Cranial Nerve on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the
 The oculomotor nerve (III),
The oculomotor nerve (III),

 The
The
File:Quiring 1950 146.png, The cranial nerves in the horse
File:Cranial nerve sheep ventral.png, Ventral view of a
brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
(including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck
This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.
Structure Bones
The head rests on the top part of the vertebra ...
, including the special senses
In medicine and anatomy, the special senses are the senses that have specialized organs devoted to them:
* vision (the eye)
* hearing and balance (the ear, which includes the auditory system and vestibular system)
* smell (the nose)
* ta ...
of vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor ...
, smell, and hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
.
The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
above the level of the first vertebra of the vertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordate ...
. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including cranial nerve zero
The terminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve 0 or simply as CN 0, is a nerve that was not included in the seminal classification of the cranial nerves as CN I through CN XII but is now generally classified as a cranial nerve. It was discovered ...
. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back.
The terminal nerve
The terminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve 0 or simply as CN 0, is a nerve that was not included in the seminal classification of the cranial nerves as CN I through CN XII but is now generally classified as a cranial nerve. It was discovered ...
s (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
s (II) emerge from the cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb ...
, and the remaining ten pairs arise from the brainstem, which is the lower part of the brain.
The cranial nerves are considered components of the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain ...
(PNS), although on a structural level the olfactory (I), optic (II), and trigeminal (V) nerves are more accurately considered part of the central nervous system (CNS).
The cranial nerves are in contrast to spinal nerves, which emerge from segments of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
.
Anatomy
Most typically, humans are considered to have twelve pairs of cranial nerves (I–XII), with theterminal nerve
The terminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve 0 or simply as CN 0, is a nerve that was not included in the seminal classification of the cranial nerves as CN I through CN XII but is now generally classified as a cranial nerve. It was discovered ...
(0) more recently canonized. The nerves are: the olfactory nerve (I), the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
(II), oculomotor nerve (III), trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
(IV), trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chew ...
(V), abducens nerve
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocul ...
(VI), facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste ...
(VII), vestibulocochlear nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the bra ...
(VIII), glossopharyngeal nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. ...
(IX), vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and righ ...
(X), accessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
(XI), and the hypoglossal nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by ...
(XII).
Terminology
Cranial nerves are generally named according to their structure or function. For example, the olfactory nerve (I) supplies smell, and the facial nerve (VII) supplies the muscles of the face. BecauseLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
was the '' lingua franca'' of the study of anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
when the nerves were first documented, recorded, and discussed, many nerves maintain Latin or Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
names, including the trochlear nerve (IV), named according to its structure, as it supplies a muscle that attaches to a pulley ( el, trochlea). The trigeminal nerve (V) is named in accordance with its three components ( la, trigeminus meaning triplets), and the vagus nerve (X) is named for its wandering course ( la, vagus).
Cranial nerves are numbered based on their position from front to back ( rostral-caudal) of their position on the brain, as, when viewing the forebrain and brainstem from below, they are often visible in their numeric order. For example, the olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) arise from the base of the forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three primary ...
, and the other nerves, III to XII, arise from the brainstem.
Cranial nerves have paths within and outside the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
. The paths within the skull are called "intracranial" and the paths outside the skull are called "extracranial". There are many holes in the skull called "foramina" by which the nerves can exit the skull. All cranial nerves are ''paired'', which means they occur on both the right and left sides of the body. The muscle, skin, or additional function supplied by a nerve, on the same side of the body as the side it originates from, is an ''ipsilateral'' function. If the function is on the opposite side to the origin of the nerve, this is known as a ''contralateral'' function.
Intracranial course
Nuclei
Grossly, all cranial nerves have aNucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
. With the exception of the olfactory nerve (I) and optic nerve (II), all the nuclei are present in the brainstem.
The midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
of the brainstem has the nuclei of the oculomotor nerve (III) and trochlear nerve (IV); the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
has the nuclei of the trigeminal nerve (V), abducens nerve (VI), facial nerve (VII) and vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII); and the medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
has the nuclei of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), vagus nerve (X), accessory nerve (XI) and hypoglossal nerve (XII). The olfactory nerve (I) emerges from the olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex ( ...
, and depending slightly on division the optic nerve (II) is considered to emerge from the lateral geniculate nuclei.
Because each nerve may have several functions, the nerve fibre
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action po ...
s that make up the nerve may collect in more than one nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
. For example, the trigeminal nerve (V), which has a sensory and a motor role, has at least four nuclei.
Exiting the brainstem
With the exception of the olfactory nerve (I) and optic nerve (II), the cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem. The oculomotor nerve (III) and trochlear nerve (IV) emerge from themidbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
, the trigeminal (V), abducens (VI), facial (VII) and vestibulocochlea (VIII) from the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
, and the glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X), accessory (XI) and hypoglossal (XII) emerge from the medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
.
The olfactory nerve (I) and optic nerve (II) emerge separately. The olfactory nerves emerge from the olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex ( ...
s on either side of the crista galli
The crista galli (Latin: "crest of the rooster") is the upper part of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone of the skull. It rises above the cribriform plate. The falx cerebri (a fold of the dura mater surrounding the brain) attaches to th ...
, a bony projection below the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
, and the optic nerves (II) emerge from the lateral colliculus, swellings on either side of the temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pro ...
s of the brain.
Ganglia
The cranial nerves give rise to a number of ganglia, collections of thecell bodies
The soma (pl. ''somata'' or ''somas''), perikaryon (pl. ''perikarya''), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. The word 'soma' comes from the Greek '' σῶ� ...
of neurons in the nerves that are outside of the brain. These ganglia are both parasympathetic and sensory ganglia.
The sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves, directly correspond to the dorsal root ganglia
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal ...
of spinal nerves and are known as cranial nerve ganglia. Sensory ganglia exist for nerves with sensory function: V, VII, VIII, IX, X. There are also a number of parasympathetic cranial nerve ganglia. Sympathetic ganglia
The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia are autonomic ganglia, of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 Afferent nerve fiber, afferent and Efferent nerve fiber, efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either s ...
supplying the head and neck reside in the upper regions of the sympathetic trunk
The sympathetic trunks (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) are a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. They are a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
Structure
The sympathetic trunk lies j ...
, and do not belong to the cranial nerves.
The ganglion of the sensory nerves, which are similar in structure to the dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
, include:
* The trigeminal ganglia
A trigeminal ganglion (or Gasserian ganglion, or semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is the sensory ganglion at the base of each of the two trigeminal nerves (CN V), occupying a cavity ( Meckel's cave) in the dura mater, covering the trige ...
of the trigeminal nerve (V), which occupies a space in the dura mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. ...
called Meckel's cave
The trigeminal cave (also known as Meckel's cave or cavum trigeminale) is a dura mater pouch containing cerebrospinal fluid.
Structure
The trigeminal cave is formed by the two layers of dura mater (endosteal and meningeal) which are part of an ev ...
. This ganglion contains only the sensory fibres of the trigeminal nerve.
* The geniculate ganglion
The geniculate ganglion (from Latin ''genu'', for "knee") is a collection of pseudounipolar sensory neurons of the facial nerve located in the facial canal of the head. It receives fibers from the facial nerve. It sends fibers that supply the la ...
of the facial nerve (VII), which occurs just after the nerve enters the facial canal
The facial canal (''canalis nervi facialis''), also known as the Fallopian canal, is a Z-shaped canal running through the temporal bone of the skull. It runs from the internal acoustic meatus to the stylomastoid foramen. It contains the facial ...
.
* A superior and inferior ganglia of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), which occurs just after it passes through the jugular foramen
A jugular foramen is one of the two (left and right) large foramina (openings) in the base of the skull, located behind the carotid canal. It is formed by the temporal bone and the occipital bone. It allows many structures to pass, including the ...
.
Additional ganglia for nerves with parasympathetic function exist, and include the ciliary ganglion
The ciliary ganglion is a bundle of nerve parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. It is 1–2 mm in diameter and in humans contains approximately 2,500 neurons. The ganglion contains postganglionic parasympath ...
of the oculomotor nerve (III), the pterygopalatine ganglion
The pterygopalatine ganglion (aka Meckel's ganglion, nasal ganglion, or sphenopalatine ganglion) is a parasympathetic ganglion found in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is largely innervated by the greater petrosal nerve (a branch of the facial n ...
of the maxillary nerve (V2), the submandibular ganglion
The submandibular ganglion (or submaxillary ganglion in older texts) is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. (The others are the otic ganglion, pterygopalatine ganglion, and ci ...
of the lingual nerve
The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3
) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerv ...
, a branch of the facial nerve (VII), and the otic ganglion
The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and inn ...
of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX).
Exiting the skull and extracranial course
After emerging from the brain, the cranial nerves travel within theskull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
, and some must leave it in order to reach their destinations. Often the nerves pass through holes in the skull, called foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
, as they travel to their destinations. Other nerves pass through bony canals, longer pathways enclosed by bone. These foramina and canals may contain more than one cranial nerve and may also contain blood vessels.
*The terminal nerve (0), is a thin network of fibers associated with the dura and lamina terminalis running rostral to the olfactory nerve, with projections through the cribriform plate.
* The olfactory nerve (I), passes through perforations in the in
cribriform plate
In mammalian anatomy, the cribriform plate (Latin for lit. ''sieve-shaped''), horizontal lamina or lamina cribrosa is part of the ethmoid bone. It is received into the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone and roofs in the nasal cavities. It supp ...
part of the ethmoid bone
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a ...
. The nerve fibres end in the upper nasal cavity.
* The optic nerve (II) passes through the optic foramen
The ''optic foramen'' is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is b ...
in the sphenoid bone as it travels to the eye.
* The oculomotor nerve (III), trochlear nerve (IV), abducens nerve (VI) and the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (V1) travel through the cavernous sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The cave ...
into the superior orbital fissure, passing out of the skull into the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
.
* The maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (V2) passes through foramen rotundum
The foramen rotundum is a circular hole in the sphenoid bone of the skull. It connects the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. It allows for the passage of the maxillary nerve (V2), a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
Structure
T ...
in the sphenoid bone.
* The mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V3) passes through foramen ovale of the sphenoid bone.
* The facial nerve (VII) and vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) both enter the internal auditory canal
The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa ...
in the temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. ...
. The facial nerve then reaches the side of the face by using the stylomastoid foramen, also in the temporal bone. Its fibers then spread out to reach and control all of the muscles of facial expression. The vestibulocochlear nerve reaches the organs that control balance and hearing in the temporal bone and therefore does not reach the external surface of the skull.
* The glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X) and accessory nerve (XI) all leave the skull via the jugular foramen to enter the neck. The glossopharyngeal nerve provides sensation to the upper throat and the back of the tongue, the vagus supplies the muscles in the larynx and continues downward to supply parasympathetic supply to the chest and abdomen. The accessory nerve controls the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles in the neck and shoulder.
*The hypoglossal nerve (XII) exits the skull using the hypoglossal canal in the occipital bone.
Development
The cranial nerves are formed from the contribution of two specialized embryonic cell populations,cranial neural crest
The cranial neural crest is one of the four regions of the neural crest.
The cranial neural crest arises in the anterior and populates the face and the pharyngeal arches giving rise to bones, cartilage, nerves and connective tissue. The endocraniu ...
and ectodermal placodes. The components of the sensory nervous system of the head are derived from the neural crest and from an embryonic cell population developing in close proximity, the cranial sensory placodes (the olfactory, lens, otic, trigeminal, epibranchial and paratympanic placodes). The dual origin cranial nerves are summarized in the following Table:
Contributions of neural crest cells and placodes to ganglia and cranial nerves
Abbreviations: CN, cranial nerve; m, purely motor nerve; mix, mixed nerve (sensory and motor); NC, neural crest; PA, pharyngeal (branchial) arch; r, rhombomere; s, purely sensory nerve. * There is no known ganglion of the accessory nerve. The cranial part of the accessory nerve sends occasional branches to the superior ganglion of the vagus nerve.
Function
The cranial nerves provide motor and sensory supply mainly to the structures within the head and neck. The sensory supply includes both "general" sensation such as temperature and touch, and "special" senses such astaste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste (flavor). Taste is the perception produced or stimulated when a substance in the mouth reacts chemically with taste receptor ...
, vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, smell, balance and hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
. The vagus nerve (X) provides sensory and autonomic (parasympathetic) supply to structures in the neck and also to most of the organs in the chest and abdomen.
Terminal nerve (0)
Theterminal nerve
The terminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve 0 or simply as CN 0, is a nerve that was not included in the seminal classification of the cranial nerves as CN I through CN XII but is now generally classified as a cranial nerve. It was discovered ...
(0) may not have a role in humans, although it has been implicated in hormonal responses to smell, sexual response and mate selection.
Smell (I)
The olfactory nerve (I) conveys information giving rise to the sense of smell. Damage to the olfactory nerve (I) can cause an inability to smell (anosmia
Anosmia, also known as smell blindness, is the loss of the ability to detect one or more smells. Anosmia may be temporary or permanent. It differs from hyposmia, which is a decreased sensitivity to some or all smells.
Anosmia can be due to a nu ...
), a distortion in the sense of smell (parosmia
Parosmia (from the Greek παρά ''pará'' and ὀσμή ''osmḗ'' "smell") is a dysfunctional smell detection characterized by the inability of the brain to correctly identify an odor's "natural" smell. Instead, the natural odor is usually tr ...
), or a distortion or lack of taste.
Vision (II)
Theoptic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
(II) transmits visual information.
Damage to the optic nerve (II) affects specific aspects of vision that depend on the location of the damage. A person may not be able to see objects on their left or right sides ( homonymous hemianopsia), or may have difficulty seeing objects from their outer visual fields ( bitemporal hemianopsia) if the optic chiasm
In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma (; , ), is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrat ...
is involved. Inflammation (optic neuritis
Optic neuritis describes any condition that causes inflammation of the optic nerve; it may be associated with demyelinating diseases, or infectious or inflammatory processes.
It is also known as optic papillitis (when the head of the optic nerv ...
) may impact the sharpness of vision or colour detection
Eye movement (III, IV, VI)
 The oculomotor nerve (III),
The oculomotor nerve (III), trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
(IV) and abducens nerve
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocul ...
(VI) coordinate eye movement
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interest ...
. The oculomotor nerve controls all muscles of the eye except for the superior oblique muscle
The superior oblique muscle, or obliquus oculi superior, is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit (i.e. from beside the nose) which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular mu ...
controlled by the trochlear nerve (IV), and the lateral rectus muscle
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
controlled by the abducens nerve (VI). This means the ability of the eye to look down and inwards is controlled by the trochlear nerve (IV), the ability to look outwards is controlled by the abducens nerve (VI), and all other movements are controlled by the oculomotor nerve (III)
Damage to these nerves may affect the movement of the eye. Damage may result in double vision (diplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced horizontally or vertically in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often v ...
) because the movements of the eyes are not synchronized. Abnormalities of visual movement may also be seen on examination, such as jittering (nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the invol ...
).
Damage to the oculomotor nerve (III) can cause double vision and inability to coordinate the movements of both eyes (strabismus
Strabismus is a vision disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is focused on an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
), also eyelid drooping ( ptosis) and pupil dilation ( mydriasis). Lesions may also lead to inability to open the eye due to paralysis of the levator palpebrae
The levator palpebrae superioris ( la, elevating muscle of upper eyelid) is the muscle in the orbit that elevates the upper eyelid.
Structure
The levator palpebrae superioris originates from inferior surface of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bon ...
muscle. Individuals suffering from a lesion to the oculomotor nerve may compensate by tilting their heads to alleviate symptoms due to paralysis of one or more of the eye muscles it controls.
Damage to the trochlear nerve (IV) can also cause double vision with the eye adducted and elevated. The result will be an eye which can not move downwards properly (especially downwards when in an inward position). This is due to impairment in the superior oblique muscle.
Damage to the abducens nerve (VI) can also result in double vision. This is due to impairment in the lateral rectus muscle, supplied by the abducens nerve.
Trigeminal nerve (V)
Thetrigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chew ...
(V) and its three main branches the ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) provide sensation to the skin of the face and also controls the muscles of chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, th ...
.
Damage to the trigeminal nerve leads to loss of sensation in an affected area. Other conditions affecting the trigeminal nerve (V) include trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, or trifacial neuralgia is a long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as ...
, herpes zoster, sinusitis pain, presence of a dental abscess
A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus associated with a tooth. The most common type of dental abscess is a periapical abscess, and the second most common is a periodontal abscess. In a periapical abscess, usually the origin is a ba ...
, and cluster headache
Cluster headache (CH) is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent severe headaches on one side of the head, typically around the eye(s). There is often accompanying eye watering, nasal congestion, or swelling around the eye on the af ...
s.
Facial expression (VII)
The facial nerve (VII) controls most muscles of facial expression, supplies the sensation of taste from the front two-thirds of the tongue, and controls thestapedius muscle
The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle in the human body. At just over one millimeter in length, its purpose is to stabilize the smallest bone in the body, the stapes or strirrup bone of the middle ear.
Structure
The stapedius emerges from ...
. Most muscles are supplied by the cortex on the opposite side of the brain; the exception is the frontalis muscle
The frontalis muscle () is a muscle which covers parts of the forehead of the skull. Some sources consider the frontalis muscle to be a distinct muscle. However, Terminologia Anatomica currently classifies it as part of the occipitofrontalis muscle ...
of the forehead, in which the left and the right side of the muscle both receive inputs from both sides of the brain.
Damage to the facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste ...
(VII) may cause facial palsy
Facial nerve paralysis is a common problem that involves the paralysis of any structures innervated by the facial nerve. The pathway of the facial nerve is long and relatively convoluted, so there are a number of causes that may result in facial ...
. This is where a person is unable to move the muscles on one or both sides of their face. The most common cause of this is Bell's palsy, the ultimate cause of which is unknown. Patients with Bell's palsy often have a drooping mouth on the affected side and often have trouble chewing because the buccinator muscle
The buccinator () is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head ...
is affected. The facial nerve is also the most commonly affected cranial nerve in blunt trauma.
Hearing and balance (VIII)
Thevestibulocochlear nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the bra ...
(VIII) supplies information relating to balance and hearing via its two branches, the vestibular
The Vestibular (from pt, vestíbulo, "entrance hall") is a competitive examination and is the primary and widespread entrance system used by Brazilian universities to select the students admitted.
The Vestibular usually takes place from Nove ...
and cochlear nerve
The cochlear nerve (also auditory nerve or acoustic nerve) is one of two parts of the vestibulocochlear nerve, a cranial nerve present in amniotes, the other part being the vestibular nerve. The cochlear nerve carries auditory sensory informatio ...
s. The vestibular part is responsible for supplying sensation from the vestibules and semicircular canal
In mathematics (and more specifically geometry), a semicircle is a one-dimensional locus of points that forms half of a circle. The full arc of a semicircle always measures 180° (equivalently, radians, or a half-turn). It has only one line o ...
of the inner ear, including information about balance
Balance or balancing may refer to:
Common meanings
* Balance (ability) in biomechanics
* Balance (accounting)
* Balance or weighing scale
* Balance as in equality or equilibrium
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Balance'' (1983 film), a Bulgaria ...
, and is an important component of the vestibuloocular reflex, which keeps the head stable and allows the eyes to track moving objects. The cochlear nerve transmits information from the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory or ...
, allowing sound to be heard.
When damaged, the vestibular nerve may give rise to the sensation of spinning and dizziness (vertigo
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties w ...
). Function of the vestibular nerve may be tested by putting cold and warm water in the ears and watching eye movements caloric stimulation. Damage to the vestibulocochlear nerve can also present as repetitive and involuntary eye movements (nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the invol ...
), particularly when the eye is moving horizontally. Damage to the cochlear nerve will cause partial or complete deafness
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written ...
in the affected ear.
Oral sensation, taste, and salivation (IX)
 The
The glossopharyngeal nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. ...
(IX) supplies the stylopharyngeus muscle
The stylopharyngeus is a muscle in the head that stretches between the temporal styloid process and the pharynx.
Structure
The stylopharyngeus is a long, slender muscle, cylindrical above, flattened below. It arises from the medial side of the ...
and provides sensation to the oropharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
and back of the tongue. The glossopharyngeal nerve also provides parasympathetic input to the parotid gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the ma ...
.
Damage to the nerve may cause failure of the gag reflex The pharyngeal reflex or gag reflex is a reflex muscular contraction of the back of the throat, evoked by touching the roof of the mouth, the back of the tongue, the area around the tonsils, the uvula, and the back of the throat. It, along with ot ...
; a failure may also be seen in damage to the vagus nerve (X).
Vagus nerve (X)
Thevagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and righ ...
(X) provides sensory and parasympathetic supply to structures in the neck and also to most of the organs in the chest and abdomen.
Loss of function of the vagus nerve (X) will lead to a loss of parasympathetic supply to a very large number of structures. Major effects of damage to the vagus nerve may include a rise in blood pressure and heart rate. Isolated dysfunction of only the vagus nerve is rare, but – if the lesion is located above the point at which the vagus first branches off – can be indicated by a hoarse voice, due to dysfunction of one of its branches, the recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and ...
.
Damage to this nerve may result in difficulties swallowing.
Shoulder elevation and head-turning (XI)
Theaccessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
(XI) supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the ...
s.
Damage to the accessory nerve (XI) will lead to weakness in the trapezius muscle on the same side as the damage. The trapezius lifts the shoulder when shrug
A shrug is a gesture performed by raising both shoulders, and is a representation of an individual either being indifferent about something or not knowing an answer to a question. The shoulder-raising action may be accompanied by rotating the pal ...
ging, so the affected shoulder will not be able to shrug and the shoulder blade (scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on eith ...
) will protrude into a winged position. Depending on the location of the lesion there may also be weakness present in the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which acts to turn the head so that the face points to the opposite side.
Tongue movement (XII)
Thehypoglossal nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by ...
(XII) supplies the intrinsic muscles of the tongue, controlling tongue movement. The hypoglossal nerve (XII) is unique in that it is supplied by the motor cortices of both hemispheres of the brain.
Damage to the nerve may lead to fasciculations or wasting ( atrophy) of the muscles of the tongue. This will lead to weakness of tongue movement on that side. When damaged and extended, the tongue will move towards the weaker or damaged side, as shown in the image. The fasciculations of the tongue are sometimes said to look like a "bag of worms". Damage to the nerve tract or nucleus will not lead to atrophy or fasciculations, but only weakness of the muscles on the same side as the damage.
Clinical significance
Examination
Doctors,neurologist
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
s and other medical professionals may conduct a cranial nerve examination
The cranial nerve exam is a type of neurological examination. It is used to identify problems with the cranial nerves by physical examination. It has nine components. Each test is designed to assess the status of one or more of the twelve cranial ...
as part of a neurological examination
A neurological examination is the assessment of sensory neuron and motor responses, especially reflexes, to determine whether the nervous system is impaired. This typically includes a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical hist ...
to examine the cranial nerves. This is a highly formalised series of steps involving specific tests for each nerve. Dysfunction of a nerve identified during testing may point to a problem with the nerve or of a part of the brain.
A cranial nerve exam starts with observation of the patient, as some cranial nerve lesions may affect the symmetry of the eyes or face. Vision may be tested by examining the visual field
The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments". Or simply, visual field can be defined as the entire area that can be seen when an eye is fixed straight at a point ...
s, or by examining the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
with an ophthalmoscope
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part ...
, using a process known as funduscopy. Visual field testing may be used to pin-point structural lesions in the optic nerve, or further along the visual pathways. Eye movement is tested and abnormalities such as nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the invol ...
are observed for. The sensation of the face is tested, and patients are asked to perform different facial movements, such as puffing out of the cheeks. Hearing is checked by voice and tuning fork
A tuning fork is an acoustic resonator in the form of a two-pronged fork with the prongs ( tines) formed from a U-shaped bar of elastic metal (usually steel). It resonates at a specific constant pitch when set vibrating by striking it agains ...
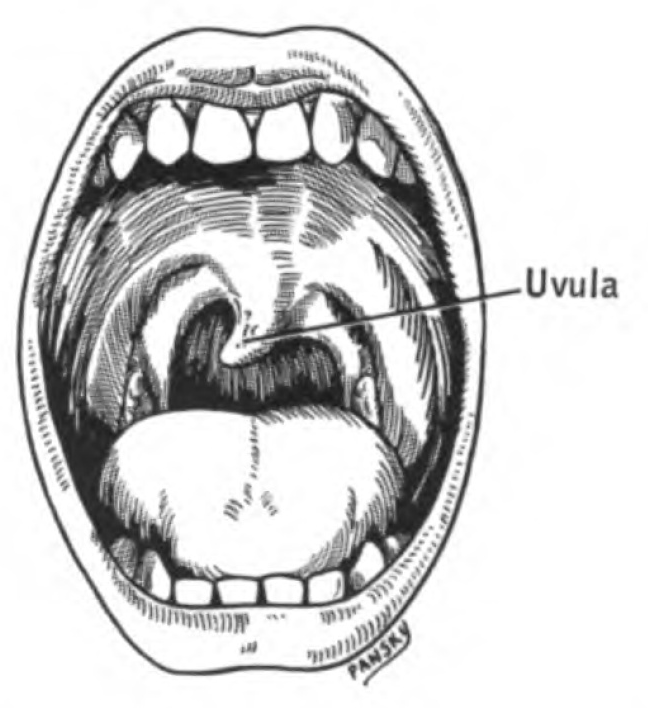
s. The patient's uvula
The palatine uvula, usually referred to as simply the uvula, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers. It also conta ...
is examined. After performing a shrug and head turn, the patient's tongue function is assessed by various tongue movements.
Smell is not routinely tested, but if there is suspicion of a change in the sense of smell, each nostril is tested with substances of known odors such as coffee or soap. Intensely smelling substances, for example ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
, may lead to the activation of pain receptors
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, ...
of the trigeminal nerve (V) located in the nasal cavity and this can confound olfactory testing.
Damage
Compression
Nerves may be compressed because of increasedintracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult ...
, a mass effect
''Mass Effect'' is a military science fiction media franchise created by Casey Hudson, Drew Karpyshyn and Preston Watamaniuk. The franchise depicts a distant future where humanity and several alien civilizations have colonized the known unive ...
of an intracerebral haemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as cerebral bleed, intraparenchymal bleed, and hemorrhagic stroke, or haemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain, into its ventricles, or into both. It is one kind of bleed ...
, or tumour that presses against the nerves and interferes with the transmission of impulses along the nerve. Loss of function of a cranial nerve may sometimes be the first symptom of an intracranial
The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull minus the mandible is called the ''cranium''. The cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in ...
or skull base
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Structure
Structures found at the base of the skull are for ...
cancer.
An increase in intracranial pressure may lead to impairment of the optic nerves (II) due to compression of the surrounding veins and capillaries, causing swelling of the eyeball ( papilloedema). A cancer, such as an optic nerve glioma
Optic nerve glioma (or optic glioma), a form of glioma which affects the optic nerve, is often one of the central nervous system manifestations of neurofibromatosis 1.
Optic gliomas are usually pilocytic tumors, and can involve the optic nerve o ...
, may also impact the optic nerve (II). A pituitary tumour
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.optic chiasm
In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma (; , ), is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrat ...
of the optic nerve (II), leading to visual field loss. A pituitary tumour may also extend into the cavernous sinus, compressing the oculuomotor nerve (III), trochlear nerve (IV) and abducens nerve (VI), leading to double-vision and strabismus
Strabismus is a vision disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is focused on an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
. These nerves may also be affected by herniation of the temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pro ...
s of the brain through the falx cerebri
The falx cerebri (also known as the cerebral falx) is a large, crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that descends vertically into the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres of the human brain,Saladin K. "Anatomy & Physiology: The Uni ...
.
The cause of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, or trifacial neuralgia is a long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as ...
