|
Diaphragma Sellae
The diaphragma sellae or sellar diaphragm is a flat piece of dura mater with a circular hole allowing the vertical passage of the pituitary stalk. It retains the pituitary gland beneath it in the fossa hypophyseos as it almost completely roofs the fossa hypophyseos of the sella turcica, a part of the sphenoid bone. It has a posterior boundary at the dorsum sellae and an anterior boundary at the tuberculum sellae along with the two small eminences (one on either side) called the middle clinoid processes. The diaphragma sellae is innervated by the first division of the cranial trigeminal nerve. Surgical Significance Violation of the diaphragma sellae during an endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary tumor resection will result in a cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentorium Cerebelli
The cerebellar tentorium or tentorium cerebelli (Latin for "tent of the cerebellum") is an extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the inferior portion of the occipital lobes. Structure The cerebellar tentorium is an arched wikt:lamina, lamina, elevated in the middle, and inclining downward toward the circumference. It covers the top of the cerebellum The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ..., and supports the occipital lobes of the brain. Its anterior border is free and concave, and bounds a large oval opening, the tentorial incisure, through which pass the cerebral peduncles. It is attached, behind, by its convex border, to the transverse ridges upon the inner surface of the occipital bone, and there encloses the transverse sinuses; in front, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dura Mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The other two meningeal layers are the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. It envelops the arachnoid mater, which is responsible for keeping in the cerebrospinal fluid. It is derived primarily from the neural crest cell population, with postnatal contributions of the paraxial mesoderm. Structure The dura mater has several functions and layers. The dura mater is a membrane that envelops the arachnoid mater. It surrounds and supports the dural sinuses (also called dural venous sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) and carries blood from the brain toward the heart. Cranial dura mater has two layers called ''lamellae'', a superficial layer (also called the periosteal layer), which serves as the skull's inner periosteum, called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
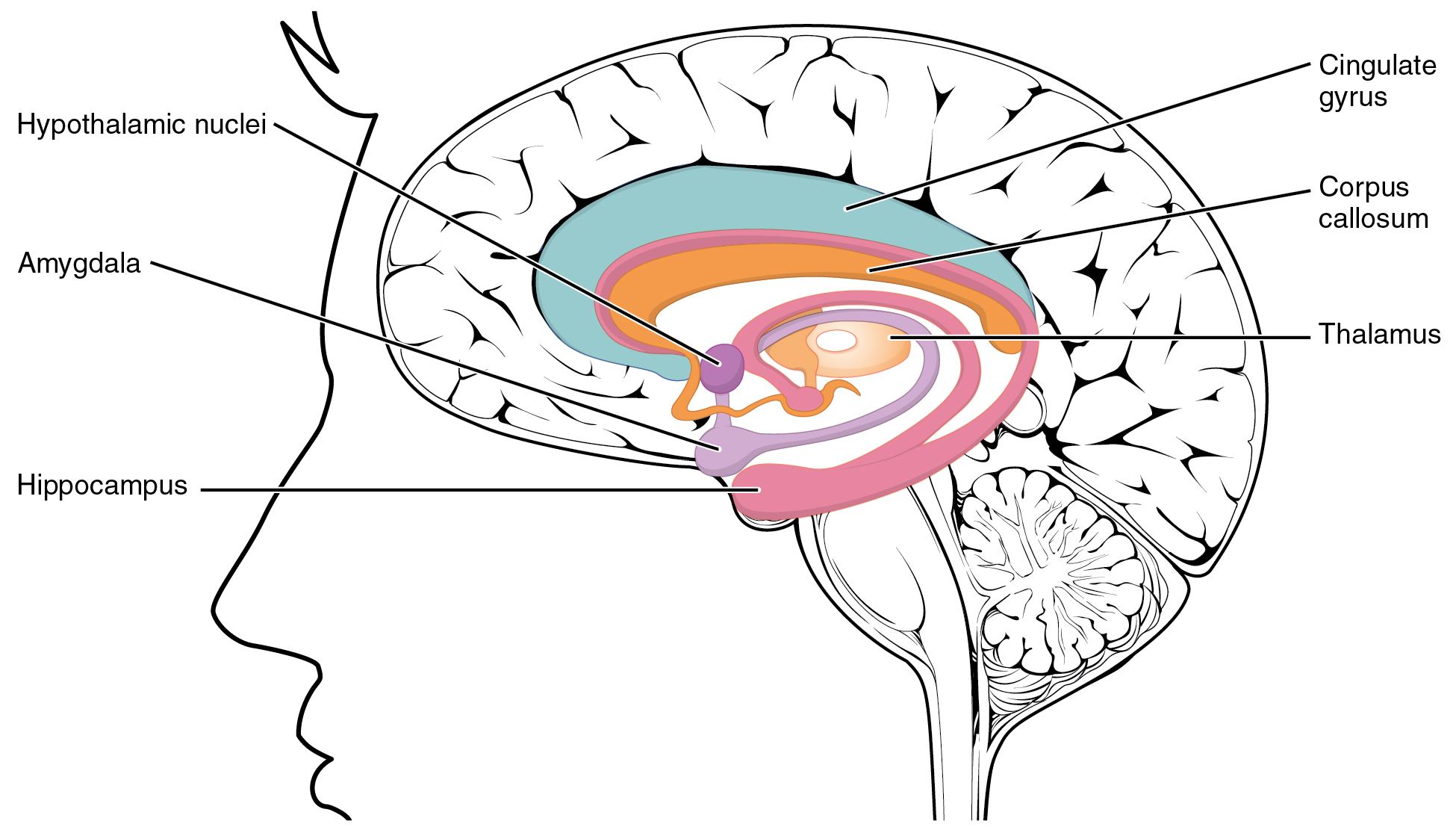
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity (sella turcica) covered by a dural fold (diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossa Hypophyseos
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa. Structure The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa. The sella turcica's most inferior portion is known as the hypophyseal fossa (the "seat of the saddle"), and contains the pituitary gland (hypophysis). In front of the hypophyseal fossa is the tuberculum sellae. Completing the formation of the saddle posteriorly is the dorsum sellae, which is continuous with the clivus, inferoposteriorly. The dorsum sellae is terminated laterally by the posterior clinoid processes. Development It is widely believed that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sella Turcica
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa. Structure The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa. The sella turcica's most inferior portion is known as the hypophyseal fossa (the "seat of the saddle"), and contains the pituitary gland (hypophysis). In front of the hypophyseal fossa is the tuberculum sellae. Completing the formation of the saddle posteriorly is the dorsum sellae, which is continuous with the clivus, inferoposteriorly. The dorsum sellae is terminated laterally by the posterior clinoid processes. Development It is widely believed that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoid Bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit (anatomy), orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two Lesser wing of sphenoid bone, lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal conchae are situated at the anterior and inferior part of the body. Intrinsic ligaments of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum Sellae
The dorsum sellae is part of the sphenoid bone in the skull. Together with the basilar part of the occipital bone it forms the clivus. In the sphenoid bone, the anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on either side, called the middle clinoid processes, while the posterior boundary is formed by a square-shaped plate of bone, the dorsum sellae, ending at its superior angles in two tubercles, the posterior clinoid processes In the sphenoid bone, the anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on either side, called the anterior clinoid processes, while the posterior boundary is formed by a square-shaped plate of bone, the dorsum s ..., the size and form of which vary considerably in different individuals. Additional images File:Gray569.png, Tentorium cerebelli from above. File:Slide2iiii.JPG, Dorsum sellae References External links * * Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculum Sellae
The tuberculum sellae (or the tubercle of the sella turcica) is a part of the sphenoid bone that is an elevation behind the chiasmatic groove The superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone is bounded behind by a ridge, which forms the anterior border of a narrow, transverse groove, the chiasmatic groove (optic groove, prechiasmatic sulcus), above and behind which lies the optic c .... A variable slight to prominent median elevation forming the posterior boundary of the chiasmatic groove and the anterior boundary of the hypophysial fossa. Additional Images File:Slide1iiii.JPG, Tuberculum sellae References External links * Diagram at uni-mainz.de Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Clinoid Processes
The anterior boundary of the sella turcica is completed by two small eminences, one on either side, called the middle clinoid processes. It is found lateral to the sella turcica. Etymology Clinoid likely comes from the Greek root ''klinein'' or the Latin Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ... ''clinare'', both meaning "sloped" as in "inclined." References Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge from the cerebrum, and the remaining ten pairs arise from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name ("trigeminal", ) derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V), the maxillary nerve (V), and the mandibular nerve (V). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it. The motor division of the trigeminal nerve derives from the basal plate of the embryonic pons, and the sensory division originates in the cranial neural crest. Sensory information from the face and body is proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |