|
Dravyasamgraha Front
' (Devnagari: द्रव्यसंग्रह) (Compendium of substances) is a 10th-century Jain text in Jain Sauraseni Prakrit by Acharya Nemicandra belonging to the Digambara Jain tradition. It is a composition of 58 ''gathas'' (verses) giving an exposition of the six '' dravyas'' (substances) that characterize the Jain view of the world: sentient ''( jīva)'', non-sentient ''(pudgala)'', principle of motion ''(dharma)'', principle of rest ''(adharma)'', space ''(ākāśa)'' and time ''(kāla)''.Acarya Nemicandra; Nalini Balbir (2010) p. 1 of Introduction It is one of the most important Jain works and has gained widespread popularity. ' has played an important role in Jain education and is often memorized because of its comprehensiveness as well as brevity. Author 10th century Jain Acarya, Nemicandra Siddhānta Cakravartin is regarded as the author of '. He was the teacher of Camundaraya—the general of the Western Ganga Dynasty of Karnataka. Nemicandra was a proli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahāvīra, Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''Ahimsa in Jainism, ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''Achourya, asteya'' (not stealing), ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahubali
Bahubali (), a much revered figure among Jains, was the son of Rishabadeva (the first ''tirthankara'' of Jainism) and the brother of Bharata Chakravartin. He is said to have meditated motionless for a year in a standing posture (''kayotsarga'') and that during this time, climbing plants grew around his legs. After his one year of meditation, Bahubali is said to have attained omniscience ('' Kevala Gyana''). Bahubali's other names are Kammateswara, Gommateshwara because of the Gommateshwara statue dedicated to him. Legends The '' Adipurana'', a 9th-century Sanskrit poem, deals with the ten lives of the first ''tirthankara'', Rishabhanatha and his two sons Bharata and Bahubali. It was composed by Jinasena, a ''Digambara monk''. Family life According to Jain texts, Bahubali was born to Rishabhanatha and Sunanda during the Ikshvaku dynasty in Ayodhya. He is said to have excelled in studying medicine, archery, floriculture, and the knowledge of precious gems. Bahubali had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karma In Jainism
Karma is the basic principle within an overarching psycho-cosmology in Jainism. Human moral actions form the basis of the transmigration of the soul ('). The soul is constrained to a cycle of rebirth, trapped within the temporal world ('), until it finally achieves liberation ('). Liberation is achieved by following a path of purification. Jains believe that karma is a physical substance that is everywhere in the universe. Karma particles are attracted to the soul by the actions of that soul. Karma particles are attracted when we do, think, or say things, when we kill something, when we lie, when we steal and so on. Karma not only encompasses the causality of transmigration, but is also conceived of as an extremely subtle matter, which infiltrates the soul—obscuring its natural, transparent and pure qualities. Karma is thought of as a kind of pollution, that taints the soul with various colours ('' leśyā''). Based on its karma, a soul undergoes transmigration and reinca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajiva
''Ajiva'' (Sanskrit) is anything that has no soul or life, the polar opposite of " jīva" (soul). Because ''ajiva'' has no life, it does not accumulate ''karma'' and cannot die. Examples of ajiva include chairs, computers, paper, plastic, etc. Five categories of Ajiva In Jainism, there are five categories which ''ajīva'' can be placed into. Out of these, four categories, ''Dharma'' (medium of motion), ''Adharma'' (medium of rest), ''Akasha'' (space) and ''Pudgala'' (matter) are described as the ''asti-kaya dravya's'' (substances which possess constituent parts extending in space) while the fifth category ''Kala'' is an ''anasti-kaya dravya'' (which has no extension in space). Dharma-Astikaya Dharmastikaya is formed from the two words: Dharma & Astikaya. Dharma here isn't referring to religion, but instead its referring to the medium of motion. Astikay itself is formed of two words: Asti & Kaya. Asti means space, body or mode and Kaya means collection. So Astikaya means a col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiva
''Jiva'' ( sa, जीव, IAST: ) is a living being or any entity imbued with a life force in Hinduism and Jīva (Jainism), Jainism. The word itself originates from the Sanskrit verb-root ''jīv'', which translates as 'to breathe' or 'to live'. The ''jiva'', as a metaphysical entity, has been described in various scriptures such as the Bhagavad Gita and the Upanishads. Each subschool of Vedanta describes the role of the ''jiva'' with the other metaphysical entities in varying capacities. Described in the scriptures A common metaphysical entity discussed in the scriptures (such as the Bhagavad Gita, Upanishad and Vachanamrut) in the seven schools of Vedanta is the ''jiva'' or Ātman (Hinduism), ''atman'': the soul or self. Bhagavad Gita Chapter 2 of the Bhagavad Gita contains verses describing the ''jiva''. For example, the ''jiva'' is described as eternal and indestructible in chapter 2, verse 20: Upanishads बालाग्रशतभागस्य शतधा � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
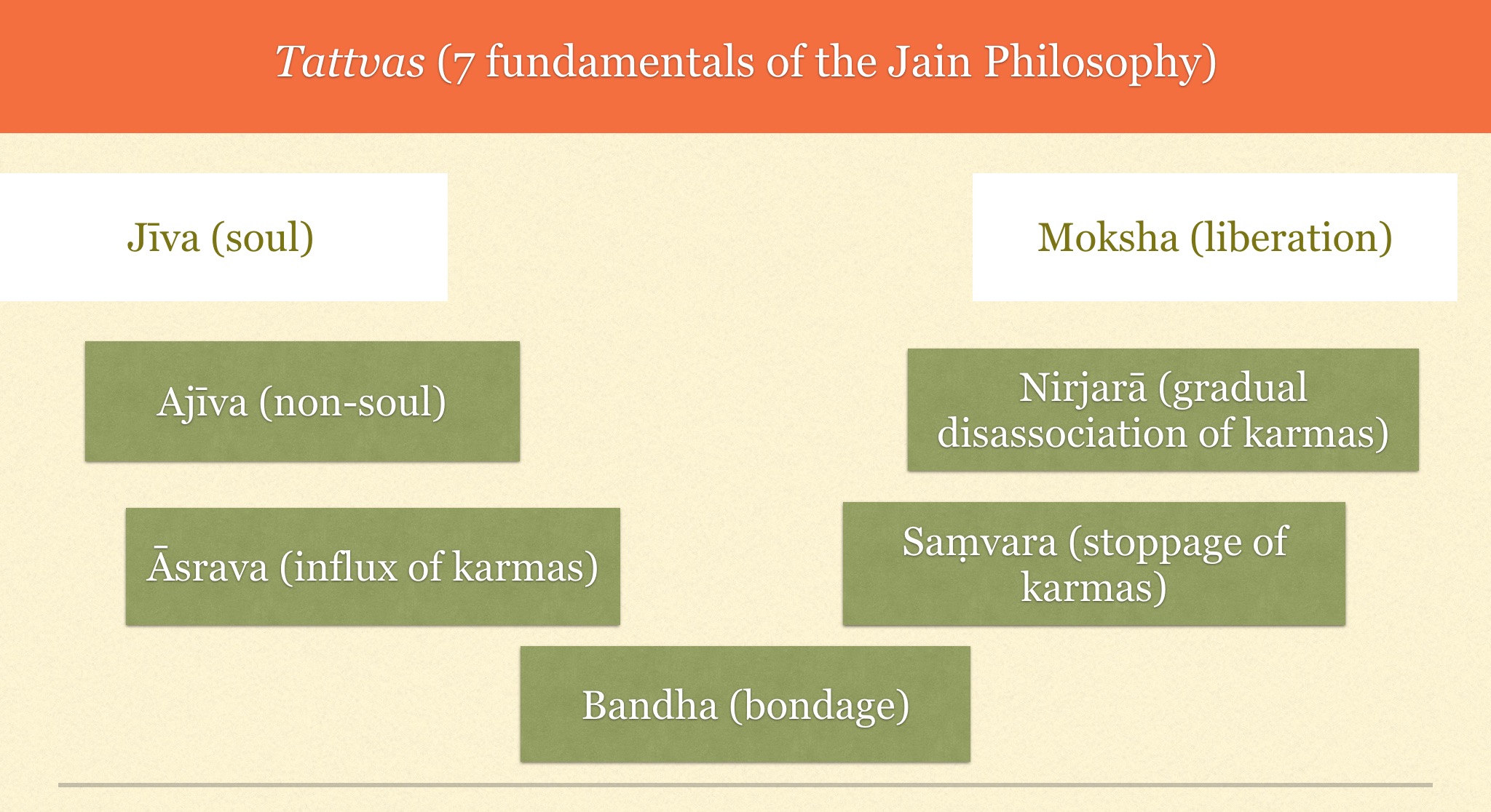
Tattva (Jainism)
Jain philosophy explains that seven ''tattva'' (truths or fundamental principles) constitute reality. These are:— #'' jīva''- the soul which is characterized by consciousness #''ajīva''- the non-soul #''āsrava'' (influx)- inflow of auspicious and evil karmic matter into the soul. #''bandha'' (bondage)- mutual intermingling of the soul and ''karmas''. #''samvara'' (stoppage)- obstruction of the inflow of karmic matter into the soul. #''nirjara'' (gradual dissociation)- separation or falling-off of part of karmic matter from the soul. #''mokṣha'' (liberation)- complete annihilation of all karmic matter (bound with any particular soul). The knowledge of these reals is said to be essential for the liberation of the soul. However, as per one sect of Jain i.e. Shwetamber (Sthanakwasi), there are total nine tattva (truths or fundamental principles). Seven tattva are same as above but 2 more tattva are there namely: Overview The first two are the two ontological catego ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arya Meter
''Āryā meter'' is a meter used in Sanskrit, Prakrit and Marathi verses. A verse in metre is in four metrical lines called ''pāda''s. Unlike the majority of meters employed in classical Sanskrit, the meter is based on the number of s (morae) per . A short syllable counts for one , and a long syllable (that is, one containing a long vowel, or a short vowel followed by two consonants) counts for two s. It is believed that meter was taken from the gatha meter of Prakrit. metre is common in Jain Prakrit texts and hence considered as favourite metre of early authors of Jainism. The earlier form of the metre is called old , which occurs in a some very early Prakrit and Pàli texts. Āryā The basic verse has 12, 18, 12 and 15 s in the first, second, third, and fourth ''pāda''s respectively. An example is the following from Kālidāsa's play ''Abhijñānaśākuntalam'' (c. 400 CE): : : : : : : : – u u , – – , u u – : u – u , – – , u – u , – – , – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nalini Balbir
Nalini Balbir (born 1955) is a French Indologist who lives in Paris. She is a scholar of Sanskrit, Prakrit, Pali, Jainism, Buddhism and Hinduism. She was a direct student of Indologist Colette Caillat. She is known for her work on the publication of the Catalogue of the Jain Manuscripts of the British Library published by the Institute of Jainology. Biography Nalini Balbir was born of a French mother and an Indian father. She started her career as a teacher of French, Latin and Greek in secondary schools (1977 to 1980), before completing her PhD in Indian Studies (Études indiennes) with the edition and annotated translation of the ''Danastaka-katha'', a book of Jain narratives in Sanskrit, which was published in 1982. Between 1982-1988 she was a Research scholar in the Centre national de la recherche scientifique, where she completed her DLitt in Indian Studies with a magisterial work on the complex Jaina ''Avasyaka'' literature which was published in 1993 under the title ''Avasy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancastikayasara
''Pañcastikayasara'' (en: the essence of reality), is an ancient Jain text authored by Acharya Kundakunda. Kundakunda explains the Jain concepts of ''dravya'' (substance) and Ethics. The work serves as a brief version of the Jaina philosophy. There are total 180 verses written in Prakrit language. The text is about five (''panch'') ''āstikāya'', substances that have both characteristics, viz. existence as well as body. Āstikāya The five ''āstikāya'' mentioned in the text are :— # Jīva (soul), # Pudgala (matter), #Dharma (medium of motion), #''Adharma Adharma is the Sanskrit antonym of dharma. It means "that which is not in accord with the dharma". Connotations include betrayal, discord, disharmony, unnaturalness, wrongness, evil, immorality, unrighteousness, wickedness, and vice..In Indian ...'' (medium of rest), and # Akasa (space) Notes References * * {{Jainism Topics Atomism Jain texts Ancient Indian literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kundakunda
Kundakunda was a Digambara Jain monk and philosopher, who likely lived in the 2nd CE century CE or later. His date of birth is māgha māsa, śukla pakṣa, pañcamī tithi, on the day of Vasant Panchami. He authored many Jain texts such as: '' Samayasara, Niyamasara, Pancastikayasara, Pravachanasara, Astapahuda'' and ''Barasanuvekkha''. He occupies the highest place in the tradition of the Digambara Jain acharyas. All Digambara Jains say his name before starting to read the scripture. He spent most of his time at Ponnur Hills, Tamil Nadu and later part of life at Kundadri, Shimoga, Karnataka, Names His proper name was ''Padmanandin'', he is popularly referred to as Kundakunda possibly because the modern village of Konakondla in Anantapur district of Andhra Pradesh which is his birth place. He is also presumed to be the one being alluded to by names such as ''Elacarya'', ''Vakragriva'', ''Grdhrapiccha'' or ''Mahamati''. He is also called Thiruvalluvar, the author of tamil cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattvarthasutra
''Tattvārthasūtra'', meaning "On the Nature '' ''artha">nowiki/>''artha''.html" ;"title="artha.html" ;"title="nowiki/>''artha">nowiki/>''artha''">artha.html" ;"title="nowiki/>''artha">nowiki/>''artha''of Reality [''tattva'']" (also known as ''Tattvarth-adhigama-sutra'' or ''Moksha-shastra'') is an ancient Jain text written by ''Acharya (Jainism), Acharya'' Umaswami in Sanskrit, sometime between the 2nd- and 5th-century CE. The ''Tattvārthasūtra'' is regarded as one of the earliest, most authoritative texts in Jainism. It is accepted as authoritative in both its major sub-traditions – ''Digambara'' and ''Śvētāmbara'' – as well as the minor sub-traditions. It is a philosophical text, and its importance in Jainism is comparable with that of the ''Brahma Sutras'' and ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali'' in Hinduism. In an aphoristic sutra style of ancient Indian texts, it presents the complete Jainism philosophy in 350 sutras over 10 chapters. The text has attracted numerous c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |