|
Diptericin
Diptericin is a 9 kDa antimicrobial peptide (AMP) of flies first isolated from the blowfly ''Phormia terranova''. It is primarily active against Gram-negative bacteria, disrupting bacterial membrane integrity. The structure of this protein includes a proline-rich domain with similarities to the AMPs drosocin, pyrrhocoricin, and abaecin, and a glycine-rich domain with similarity to attacin. Diptericin is an iconic readout of immune system activity in flies, used ubiquitously in studies of ''Drosophila'' immunity. Diptericin is named after the insect order Diptera. Structure and function Diptericins are found throughout Diptera, but are most extensively characterized in ''Drosophila'' fruit flies. The mature structures of diptericins are unknown, though previous efforts to synthesize Diptericin have suggested Diptericin in ''Protophormia terraenovae'' is one linear peptide. Yet ''Drosophila melanogaster's'' Diptericin B peptide is likely cleaved into two separate peptides. Synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Providencia Rettgeri
''Providencia rettgeri'' (commonly ''P. rettgeri''), is a Gram negative bacterium that is commonly found in both water and land environments. ''P. rettgeri'' is in the genus Providencia, along with '' Providencia stuartii'', '' Providencia alcalifaciens'', and '' Providencia rustigianii''. ''P. rettgeri'' can be incubated at 37 °C in nutrient agar or nutrient broth. It was first discovered in 1904 after a waterfowl epidemic. Strains of the species have also been isolated from nematodes of the genus ''Heterorhabditis''. ''Providencia rettgeri'' also found in marine environment. Biochemical characteristics of ''Providencia rettgeri'' S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated, characterized and identified salt tolerant ''Providencia rettgeri'' from marine sponge (''Niphates erecta'') of the Saint Martin's Island Area of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Colony, morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of ''Providencia rettgeri'' are shown in the Table below. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Testacea
''Drosophila testacea'' is a member of the ''testacea'' species group of ''Drosophila''. Testacea species are specialist fruit flies that breed on the fruiting bodies of mushrooms. ''Drosophila testacea'' can be found in temperate regions of Europe, extending to east Asia. ''Drosophila testacea'' and '' Drosophila orientacea'' can produce viable hybrids, though they are separated by geography and behavioural barriers. ''Drosophila testacea'' females will also readily mate with ''Drosophila neotestacea'' males, but viable hybrids are never produced. This hybrid inviability (see Haldane's rule)) may be due to selfish X chromosomes and co-evolved suppressors. Alternately, differences in sex pheromone (e.g. vaccenyl acetate) reception could underlie female readiness and male willingness to copulate. The antimicrobial peptide gene '' Diptericin B'' has been pseudogenized in ''D. testacea'' and likely its sister species ''D. neotestacea''. See also * Drosophila testacea species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
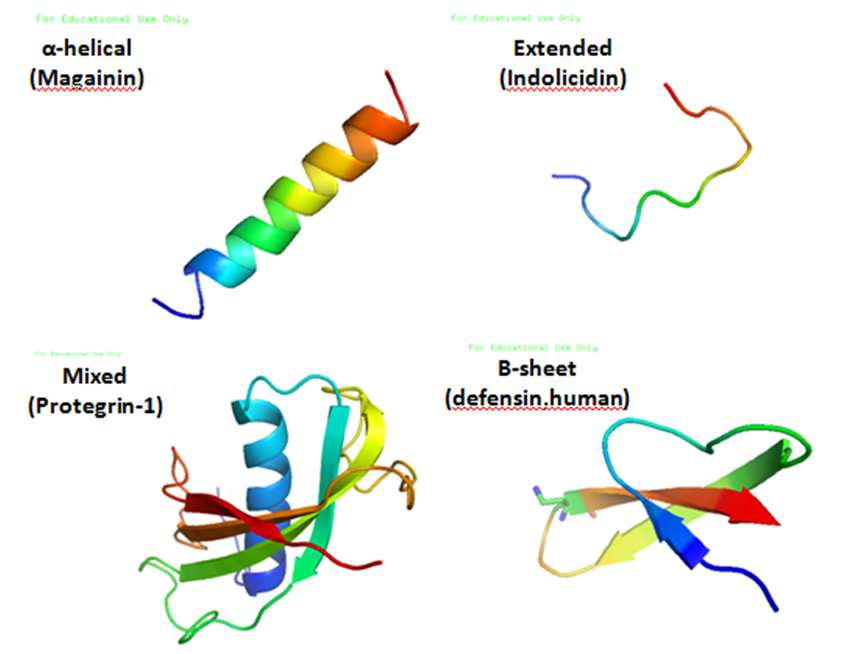
Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides are g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attacin
Attacin is a glycine-rich protein of about 20 kDa belonging to the group of antimicrobial peptides (AMP). It is active against Gram-negative bacteria. Attacin was first discovered in ''Hyalophora cecropia'', but is widely conserved in different insects from butterflies to fruit flies. See also *Diptericin Diptericin is a 9 kDa antimicrobial peptide (AMP) of flies first isolated from the blowfly '' Phormia terranova''. It is primarily active against Gram-negative bacteria, disrupting bacterial membrane integrity. The structure of this protein incl ..., a structurally related antimicrobial peptide References {{Reflist Insect immunity Antimicrobial peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Peptide
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides are ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phormia Terranova
''Protophormia terraenovae'' is commonly called northern blowfly, blue-bottle fly or blue-assed fly (blue-arsed fly in British English). It is distinguished by its deep blue coloration and large size and is an important species throughout the Northern Hemisphere. This fly is notable for its economic effect as a myiasis pest of livestock and its antibiotic benefits in maggot therapy. Also of interest is ''P. terraenovae''’s importance in forensic investigations: because of their temperature-dependent development and their prominent presence on corpses, the larvae of this species are useful in minimum post-mortem interval (mPMI) determination. Taxonomy ''Protophormia terraenovae'', of the family Calliphoridae, was named and first described by French entomologist André Jean Baptiste Robineau-Desvoidy in his 1830 “Essai sur les myodaires.” Its genus is shared by one other fly, ''Protophormia atriceps''. Both flies are a dark, undusted, metallic blue-green-black. ''P. terraen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Guttifera
''Drosophila guttifera'' is a species of vinegar fly in the Drosophila quinaria species group. Like many quinaria group species, ''D. guttifera'' feeds on rotting mushrooms. In 2015, the genome of ''Drosophila guttifera'' was sequenced by the laboratory of Sean B. Carroll providing an answer on how different wing patterns emerge in this species, relying on genetic switches called enhancers that drive the polka-dot pattern on the wings of ''D. guttifera''. These enhancers are cis-regulatory elements ''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogen ..., which can promote new wing patterns by modifying gene expression, rather than the actual protein being expressed. Further reading * Description of background on ''D. guttifera'' use in genetic studies in the Drosophila quinaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom-feeding Drosophila
Mushroom-feeding ''Drosophila'' (mycophagous ''Drosophila'') are a subset of ''Drosophila'' flies that have highly specific mushroom-breeding ecologies. Often these flies can tolerate toxic compounds from ''Amanita'' mushrooms. Species groups * ''Drosophila testacea'' species group * ''Drosophila quinaria'' species group * '' Drosophila bizonata'' species group * Some members of the ''Drosophila obscura'' species group Sequenced genomes or transcriptomes * ''Drosophila guttifera'' * ''Drosophila neotestacea'' * ''Drosophila innubila'' * ''Drosophila falleni'' * '' Drosophila phalerata'' Gallery File: Dneo f3.tif , '' D. neotestacea'' ( Testacea species group) File: Dtestacea male 2-4.tif , '' D. testacea'' ( Testacea species group) File: Dinnubila4.tif , '' D. innubila'' ( Quinaria species group) File:Dguttifera.tif, ''Drosophila guttifera'' ( Quinaria species group) Dphalerata male.tif, '' Drosophila phalerata'' ( Quinaria species group) File:Drosophila falleni infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight. Functionally similar features that have arisen through convergent evolution are ''analogous'', whereas '' homologous'' structures or traits have a common origin but can have dissimilar functions. Bird, bat, and pterosaur wings are analogous structures, but their forelimbs are homologous, sharing an ancestral state despite serving different functions. The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution, where related species evolve different traits. Convergent evolution is similar to parallel evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephritidae
The Tephritidae are one of two fly families referred to as fruit flies, the other family being the Drosophilidae. The family Tephritidae does not include the biological model organisms of the genus ''Drosophila'' (in the family Drosophilidae), which is often called the "common fruit fly". Nearly 5,000 described species of tephritid fruit fly are categorized in almost 500 genera of the Tephritidae. Description, recategorization, and genetic analyses are constantly changing the taxonomy of this family. To distinguish them from the Drosophilidae, the Tephritidae are sometimes called peacock flies, in reference to their elaborate and colorful markings. The name comes from the Greek τεφρος, ''tephros'', meaning "ash grey". They are found in all the biogeographic realms. Description For terms see Morphology of Diptera anTephritidae glossary Tephritids are small to medium-sized (2.5–10 mm) flies that are often colourful, and usually with pictured wings, the subcostal ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balancing Selection
Balancing selection refers to a number of selective processes by which multiple alleles (different versions of a gene) are actively maintained in the gene pool of a population at frequencies larger than expected from genetic drift alone. Balancing selection is rare compared to purifying selection. It can occur by various mechanisms, in particular, when the heterozygotes for the alleles under consideration have a higher fitness than the homozygote. In this way genetic polymorphism is conserved. Evidence for balancing selection can be found in the number of alleles in a population which are maintained above mutation rate frequencies. All modern research has shown that this significant genetic variation is ubiquitous in panmictic populations. There are several mechanisms (which are not exclusive within any given population) by which balancing selection works to maintain polymorphism. The two major and most studied are heterozygote advantage and frequency-dependent selection. Mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

