|
Double Layer Forces
Double layer forces occur between charged objects across liquids, typically water. This force acts over distances that are comparable to the Debye length, which is on the order of one to a few tenths of nanometers. The strength of these forces increases with the magnitude of the surface charge density (or the electrical surface potential). For two similarly charged objects, this force is repulsive and decays exponentially at larger distances, see figure. For unequally charged objects and eventually at shorted distances, these forces may also be attractive. The theory due to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO) combines such double layer forces together with Van der Waals forces in order to estimate the actual interaction potential between colloidal particles.W. B. Russel, D. A. Saville, W. R. Schowalter, Colloidal Dispersions. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1989. An electrical double layer develops near charged surfaces (or another charged objects) in aqueous s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Layer Forces Salt Dependence 1
A double is a look-alike or doppelgänger; one person or being that resembles another. Double, The Double or Dubble may also refer to: Film and television * Double (filmmaking), someone who substitutes for the credited actor of a character * ''The Double'' (1934 film), a German crime comedy film * ''The Double'' (1971 film), an Italian film * ''The Double'' (2011 film), a spy thriller film * ''The Double'' (2013 film), a film based on the Dostoevsky novella * ''Kamen Rider Double'', a 2009–10 Japanese television series ** Kamen Rider Double (character), the protagonist in a Japanese television series of the same name Food and drink * Doppio, a double shot of espresso * Dubbel, a strong Belgian Trappist beer or, more generally, a strong brown ale * A drink order of two shots of hard liquor in one glass * A "double decker", a hamburger with two patties in a single bun Games * Double, action in games whereby a competitor raises the stakes ** , in contract bridge ** Doubling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superposition Principle
The superposition principle, also known as superposition property, states that, for all linear systems, the net response caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses that would have been caused by each stimulus individually. So that if input ''A'' produces response ''X'' and input ''B'' produces response ''Y'' then input (''A'' + ''B'') produces response (''X'' + ''Y''). A function F(x) that satisfies the superposition principle is called a linear function. Superposition can be defined by two simpler properties: additivity F(x_1+x_2)=F(x_1)+F(x_2) \, and homogeneity F(a x)=a F(x) \, for scalar . This principle has many applications in physics and engineering because many physical systems can be modeled as linear systems. For example, a beam can be modeled as a linear system where the input stimulus is the load on the beam and the output response is the deflection of the beam. The importance of linear systems is that they are easier to analyze mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micelle
A micelle () or micella () (plural micelles or micellae, respectively) is an aggregate (or supramolecular assembly) of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension (also known as associated colloidal system). A typical micelle in water forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the micelle centre. This phase is caused by the packing behavior of single-tail lipids in a bilayer. The difficulty filling all the volume of the interior of a bilayer, while accommodating the area per head group forced on the molecule by the hydration of the lipid head group, leads to the formation of the micelle. This type of micelle is known as a normal-phase micelle (oil-in-water micelle). Inverse micelles have the head groups at the centre with the tails extending out (water-in-oil micelle). Micelles are approximately spherical in shape. Other p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Deposition
Particle deposition is the spontaneous attachment of particles to surfaces. The particles in question are normally colloidal particles, while the surfaces involved may be planar, curved, or may represent particles much larger in size than the depositing ones (e.g., sand grains). Deposition processes may be triggered by appropriate hydrodynamic flow conditions and favorable particle-surface interactions. Depositing particles may just form a monolayer which further inhibits additional particle deposition, and thereby one refers to ''surface blocking''. Initially attached particles may also serve as seeds for further particle deposition, which leads to the formation of thicker particle deposits, and this process is termed as ''surface ripening'' or ''fouling''. While deposition processes are normally irreversible, initially deposited particles may also detach. The latter process is known as ''particle release'' and is often triggered by the addition of appropriate chemicals or a modific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloidal Crystal
A colloidal crystal is an ordered array of colloid particles and fine grained materials analogous to a standard crystal whose repeating subunits are atoms or molecules. A natural example of this phenomenon can be found in the gem opal, where spheres of silica assume a close-packed locally periodic structure under moderate compression. Bulk properties of a colloidal crystal depend on composition, particle size, packing arrangement, and degree of regularity. Applications include photonics, materials processing, and the study of self-assembly and phase transitions. Introduction A colloidal crystal is a highly ordered array of particles which can be formed over a long range (to about a centimeter). Arrays such as this appear to be analogous to their atomic or molecular counterparts with proper scaling considerations. A good natural example of this phenomenon can be found in precious opal, where brilliant regions of pure spectral color result from close-packed domains of colloidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Aggregation
Particle agglomeration refers to formation of assemblages in a suspension and represents a mechanism leading to the functional destabilization of colloidal systems. During this process, particles dispersed in the liquid phase stick to each other, and spontaneously form irregular particle assemblages, flocs, or agglomerates. This phenomenon is also referred to as coagulation or flocculation and such a suspension is also called ''unstable''. Particle agglomeration can be induced by adding salts or other chemicals referred to as coagulant or flocculant.M. Elimelech, J. Gregory, X. Jia, R. Williams, ''Particle Deposition and Aggregation: Measurement, Modelling and Simulation'', Butterworth-Heinemann, 1998. Particle agglomeration can be a reversible or irreversible process. Particle agglomerates defined as "hard agglomerates" are more difficult to redisperse to the initial single particles. In the course of agglomeration, the agglomerates will grow in size, and as a consequence they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels. The term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture (although a narrower sense of the word '' suspension'' is distinguished from colloids by larger particle size). A colloid has a dispersed phase (the suspended particles) and a continuous phase (the medium of suspension). The dispersed phase particles have a diameter of approximately 1 nanometre to 1 micrometre. Some colloids are translucent because of the Tyndall effect, which is the scattering of light by particles in the colloid. Other colloids may be opaque or have a slight color. Colloidal suspensions are the subject of interface and colloid science. This field of study was introduced in 1845 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolytes are polymers whose repeating units bear an electrolyte group. Polycations and polyanions are polyelectrolytes. These groups dissociate in aqueous solutions (water), making the polymers charged. Polyelectrolyte properties are thus similar to both electrolytes (salts) and polymers (high molecular weight compounds) and are sometimes called polysalts. Like salts, their solutions are electrically conductive. Like polymers, their solutions are often viscous. Charged molecular chains, commonly present in soft matter systems, play a fundamental role in determining structure, stability and the interactions of various molecular assemblies. Theoretical approaches to describing their statistical properties differ profoundly from those of their electrically neutral counterparts, while technological and industrial fields exploit their unique properties. Many biological molecules are polyelectrolytes. For instance, polypeptides, glycosaminoglycans, and DNA are polyelectrolytes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yukawa Potential
In particle, atomic and condensed matter physics, a Yukawa potential (also called a screened Coulomb potential) is a potential named after the Japanese physicist Hideki Yukawa. The potential is of the form: :V_\text(r)= -g^2\frac, where is a magnitude scaling constant, i.e. is the amplitude of potential, is the mass of the particle, is the radial distance to the particle, and is another scaling constant, so that r \approx \tfrac is the approximate range. The potential is monotonically increasing in and it is negative, implying the force is attractive. In the SI system, the unit of the Yukawa potential is (1/meters). The Coulomb potential of electromagnetism is an example of a Yukawa potential with the e^ factor equal to 1, everywhere. This can be interpreted as saying that the photon mass is equal to 0. The photon is the force-carrier between interacting, charged particles. In interactions between a meson field and a fermion field, the constant is equal to the gauge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Tweezers
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers. If the object is held in air or vacuum without additional support, it can be called optical levitation. The laser light provides an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the relative refractive index between particle and surrounding medium. Levitation is possible if the force of the light counters the force of gravity. The trapped particles are usually micron-sized, or even smaller. Dielectric and absorbing particles can be trapped, too. Optical tweezers are used in biology and medicine (for example to grab and hold a single bacterium, a cell like a sperm cell or a blood cell, or a molecule like DNA), nanoengineering and nanochemistry (to study and build materials fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
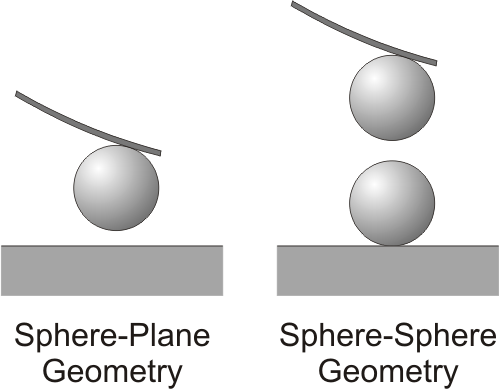
Colloidal Probe Technique
The colloidal probe technique is commonly used to measure interaction forces acting between colloidal particles and/or planar surfaces in air or in solution. This technique relies on the use of an atomic force microscope (AFM). However, instead of a cantilever with a sharp AFM tip, one uses the ''colloidal probe''. The colloidal probe consists of a colloidal particle of few micrometers in diameter that is attached to an AFM cantilever. The colloidal probe technique can be used in the ''sphere-plane'' or ''sphere-sphere'' geometries (''see figure''). One typically achieves a force resolution between 1 and 100 pN and a distance resolution between 0.5 and 2 nm. The colloidal probe technique has been developed in 1991 independently by Ducker and Butt. Since its development this tool has gained wide popularity in numerous research laboratories, and numerous reviews are available in the scientific literature. Alternative techniques to measure force between surfaces involve the surface f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |