|
Dicksoniaceae
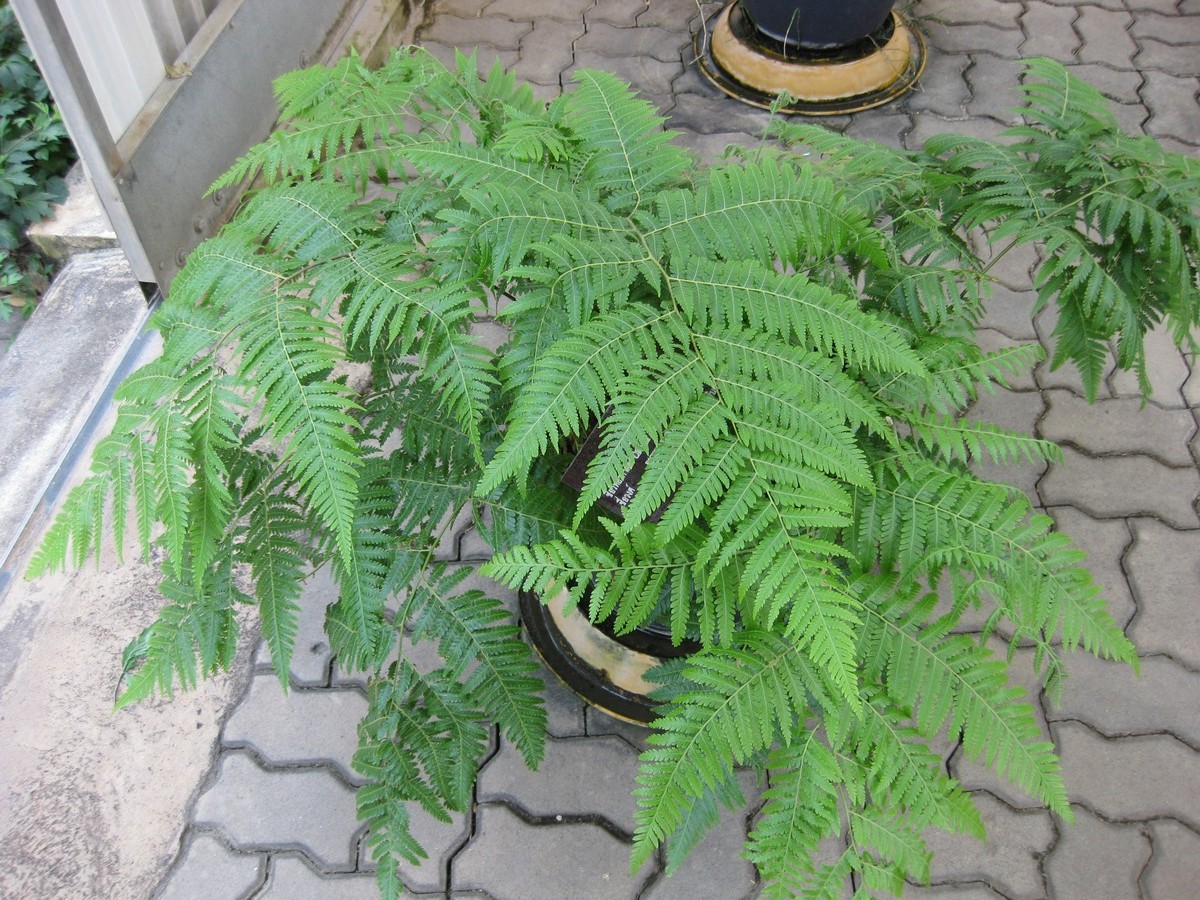
Dicksoniaceae is a group of tropical, subtropical and warm temperate ferns, treated as a family in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), and counting 30-40 species. Alternatively, the family may be sunk into a very broadly defined family Cyatheaceae ''sensu lato'' as the subfamily Dicksonioideae. Most of the genera in the family are terrestrial ferns or have very short trunks compared to tree ferns of the family Cyatheaceae ''sensu stricto''. However, some of the larger species can reach several metres in height. A number of others are epiphytes. They are found mostly in tropical regions in the Southern Hemisphere, as far south as southern New Zealand. Larger tree ferns in the genus '' Cibotium'' were formerly included in Dicksoniaceae, but are now segregated as the family Cibotiaceae. Description Species in the family are generally characterized by large pinnate fronds, 1–4 m long. The family includes several species of tree ferns, which grow a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calochlaena
''Calochlaena'' is a genus of ferns within the family Dicksoniaceae. Although these ground ferns resemble bracken, they are only distantly related. Five species are known from Melanesia, Polynesia and eastern Australia. '' Calochlaena dubia'', is a common fern of the east coast of Australia. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek ''kalos'' "beautiful" and ''chlaina'' "cloak", and refers to the soft hairs on the species. The genus was originally described by William Ralph Maxon as a subgenus of the fern genus '' Culcita'', but the differences were such that its members were raised to genus level, and are now considered to be in separate families. ''Culcita'' was restricted to two species, one from Mediterranean Europe and one from North America. Species Plants of the World Online Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. It was launched in March 2017 with the ultimate aim being "to enable users to access informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cibotium
''Cibotium'' (from Greek , ''kibṓtion'', "little chest" or "box"), also known as manfern, is a genus of 11 species of tropical tree ferns. It is the only genus in family Cibotiaceae in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I). Alternatively, the family may be treated as the subfamily Cibotioideae of a very broadly defined family Cyatheaceae, the family placement used for the genus in ''Plants of the World Online'' . Species , ''Plants of the World Online'' accepted the following species and hybrids: Some extinct species have also been placed in this genus: *†'' Cibotium iwatense'' Ogura *†'' Cibotium oregonense'' Barrington Distribution Species of the genus are distributed fairly narrowly in Hawaii (four species, plus a hybrid, collectively known as ''hāpuu''), Southeast Asia (five species), and the cloud forests of Central America and Mexico (two species). The natural habitat of ''Cibotium'' is among the dripping trees and stream gullies of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicksoniaceae
Dicksoniaceae is a group of tropical, subtropical and warm temperate ferns, treated as a family in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), and counting 30-40 species. Alternatively, the family may be sunk into a very broadly defined family Cyatheaceae ''sensu lato'' as the subfamily Dicksonioideae. Most of the genera in the family are terrestrial ferns or have very short trunks compared to tree ferns of the family Cyatheaceae ''sensu stricto''. However, some of the larger species can reach several metres in height. A number of others are epiphytes. They are found mostly in tropical regions in the Southern Hemisphere, as far south as southern New Zealand. Larger tree ferns in the genus '' Cibotium'' were formerly included in Dicksoniaceae, but are now segregated as the family Cibotiaceae. Description Species in the family are generally characterized by large pinnate fronds, 1–4 m long. The family includes several species of tree ferns, which grow a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibibyte
The byte is a units of information, unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character (computing), character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest address space, addressable unit of Computer memory, memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit computing, 8-bit definition, Computer network, network protocol documents such as Internet Protocol, The Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an Octet (computing), octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the Endianness#Bit endianness, bit endianness. The first bit is number 0, making the eighth bit number 7. The size of the byte has historically been Computer hardware, hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypodiales
The order Polypodiales encompasses the major lineages of polypod ferns, which comprise more than 80% of today's fern species. They are found in many parts of the world including tropical, semitropical and temperate areas. Description Polypodiales are unique in bearing sporangia with a vertical annulus interrupted by the stalk and stomium. These sporangial characters were used by Johann Jakob Bernhardi to define a group of ferns he called the "Cathetogyratae"; the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group has suggested reviving this name as the informal term cathetogyrates, to replace the ambiguously circumscribed term "polypods" when referring to the Polypodiales. The sporangia are born on stalks 1–3 cells thick and are often long-stalked. (In contrast, the Hymenophyllales have a stalk composed of four rows of cells.) The sporangia do not reach maturity simultaneously. Many groups in the order lack indusia, but when present, they are attached either along the edge of the indusium or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistics
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies'')'' that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms ''worms'' or ''fishes'' were used within a ''strict'' cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a ' grade', which are fruitless to precisely delineate, especially when including extinct species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coniopteris
''Coniopteris'' is an extinct genus of Mesozoic fern leaves with a fossil range from the Early Jurassic to the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. It was widespread over both hemispheres during the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, with over 130 species having been described. While traditionally assumed to have been a member of Dicksoniaceae or a close relative of '' Thyrsopteris,'' a 2020 cladistic analysis found it to be a stem group of Polypodiales. Most species of ''Coniopteris'' probably had a herbaceous habit. The genus is technically a junior synonym of the little used ''Polystichites,'' but was conserved by the ICZN in 2013. References † A dagger, obelisk, or obelus is a typographical mark that usually indicates a footnote if an asterisk has already been used. The symbol is also used to indicate death (of people) or extinction (of species). It is one of the modern descendan ... Prehistoric plant genera Early Triassic genus first appearances Cenoman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aptian
The Aptian is an age in the geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early or Lower Cretaceous Epoch or Series and encompasses the time from 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma to 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma (million years ago), approximately. The Aptian succeeds the Barremian and precedes the Albian, all part of the Lower/Early Cretaceous. The Aptian partly overlaps the upper part of the Western European Urgonian Stage. The Selli Event, also known as OAE1a, was one of two oceanic anoxic events in the Cretaceous Period, which occurred around 120 Ma and lasted approximately 1 to 1.3 million years. The Aptian extinction was a minor extinction event hypothesized to have occurred around 116 to 117 Ma.Archangelsky, Sergio.The Ticó Flora (Patagonia) and the Aptian Extinction Event" ''Acta Paleobotanica'' 41(2), 2001, pp. 115-22. Stratigraphic definitions The Aptian was named after the small city of Apt in the Provence region of France, which is also known for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous ( chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java- Manihiki- Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kergue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
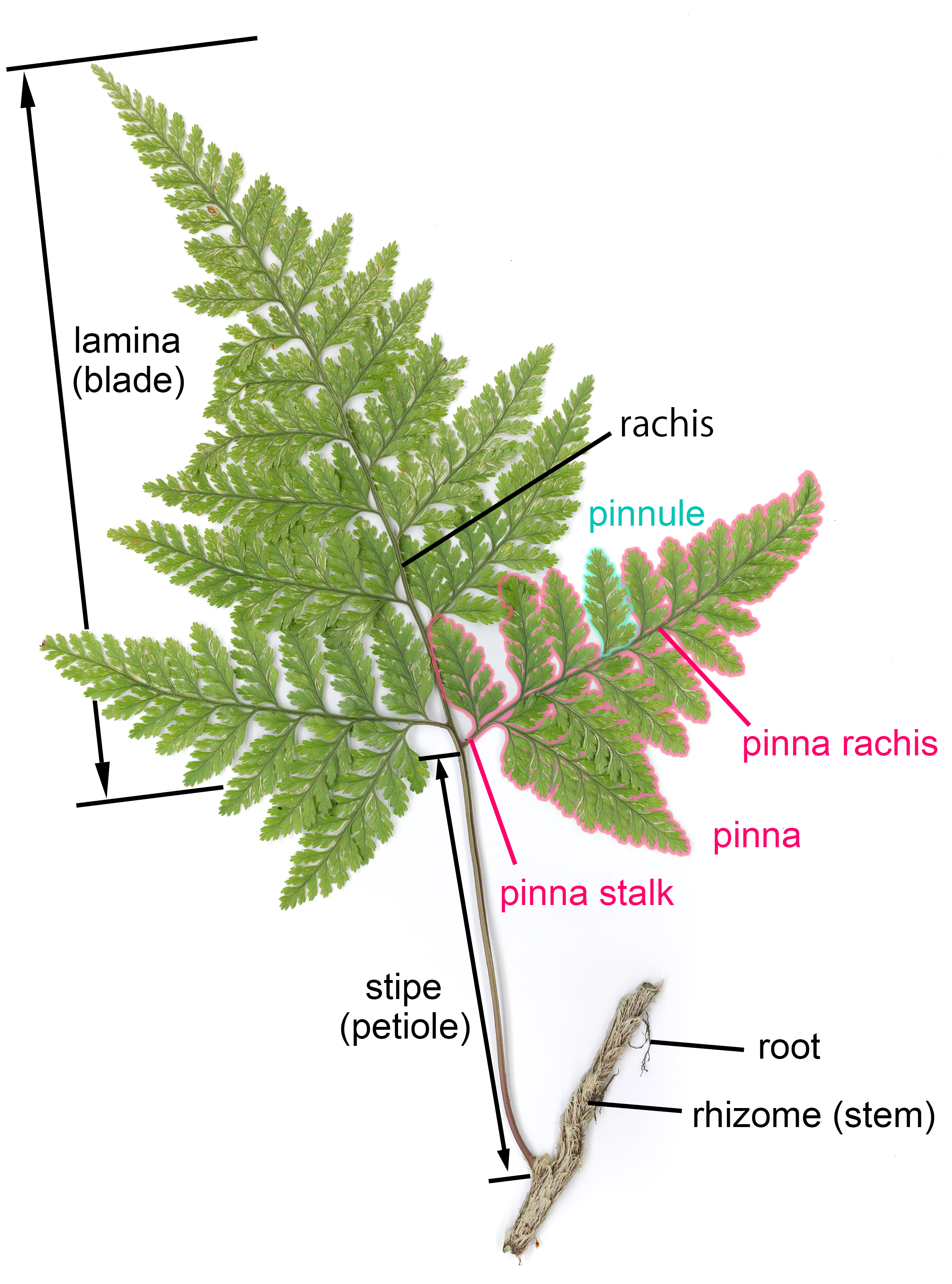
Frond
A frond is a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group. Other botanists allow the term frond to also apply to the large leaves of cycads, as well as palms (Arecaceae) and various other flowering plants, such as mimosa or sumac. "Frond" is commonly used to identify a large, compound leaf, but if the term is used botanically to refer to the leaves of ferns and algae it may be applied to smaller and undivided leaves. Fronds have particular terms describing their components. Like all leaves, fronds usually have a stalk connecting them to the main stem. In botany, this leaf stalk is generally called a Petiole (botany), petiole, but in regard to fronds specifically it is called a Stipe (botany), stipe, and it supports a flattened blade (which may be called a lamina), and the continuation of the stipe into this portion is called the rachis. The blades may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)