|
Dombra
The ''dombra'', also known as ''dombyra'' ( kz, домбыра, uz, dombira, ba, думбыра) is a long-necked Kazakh, Uzbek and Bashkir lute and a musical string instrument. The dombyra shares certain characteristics with the komuz and dutar, such as its long, thin neck and oblong body shape. It is a popular instrument mostly among Turkic communities in Central Asian countries such as Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Afghanistan. Varieties The instrument differs slightly in different regions. The Kazakh dombyra has frets and is played by strumming with the hand or plucking each string individually, with an occasional tap on the main surface of the instrument. While the strings are traditionally made of sinew, modern dombras are usually produced using nylon strings. One of the greatest dombra players was the Kazakh folk musician and composer Kurmangazy Sagyrbayuly, who had a major influence on the development of Kazakh musical culture, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurmangazy Sagyrbaev
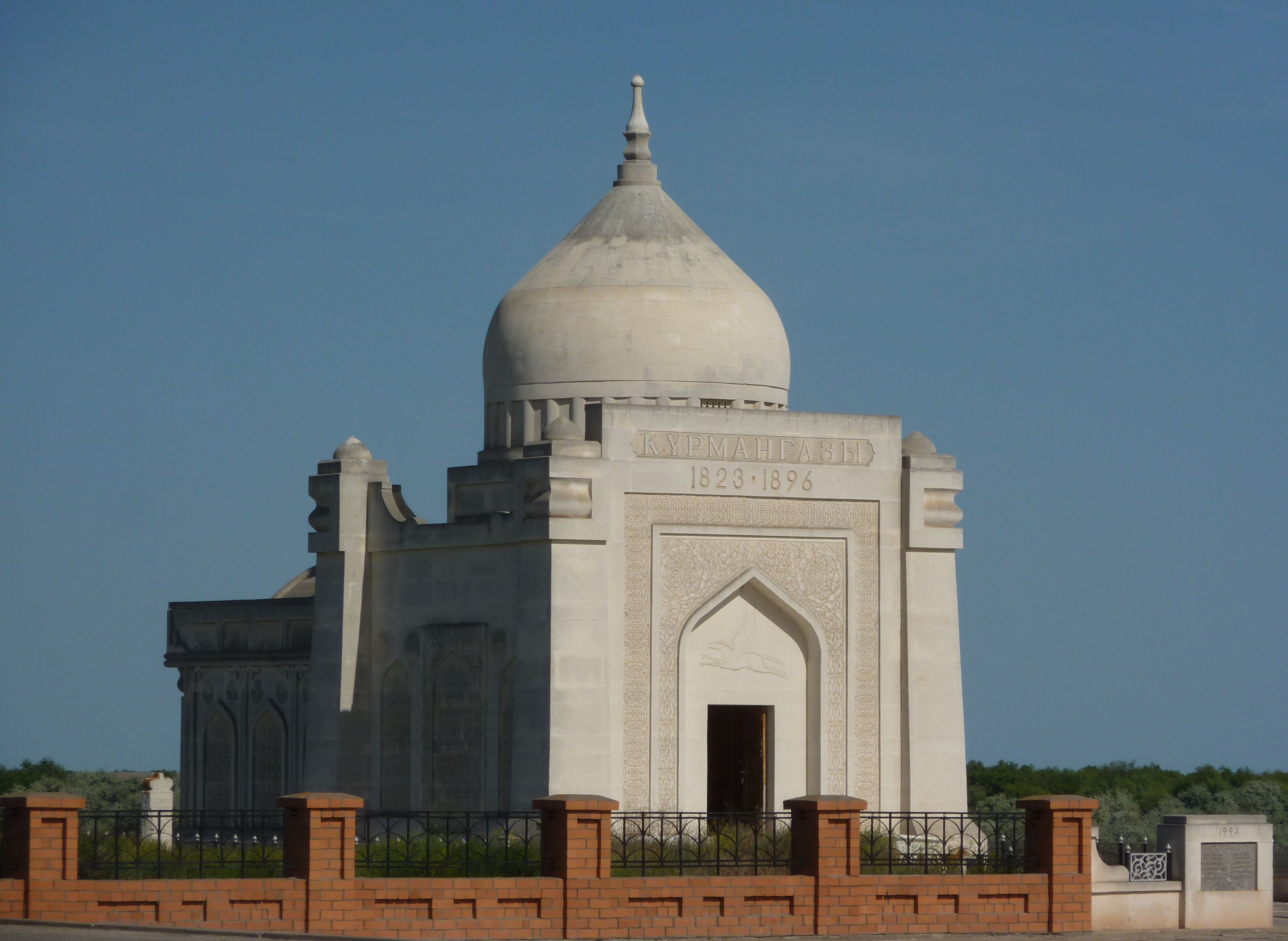
Kurmangazy Sagyrbaev ( kk, Құрманғазы Сағырбайұлы, ''Qūrmanğazy Sağyrbaıūly''; 1823–1896) was a Kazakhs, Kazakh composer, instrumentalist (kobyz, dombra), and folk artist. He influenced Kazakh musical culture. He was born in 1818 in the Bukey Horde (now Zhanakala District, West Kazakhstan Region). He is buried in the Astrakhan region of Lower Volga in today's Russian Federation. Legacy In 1993, Sagyrbaev's image has been used on the 5 Kazakhstani tenge banknote, and on a Khazakh stamp in 1998.Kazakhstan 5 Tenge Banknote.ws The Kazakh National Conservatory is officially named after Kurmangazy. References External links * 1823 births 1896 deaths 19th-century composers 19th-century male musicians Dombra players Kazakhstani co ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutar
The ''dutar'' (also ''dotar''; fa, دوتار, dutâr; russian: Дутар; tg, дутор; ug, دۇتار, ucy=Дутар, Dutar; uz, dutor; ; dng, Дутар) is a traditional Iranian long-necked two-stringed lute found in Iran and Central Asia. Its name comes from the Persian word for "two strings", دوتار ''do tār'' (< دو ''do'' "two",تار ''tār'' "string"), although the i dutar of has fourteen strings. Dutar is very popular in Tajikistan and Khorasan province of Iran. When played, the strings are usually plucked by the of Western China and strummed and plucked by the |
Kazakhs
The Kazakhs (also spelled Qazaqs; Kazakh: , , , , , ; the English name is transliterated from Russian; russian: казахи) are a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to northern parts of Central Asia, chiefly Kazakhstan, but also parts of northern Uzbekistan and the border regions of Russia, as well as Northwestern China (specifically Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture) and Mongolia (Bayan-Ölgii Province). The Kazakhs are descendants of the ancient Turkic Kipchaks, Kipchak tribes and the medieval Mongolic peoples, Mongolic tribes, and generally classified as Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol cultural group. Kazakh identity is of Middle Ages, medieval origin and was strongly shaped by the foundation of the Kazakh Khanate between 1456 and 1465, when following disintegration of the Golden Horde, several tribes under the rule of the sultans Janibek Khan, Janibek and Kerei Khan, Kerei departed from the Khanate of Abu'l-Khayr Khan in hopes of forming a powerful khanate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ... to Kazakhstan–Russia border, the north and west, China to China–Kazakhstan border, the east, Kyrgyzstan to Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border, the southeast, Uzbekistan to Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan border, the south, and Turkmenistan to Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border, the southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, known as Nur-Sultan from 2019 to 2022. Almaty, Kazakhstan's largest city, was the country's capital until 1997. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country, the largest and northernmost Muslim world, Muslim-majority cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asian
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peoples, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Uzbeks, Tatars, Turkmen, Kyrgyz, and Uyghurs; Turkic languages l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurmangazy Sagyrbayuly
Kurmangazy Sagyrbaev ( kk, Құрманғазы Сағырбайұлы, ''Qūrmanğazy Sağyrbaıūly''; 1823–1896) was a Kazakh composer, instrumentalist ( kobyz, dombra), and folk artist. He influenced Kazakh musical culture. He was born in 1818 in the Bukey Horde (now Zhanakala District, West Kazakhstan Region). He is buried in the Astrakhan region of Lower Volga in today's Russian Federation. Legacy In 1993, Sagyrbaev's image has been used on the 5 Kazakhstani tenge The tenge ( or ; kk, теңге, teñge, ; sign: ₸ ; code: KZT) is the currency of Kazakhstan. It is divided into 100 tiyn ( kk, тиын, tıyın also transliterated as ''tiyin''). History After the breakup of the Soviet Union in December ... banknote, and on a Khazakh stamp in 1998.Kazakhstan 5 Tenge Banknote.ws The Kazakh Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komuz
The komuz or qomuz ( ky, комуз , az, Qopuz, tr, Kopuz) is an ancient fretless string instrument used in Central Asian music, related to certain other Turkic string instruments, the Mongolian tovshuur, and the lute. The instrument can be found in Turkic ethnic groups, from China to Turkey. Forms of this instrument are used in China by the Naxi people and are called Huobusi, Hebisi , and Hunbusi. It is the best-known national instrument and one of the better-known Kyrgyz national symbols. The komuz is generally made from a single piece of wood (usually apricot or juniper) and has three strings traditionally made out of gut, and often from fishing line in modern times. In the most common tunings the middle string is the highest in pitch. Virtuosos frequently play the komuz in a variety of different positions; over the shoulder, between the knees and upside down. An illustration of a komuz is featured on the reverse of the one-som note. Playing style The komuz can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus '' Prunus''. Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also called apricots. Etymology ''Apricot'' first appeared in English in the 16th century as ''abrecock'' from the Middle French ''aubercot'' or later ''abricot'', from Spanish '' albaricoque'' and Catalan ''a(l)bercoc'', in turn from Arabic الْبَرْقُوق (al-barqūq, "the plums"), from Byzantine Greek βερικοκκίᾱ (berikokkíā, "apricot tree"), derived from late Greek ''πραικόκιον'' (''praikókion'', "apricot") from Latin '' ersica ("peach")praecocia'' (''praecoquus'', "early ripening"). Species Apricots are species belonging to ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca''. The taxonomic position of '' P. brigantina'' is disputed. It is grouped with plum species according to chloroplast DNA sequences, but more closel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambur
The ''tambur'' (spelled in keeping with TDK conventions) is a fretted string instrument of Turkey and the former lands of the Ottoman Empire. Like the ney, the armudi (lit. pear-shaped) kemençe and the kudüm, it constitutes one of the four instruments of the basic quartet of Turkish classical music. Of the two variants, one is played with a plectrum (''mızraplı tambur'') and the other with a bow ('' yaylı tambur''). The player is called a ''tamburî''.Tambur Republic of Turkey - Ministry of Culture and Tourism History and development There are several hypotheses as to the origin of the instrument. One suggests that it descended from the kopuz, a string instrument still in use among the Turkic peoples of Central Asia and the Caspian region. T ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Farabi
Abu Nasr Muhammad Al-Farabi ( fa, ابونصر محمد فارابی), ( ar, أبو نصر محمد الفارابي), known in the West as Alpharabius; (c. 872 – between 14 December, 950 and 12 January, 951)PDF version was a renowned early Islamic philosopher and jurist who wrote in the fields of political philosophy, metaphysics, ethics and logic. He was also a scientist, cosmologist, mathematician and music theorist. Ludwig W. Adamec (2009), ''Historical Dictionary of Islam'', pp.95–96. Scarecrow Press. . In Islamic philosophical tradition he was often called "the Second Teacher", following Aristotle who was known as "the First Teacher". He is credited with preserving the original Greek texts during the Middle Ages via his commentaries and treatises, and influencing many prominent philosophers, such as Avicenna and Maimonides. Through his works, he became well-known in the West as well as the East. Biography The existing variations in the basic accounts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Tatars
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars ( tt-Cyrl, татарлар, tatarlar) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are Russia's second-largest ethnicity after the Russians. They compose 53% of the population of Tatarstan and 25% of the population of Bashkortostan. The Volga Tatars are by far the largest group amongst the Tatars. History Tatars inhabiting the Republic of Tatarstan, a federal subject of Russia, constitute one third of all Tatars, while the other two thirds reside outside Tatarstan. Some of the communities residing outside Tatarstan developed before the Russian Revolution of 1917, as Tatars were specialized in trading. During the 14th century, Sunni Islam was adopted by many of the Tatars. Tatars became subjects of Russia after the Siege of Kazan in 1552. Russians were using the Tatar ethnonym during the 18th and 19th centuries to denote all Turkic inhabitants of the Russian Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanding
upright=1.35, Sheets of sandpaper with different grit sizes (40 (coarse), 80, 150, 240, 600 (fine)). Sandpaper and glasspaper are names used for a type of coated abrasive that consists of sheets of paper or cloth with abrasive material glued to one face. There are many varieties of sandpaper, with variations in the paper or backing, the material used for the grit, grit size, and the bond. In the modern manufacture of these products, sand and glass have been replaced by other abrasives such as aluminium oxide or silicon carbide. It is common to use the name of the abrasive when describing the paper, e.g. "aluminium oxide paper", or "silicon carbide paper". Sandpaper is produced in a range of grit sizes and is used to remove material from surfaces, whether to make them smoother (for example, in painting and wood finishing), to remove a layer of material (such as old paint), or sometimes to make the surface rougher (for example, as a preparation for gluing). The grit size of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
_b.jpg)