, in which one side of the face is exquisitely painful, is thought to be compression of the nerve by an artery as the nerve emerges from the brain stem. An acoustic neuroma
A vestibular schwannoma (VS), also called acoustic neuroma, is a benign tumor that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve that passes from the inner ear to the brain. The tumor originates when Schwann cells that form the insulating myelin sheath ...
, particularly at the junction between the pons and medulla, may compress the facial nerve (VII) and vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII), leading to hearing and sensory loss on the affected side.
Stroke
Occlusion of blood vessels that supply the nerves or their nuclei, anischemic
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems w ...
stroke, may cause specific signs and symptoms relating to the damaged area. If there is a stroke of the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
, pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
or medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
, various cranial nerves may be damaged, resulting in dysfunction and symptoms of a number of different syndromes. Thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (t ...
, such as a cavernous sinus thrombosis
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The ca ...
, refers to a clot (thrombus
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of ...
) affecting the venous drainage from the cavernous sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The cave ...
, affects the optic (II), oculomotor (III), trochlear (IV), opthalamic branch of the trigeminal nerve (V1) and the abducens nerve (VI).
Inflammation
Inflammation of a cranial nerve can occur as a result of infection, such as viral causes like reactivated herpes simplex virus, or can occur spontaneously. Inflammation of the facial nerve (VII) may result in Bell's palsy. Multiple sclerosis, an inflammatory process resulting in a loss of themyelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
sheathes which surround the cranial nerves, may cause a variety of shifting symptoms affecting multiple cranial nerves. Inflammation may also affect other cranial nerves. Other rarer inflammatory causes affecting the function of multiple cranial nerves include sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly a ...
, miliary tuberculosis
To disseminate (from lat. ''disseminare'' "scattering seeds"), in the field of communication, is to broadcast a message to the public without direct feedback from the audience.
Meaning
Dissemination takes on the theory of the traditional vie ...
, and inflammation of arteries, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), previously known as Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), is a rare long-term systemic disorder that involves the formation of granulomas and inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis). It is a form of vasculitis ...
.
Other
Trauma to the skull, disease of bone, such as Paget's disease, and injury to nerves during surgery are other causes of nerve damage.History
The Graeco-Roman anatomistGalen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one ...
(AD 129–210) named seven pairs of cranial nerves. Much later, in 1664, English anatomist Sir Thomas Willis
Thomas Willis FRS (27 January 1621 – 11 November 1675) was an English doctor who played an important part in the history of anatomy, neurology and psychiatry, and was a founding member of the Royal Society.
Life
Willis was born on his pare ...
suggested that there were actually 9 pairs of nerves. Finally, in 1778, German anatomist Samuel Soemmering named the 12 pairs of nerves that are generally accepted today. However, because many of the nerves emerge from the brain stem as rootlets, there is continual debate as to how many nerves there actually are, and how they should be grouped. For example, there is reason to consider both the olfactory (I) and optic (II) nerves to be brain tracts, rather than cranial nerves.
Other animals
Cranial nerves are also present in othervertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s. Other amniotes (non- amphibian tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s) have cranial nerves similar to those of humans. In anamniote
The anamniotes are an informal group of craniates comprising all fishes and amphibians, which lay their eggs in aquatic environments. They are distinguished from the amniotes (reptiles, birds and mammals), which can reproduce on dry land either ...
s (fishes and amphibians), the accessory nerve (XI) and hypoglossal nerve (XII) do not exist, with the accessory nerve (XI) being an integral part of the vagus nerve (X); the hypoglossal nerve (XII) is represented by a variable number of spinal nerves emerging from vertebral segments fused into the occiput. These two nerves only became discrete nerves in the ancestors of amniotes. The very small terminal nerve
The terminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve 0 or simply as CN 0, is a nerve that was not included in the seminal classification of the cranial nerves as CN I through CN XII but is now generally classified as a cranial nerve. It was discovered ...
(nerve N or O) exists in humans but may not be functional. In other animals, it appears to be important to sexual receptivity based on perceptions of pheromones
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
.
sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated ...
's brain. The exits of the various cranial nerves are marked with red.
See also
* Cranial nerve mnemonicsReferences
External links
{{Authority control