böhme of the Eberhard-Karls-University Tübingen, Germany, published a detailed analysis of the teeth and age of the specimens, and came to the conclusion that it could be the oldest hominin, meaning that it could be the oldest direct ancestors of humans after splitting from that of the chimpanzees. Their simultaneous study also clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene First Appearances
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Apes
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griphopithecus Suessi
''Griphopithecus suessi'' is a prehistoric species of kenyapith hominid from the Miocene of Austria and Slovakia, dated to approximately 15 million years ago. ''G. suessi'' is based on a single lower molar, with three other isolated teeth and two fragmentary pieces of postcrania referred to it. ''Austriacopithecus'' is a synonym. ''G. suessi'' has an estimated mean body weight of 48 kg, similar to that observed in the common chimpanzee The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative th .... References Miocene primates of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1902 Prehistoric Germany Prehistoric Austria Prehistoric Slovakia Fossils of Austria {{paleo-primate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griphopithecus Alpani
''Griphopithecus alpani'' is a species of prehistoric ape from the Miocene of Turkey Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in .... References Miocene primates of Asia Fossil taxa described in 1974 Prehistoric Anatolia {{paleo-primate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouranopithecus Turkae
''Ouranopithecus turkae'' is a prehistoric species of ''Ouranopithecus'' from the Late Miocene of Turkey. This is known from the Corakyerler locality, central Anatolia. It is known only from three cranial fossils. Dated faunal remains associated with the ''O. turkae'' fossils have been attributed to the late Miocene 8.7 – 7.4 million years ago, making ''O. turkae'' one of the youngest Eurasian great apes ever known. Etymology ''Ouranopithecus'' due to its similarities with its probable sister taxon '' O. macedoniensis''. ''Turkae'' after the discovery of the holotype fossils in the Republic of Turkey. Habitat Associated faunal remains suggest ''O. turkae'' lived in either open woodland or an open savannah type environment. Morphology The morphology of ''O. turkae'' is difficult to determine due to the complete lack of post-cranial remains. The post-canine dentary is second only to that of Gigantopithecus in size, perhaps suggesting a large body size. It is unknown whether th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouranopithecus Macedoniensis
''Ouranopithecus macedoniensis'' is a prehistoric species of ''Ouranopithecus'' from the Late Miocene of Greece. See more detail at ''Ouranopithecus''. This species is known from three localities in Northern Greece. The type location is Ravin de la Pluie. The other localities are Chalkidiki and Xirochori. It is known from a large collection of cranial fossils and few postcranial. The material has been dated to the late Miocene 9.6 – 8.7 million years old, so slightly earlier than '' O. turkae''. To some this suggests ''O. turkae'' is the direct descendant of ''O. macedoniensis'', although it is generally accepted that they are sister taxa. Etymology The specific epithet ''macedoniensis'' is due to the holotype fossil's discovery location in Macedonia, Greece. Habitat Examination of dental remains of ''O. macedoniensis'' and associated bovid species indicate a habitat of low tree cover and a rich herbaceous layer. Morphology ''O. macedoniensis'' had a large, broad face with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 12.779. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the mass media, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)