|
Dresden Basin
The Dresden BasinDickinson (1964). pp. 624-625. (german: (Dresdner) Elbtalkessel or ''Dresdner Elbtalweitung'') is a roughly 45 km long and 10 km wide area of the Elbe Valley between the towns of Pirna and Meißen.Elkins (1972), pp. 293-4. The city of Dresden lies in the Dresden Basin. Geography The Dresden Basin is formed by the foothills and flanks of the Eastern Ore Mountains and western Lusatian Highlands and the northwestern slopes of Saxon Switzerland. Geologically it is a rift valley and its most important river, the Elbe flows through it in wide meanders. The region is climatically milder than the surrounding area, so that on the northern slopes of the hills vineyards may be cultivated (Saxon Wine Route). In addition, there is intensive fruit farming. The valley climate is significantly drier (average annual precipitation below 700 mm) and warmer (average air temperature 8.5 °C, in Dresden city centre 9.9 °C) than the surrounding hills. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lange Diercke Sachsen Dresden Und Umgegend
Lange may refer to: People *Lange (surname), a German surname *Lange (musician) (born 1974), British DJ *Lange (Brazilian footballer) (born 1966), Brazilian footballer Companies * Lange (ski boots), a producer of ski boots used in alpine (downhill) skiing * Lange Aviation, manufacturer of gliders * Lange Textbooks, an imprint of McGraw-Hill Education * A. Lange & Söhne, watchmakers Places * Lange (crater), a crater on Mercury * Lange Island, Bastian Islands * Lange Peak, Antarctica * Lange, Estonia, village in Haaslava Parish, Tartu County, Estonia * Lange, Western Australia * Langhe, a region in Piedmont, Italy * Lange, a tributary of the Oker in Germany * ''Lange Eylant'', the Dutch term for Long Island See also *Lang (other) *Laing (other) Laing may refer to: People *Laing (surname),_a_Scottish_surname _Companies *Arriva_UK_Trains.html" ;"title="ong (Scots lang) but this is a mispronounciatio ..., a Scottish surname Companies *Arriva UK Trains">ong ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards are often characterised by their ''terroir'', a French term loosely translating as "a sense of place" that refers to the specific geographical and geological characteristics of grapevine plantations, which may be imparted to the wine itself. History The earliest evidence of wine production dates from between 6000 and 5000 BC. Wine making technology improved considerably with the ancient Greeks but it wasn't until the end of the Roman Empire that cultivation techniques as we know them were common throughout Europe. In medieval Europe the Church was a staunch supporter of wine, which was necessary for the celebration of the Mass. During the lengthy instability of the Middle Ages, the monasteries maintained and developed viticultural prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of , and the sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants. The term Saxony has been in use for more than a millennium. It was used for the medieval Duchy of Saxony, the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Saxony, and twice for a republic. The first Free State of Saxony was established in 1918 as a constituent state of the Weimar Republic. After World War II, it was under Soviet occupation before it became part of the communist East Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Regions Of Germany
This division of Germany into major natural regions takes account primarily of geomorphological, geological, hydrological, and pedological criteria in order to divide the country into large, physical units with a common geographical basis. Political boundaries play no part in this, apart from defining the national border. In addition to a division of Germany by ''natural regions'', the federal authorities have also produced a division by so-called ''landscape areas (Landschaftsräume)'' that is based more on human utilisation of various regions and so has clearly different boundaries. Groundwork by the Federal Institute of Regional Studies (BfL) The natural region classification of Germany, as used today by the Federal Office for Nature Conservation (''Bundesamt für Naturschutz'' or BfN) and by most state institutions, is largely based on the work in producing the Handbook of Natural Region Divisions of Germany between the years 1953 to 1962. This divided the present federal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
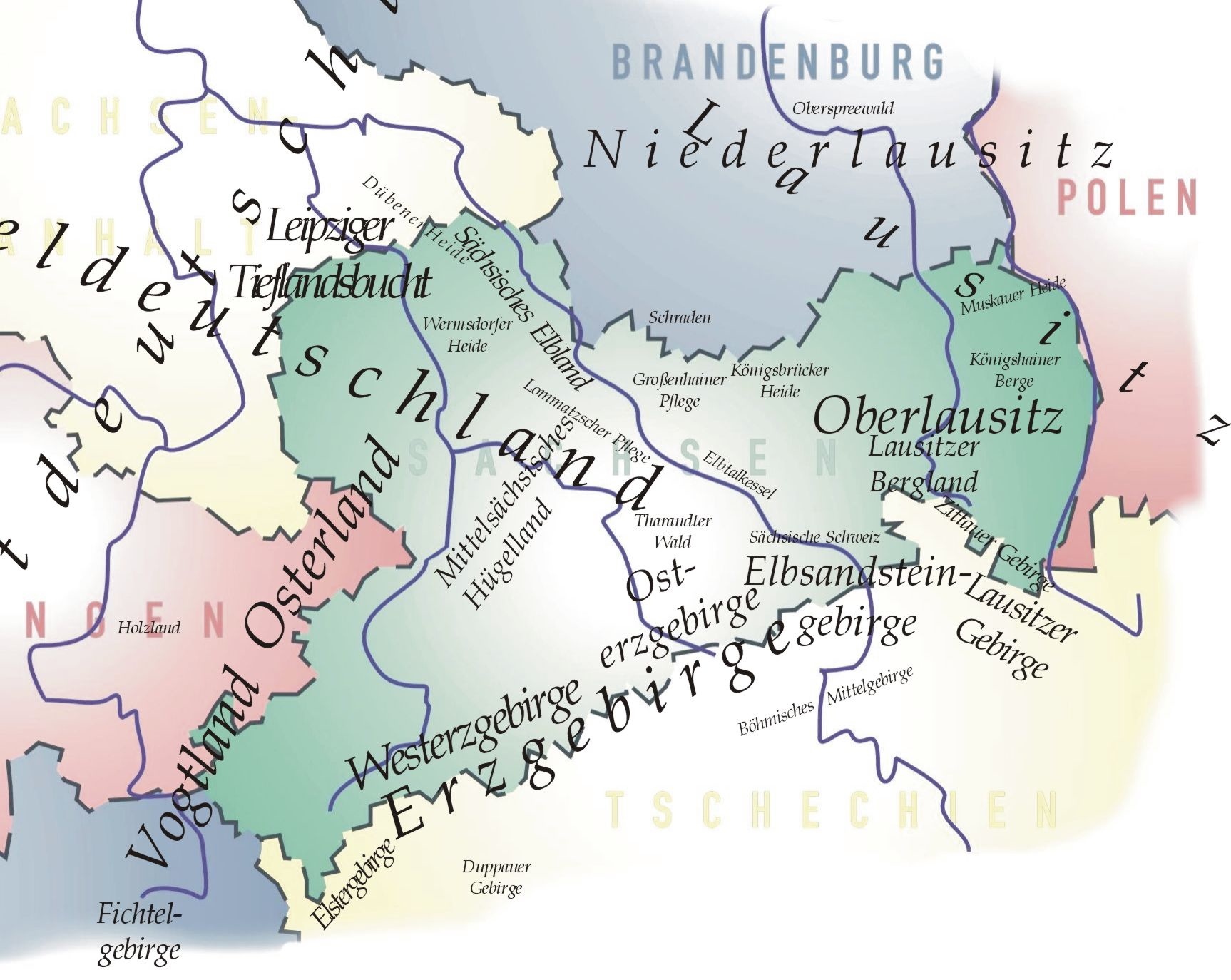
List Of Regions Of Saxony
A classification of the various regions of Saxony cannot be achieved in any uniform or standard way, as the commonly used names usually represent a mixture of historical regions and geographical features. Many well-known names of regions, such as Lusatia, comprise a mixture of natural habitats and geological zones, while other, scientifically assigned, names are only known in university departments. The following list contains, in alphabetical order, both those names that are commonly used, as well as those only known regionally or used in the scientific field. They are listed by their English names with their German names in brackets. Names of settlements or other geographic features are omitted here. Overall, across much of the area, Saxony belongs both to Eastern Germany and Central Germany. However, on a smaller scale there are many regions and landscapes that overlap the boundaries of the Free State and extend beyond it: * Bahra Valley (''Bahratal'') * Biela Valley (''Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coswig (Sachsen)
Coswig (; hsb, Kosowiki) is a town in the district of Meißen, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the right bank of the Elbe, approximately 9 km southeast of Meißen, and 13 km northwest of Dresden. It is the home of Fachkrankenhaus Coswig, a hospital specializing in thoracic surgery. The town can be reached from Dresden by Dresdner Verkehrsbetriebe's tram route 4, or from both Dresden and Meißen by Dresden S-Bahn line S1 and further regional railway lines at Coswig's railway station. Sights *Villa Teresa, the home of Eugene d'Albert and Teresa Carreño in Coswig, now a museum Twin towns – sister cities Coswig is twinned with: * Lovosice, Czech Republic * Ravensburg, Germany Notable people *Monika Mrklas (born 1942), cross-country skier and cyclist *Hans-Ulrich Thomale (born 1944), footballer and coach *Heinz Werner (1928–2019), porcelain artist Associated with Coswig *Teresa Carreño (1853–1917), pianist, composer *Eugene d'Albert Eugen (origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radebeul
Radebeul ( hsb, Radobyle) is a town (''große Kreisstadt'') in the Elbe valley in the district of Meißen (district), Meißen in Saxony, Germany, a suburb of Dresden. It is well known for its viticulture, a museum dedicated to writer Karl May, and a narrow gauge railway connecting Radebeul with the castle of Moritzburg, Saxony, Moritzburg and the town of Radeburg. The Meißen area, where Radebeul is located, is one of the northeasternmost areas where wine is grown in the 21st century. It is sometimes called the "Nice of Saxony" for its pleasant landscape and mild climate. History A village Radebeul was first mentioned in 1349. In 1905 it absorbed the neighboring village of Serkowitz. On April 1, 1924 Radebeul became a town. Meanwhile, the neighboring village of Kötzschenbroda had taken over Lindenau in 1920, and Naundorf, Zitzschewig und Niederlößnitz by 1924, when it was made a town as well. In 1934 Wahnsdorf and Oberlößnitz joined Radebeul, and on January 1, 1935 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidenau (Sachsen)
Heidenau is a town in the Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge district, in Saxony, Germany. The town is situated on the left bank of the Elbe, 13 km southeast of Dresden Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ... (centre). In 2015, it became known for riots by local far-right forces against the arrival of refugees. In August 2015, authorities were forced to impose a temporary ban on assemblies in Heidenau due to continuous harassment of asylum-seekers. References External links * Populated riverside places in Germany Populated places on the Elbe {{SächsischeSchweizOsterzgebirge-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was established i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Educational, Scientific And Cultural Organization
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain " cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
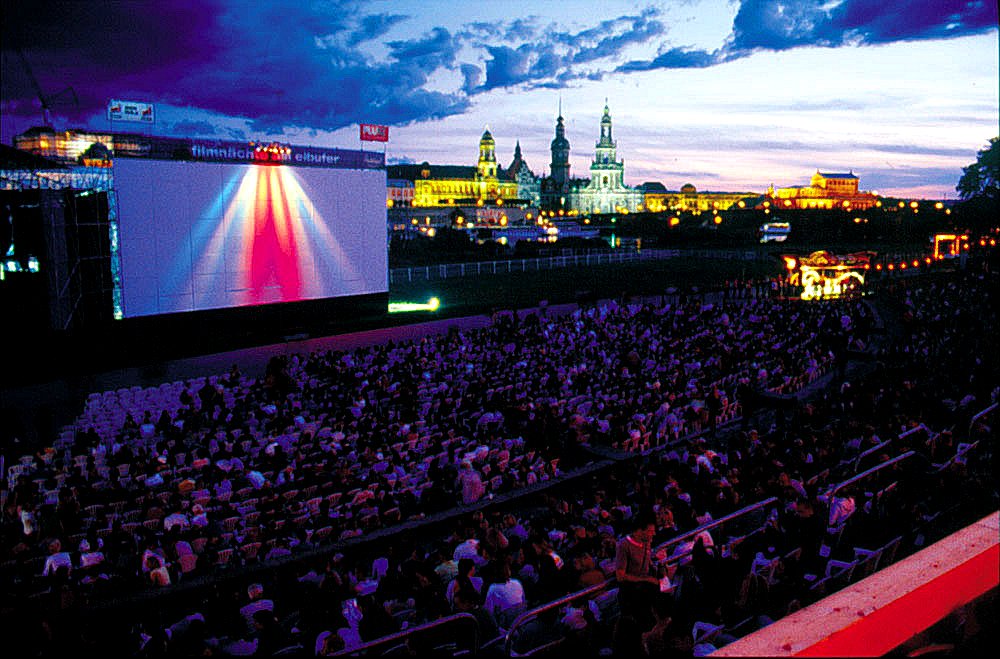
Dresden Elbe Valley
The Dresden Elbe Valley is a cultural landscape and former World Heritage Site stretching along the Elbe river in Dresden, the state capital of Saxony, Germany. The valley, extending for some and passing through the Dresden Basin, is one of two major cultural landscapes built up over the centuries along the Central European river Elbe, along with the Dessau-Wörlitz Garden Realm downstream. With respect to its scenic and architectural values, including the Dresden urban area as well as natural river banks and slopes, the Elbe Valley was entered on the World Heritage Site list of the UNESCO in 2004. However, in July 2006 it was designated a World Heritage in Danger and finally delisted in June 2009, in the course of the construction of the Waldschlösschen Bridge river crossing. Description The cultural landscape comprises the Dresden urban area along the Elbe meanders, stretching from the Loschwitz district in the southeast down to the Ostragehege plains in the northwest. The fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |