|
Dithioacetal
In organosulfur chemistry, thioacetals are the sulfur (''thio-'') analogues of acetals (). There are two classes: the less-common monothioacetals, with the formula , and the dithioacetals, with the formula (symmetric dithioacetals) or (asymmetric dithioacetals). The symmetric dithioacetals are relatively common. They are prepared by condensation of thiols () or dithiols (two groups) with aldehydes (). These reactions proceed via the intermediacy of hemithioacetals (): #Thiol addition to give hemithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(O) -> R'CH(SR)OH #Thiol addition with loss of water to give dithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(OH)SR -> R'CH(SR)2 + H2O Such reactions typically employ either a Lewis acid or Brønsted acid as catalyst. Dithioacetals generated from aldehydes and either 1,2-ethanedithiol or 1,3-propanedithiol are especially common among this class of molecules for use in organic synthesis.P. Stütz And P. A. Stadler "3-alkylated And 3-acylated Indoles From A Common Precurso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioacetal
In organosulfur chemistry, thioacetals are the sulfur (''thio-'') analogues of acetals (). There are two classes: the less-common monothioacetals, with the formula , and the dithioacetals, with the formula (symmetric dithioacetals) or (asymmetric dithioacetals). The symmetric dithioacetals are relatively common. They are prepared by condensation of thiols () or dithiols (two groups) with aldehydes (). These reactions proceed via the intermediacy of hemithioacetals (): #Thiol addition to give hemithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(O) -> R'CH(SR)OH #Thiol addition with loss of water to give dithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(OH)SR -> R'CH(SR)2 + H2O Such reactions typically employ either a Lewis acid or Brønsted acid as catalyst. Dithioacetals generated from aldehydes and either 1,2-ethanedithiol or 1,3-propanedithiol are especially common among this class of molecules for use in organic synthesis.P. Stütz And P. A. Stadler "3-alkylated And 3-acylated Indoles From A Common Precursor: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithioacetal
In organosulfur chemistry, thioacetals are the sulfur (''thio-'') analogues of acetals (). There are two classes: the less-common monothioacetals, with the formula , and the dithioacetals, with the formula (symmetric dithioacetals) or (asymmetric dithioacetals). The symmetric dithioacetals are relatively common. They are prepared by condensation of thiols () or dithiols (two groups) with aldehydes (). These reactions proceed via the intermediacy of hemithioacetals (): #Thiol addition to give hemithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(O) -> R'CH(SR)OH #Thiol addition with loss of water to give dithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(OH)SR -> R'CH(SR)2 + H2O Such reactions typically employ either a Lewis acid or Brønsted acid as catalyst. Dithioacetals generated from aldehydes and either 1,2-ethanedithiol or 1,3-propanedithiol are especially common among this class of molecules for use in organic synthesis.P. Stütz And P. A. Stadler "3-alkylated And 3-acylated Indoles From A Common Precurso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
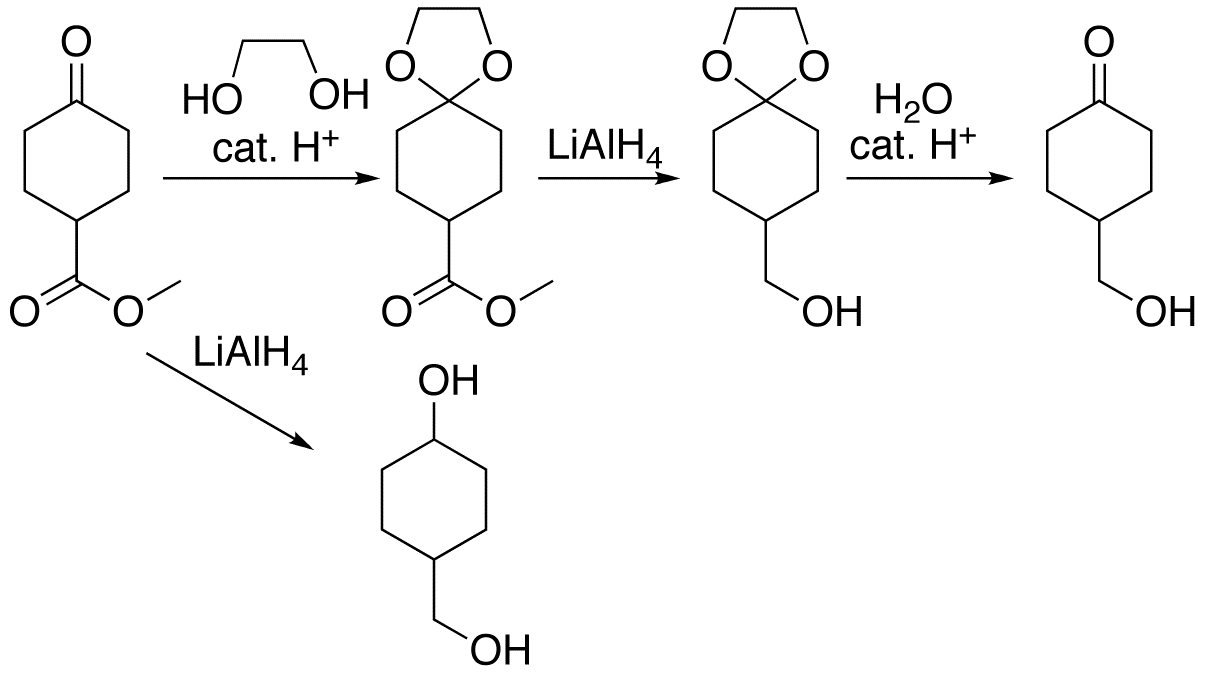
Dithioacetal Synthesis V
In organosulfur chemistry, thioacetals are the sulfur (''thio-'') analogues of acetals (). There are two classes: the less-common monothioacetals, with the formula , and the dithioacetals, with the formula (symmetric dithioacetals) or (asymmetric dithioacetals). The symmetric dithioacetals are relatively common. They are prepared by condensation of thiols () or dithiols (two groups) with aldehydes (). These reactions proceed via the intermediacy of hemithioacetals (): #Thiol addition to give hemithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(O) -> R'CH(SR)OH #Thiol addition with loss of water to give dithioacetal: #::RSH + R'CH(OH)SR -> R'CH(SR)2 + H2O Such reactions typically employ either a Lewis acid or Brønsted acid as catalyst. Dithioacetals generated from aldehydes and either 1,2-ethanedithiol or 1,3-propanedithiol are especially common among this class of molecules for use in organic synthesis.P. Stütz And P. A. Stadler "3-alkylated And 3-acylated Indoles From A Common Precurso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corey–Seebach Reaction
The Corey–Seebach reaction, or Seebach Umpolung is a name reaction of organic chemistry that allows for acylation by converting aldehydes into lithiated dithiane#1,3-Dithianes, 1,3-dithianes. The lithiated 1,3-dithianes serves as an acyl anion equivalent, undergoing alkylation with electrophiles. The reaction is of pedagogical value, but it is cumbersome, so it is not widely used. Implementation The aldehyde is first converted into a dithiane, usually with 1,3-propanedithiol. The resulting 1,3-dithiane is then lithiated with the use of N-butyllithium, butyllithium. The 2-lithio-1,3-dithiane reacts with electrophiles to give a 2-alkyl-1,3-dithiane. Finally, the 2-alkyl-1,3-dithiane can be converted to a carbonyl by hydrolysis, usually with the use of mercury(II) oxide. Alternatively the 2-alkyl-1,3-dithiane can be reduced to an alkane. : Scope The lithiated 1,3-dithiane can react with alkyl halides, epoxides, ketones, acyl halides, and iminium salts, which after hydrolysis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioketal
In organosulfur chemistry, a thioketal is the sulfur analogue of a ketal (), with one of the oxygen replaced by sulfur (as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix), giving the structure . A dithioketal has ''both'' oxygens replaced by sulfur (). Thioketals can be obtained by reacting ketones () or aldehydes () with thiols (). An oxidative cleavage mechanism has been proposed for dithioketals, which involves thioether oxidation, the formation of thionoiums, and hydrolysis, resulting in the formation of aldehyde and ketone products. Thioketal moieties are found to be responsive to reactive oxygen species (ROS). In the presence of ROS, thioketals can be selectively cleaved. ROS successfully cleave heterobifunctional thioketal linkers, which have been found to have therapeutic potential, as they can produce ROS-responsive agents with two different functionalities. Ketones can be reduced at neutral pH via conversion to thioketals; the thioketal prepared from the ketone can be easily redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozingo Reduction
The Mozingo reduction, also known as Mozingo reaction or thioketal reduction, is a chemical reaction capable of fully reducing a ketone or aldehyde to the corresponding alkane via a dithioacetal. The reaction scheme is as follows: The ketone or aldehyde is activated by conversion to cyclic dithioacetal by reaction with a dithiol (nucleophilic substitution) in presence of a H+ donating acid. The cyclic dithioacetal structure is then hydrogenolyzed using Raney nickel. Raney nickel is converted irreversibly to nickel sulfide. This method is milder than either the Clemmensen or Wolff-Kishner reductions, which employ strongly acidic or basic conditions, respectively, that might interfere with other functional groups. History The reaction is named after Ralph Mozingo, who reported the cleavage of thioether In organic chemistry, an organic sulfide (British English sulphide) or thioether is an organosulfur functional group with the connectivity as shown on right. Like many other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,3-dithiane
A dithiane is a heterocyclic compound composed of a cyclohexane core structure wherein two methylene bridges (-- units) are replaced by sulfur centres. The three isomeric parent heterocycles are 1,2-dithiane, 1,3-dithiane and 1,4-dithiane. 1,3-Dithianes 1,3-Dithianes are protecting group of some carbonyl-containing compounds due to their inertness to many conditions. They form by treatment of the carbonyl compound with 1,3-propanedithiol under conditions that remove water from the system. The protecting group can be removed with mercuric reagents, a process that exploits the high affinity of Hg(II) for thiolates. 1,3-Dithianes are also employed in umpolung reactions, such as the Corey–Seebach reaction:T. W. Green, P. G. M. Wuts, "Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis" Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1999. . : Typically, in organic synthesis, ketones and aldehydes are protected as their dioxolane Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umpolung
In organic chemistry, umpolung () or polarity inversion is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group. This modification allows secondary reactions of this functional group that would otherwise not be possible. The concept was introduced by D. Seebach (hence the German word for reversed polarity) and E.J. Corey. Polarity analysis during retrosynthetic analysis tells a chemist when umpolung tactics are required to synthesize a target molecule. Introduction The vast majority of important organic molecules contain heteroatoms, which polarize carbon skeletons by virtue of their electronegativity. Therefore, in standard organic reactions, the majority of new bonds are formed between atoms of opposite polarity. This can be considered to be the "normal" mode of reactivity. One consequence of this natural polarization of molecules is that 1,3- and 1,5- heteroatom substituted carbon skeletons are extremely easy to synthesize (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deprotonated
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch331/protstructure/PS_2A3_AA_Charges.html, accessed 12/2/2020 The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when a proton is added (transferred) to a Brønsted–Lowry base, is protonation (or hydronation). The species formed is the conjugate acid of that base. A species that can either accept or donate a proton is referred to as amphiprotic. An example is the H2O (water) molecule, which can gain a proton to form the hydronium ion, H3O+, or lose a proton, leaving the hydroxide ion, OH−. The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its p''K''a value. A low p''K''a value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protective Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the acet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and ''electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''cationoid' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |