|
Cavernous Sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica. Structure The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses of the head. It is a network of veins that sit in a cavity. It sits on both sides of the sphenoidal bone and pituitary gland, approximately 1 × 2 cm in size in an adult. The carotid siphon of the internal carotid artery, and cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI all pass through this blood filled space. Both sides of cavernous sinus is connected to each other via intercavernous sinuses. The cavernous sinus lies in between the inner and outer layers of dura mater. Nearby structures * Above: optic tract, optic chiasma, internal carotid artery. * Inferiorly: foramen lacerum, and the junction of the body and greater wing of sphenoid bone. * Medially: pituitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Cerebral Vein
The middle cerebral veins are the superficial middle cerebral vein and the deep middle cerebral vein. * The superficial middle cerebral vein (superficial Sylvian vein) begins on the lateral surface of the hemisphere, running along the lateral sulcus, and ends either in the cavernous sinus or the sphenoparietal sinus. * The deep middle cerebral vein (deep Sylvian vein) receives tributaries from the insula and neighboring gyri, and runs in the lower part of the lateral sulcus. Connections The superficial middle cerebral vein is connected: # with the superior sagittal sinus by the superior anastomotic vein (vein of Trolard) where the latter opens into one of the superior cerebral veins; # with the transverse sinus by the inferior anastomotic vein (vein of Labbé) which courses over the temporal lobe The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Tract
In neuroanatomy, the optic tract () is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. It is composed of two individual tracts, the left optic tract and the right optic tract, each of which conveys visual information exclusive to its respective contralateral half of the visual field. Each of these tracts is derived from a combination of temporal and nasal retinal fibers from each eye that corresponds to one half of the visual field. In more specific terms, the optic tract contains fibers from the ipsilateral temporal hemiretina and contralateral nasal hemiretina. Visual system The optic tract carries retinal information relating to the whole visual field. Specifically, the left optic tract corresponds to the right visual field, while the right optic tract corresponds to the left visual field. To form the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Middle Cerebral Vein
The middle cerebral veins are the superficial middle cerebral vein and the deep middle cerebral vein. * The superficial middle cerebral vein (superficial Sylvian vein) begins on the lateral surface of the hemisphere, running along the lateral sulcus, and ends either in the cavernous sinus or the sphenoparietal sinus. * The deep middle cerebral vein (deep Sylvian vein) receives tributaries from the insula and neighboring gyri, and runs in the lower part of the lateral sulcus. Connections The superficial middle cerebral vein is connected: # with the superior sagittal sinus by the superior anastomotic vein (vein of Trolard) where the latter opens into one of the superior cerebral veins; # with the transverse sinus by the inferior anastomotic vein (vein of Labbé) which courses over the temporal lobe The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoparietal Sinus
The sphenoparietal sinus is a paired dural venous sinus situated along the posterior edge of the lesser wing of either sphenoid bone. It drains into the cavernous sinus. Anatomy A sphenoparietal sinus is situated under each lesser wing of the sphenoid bone near the posterior edge of this bone, between the anterior cranial fossa and middle cranial fossa. It terminates by draining into the anterior part of the cavernous sinus. Tributaries A sphenoparietal sinus receives small veins from the adjacent dura and sometimes the frontal ramus of the middle meningeal vein, communicating rami from the superficial middle cerebral vein, temporal lobe veins, and the anterior temporal diploic veins The diploic veins are large, thin-walled valveless veins that channel in the diploë between the inner and outer layers of the cortical bone in the skull. They are lined by a single layer of endothelium supported by elastic tissue. They develop fu .... References Additional images File:Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Ophthalmic Vein
The inferior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. It begins from a venous network in the front of the orbit, then passes backwards through the lower orbit. It drains several structures of the orbit. It may end by splitting into two branches, one draining into the pterygoid venous plexus and the other ultimately (i.e. directly or indirectly) into the cavernous sinus. Structure The inferior ophthalmic vein - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. Origin The inferior ophthalmic vein originates from a venous network at the anterior part of the floor and anterior part of the medial wall of the orbit. Course The inferior ophthalmic vein passes posterior-ward through the inferior orbit. Distribution The inferior ophthalmic vein drains venous blood from the inferior rectus muscle, inferior oblique muscle, later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Ophthalmic Vein
The superior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. It is fromed by the union of the angular vein, and supraorbital vein. It passes backwards within the orbit alongside the ophthalmic artery, then exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to drain into the cavernous sinus. The superior ophthalmic vein can be a path for the spread of infection from the danger triangle of the face to the cavernous sinus and the pterygoid plexus. It may also be affected by an arteriovenous fistula of the cavernous sinus. Structure The superior ophthalmic vein - together with the inferior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit (with the superior ophthalmic vein being the larger of the two). The superior ophthalmic vein drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. The superior ophthalmic vein is the largest and the most consistently present vein of the orbit. It usually measures 2-10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrous Temporal Bone
The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word ''petrosus'', meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. The petrous bone is important for studies of ancient DNA from skeletal remains, as it tends to contain extremely well-preserved DNA. Base The base is fused with the internal surfaces of the squamous and mastoid parts. Apex The apex, which is rough and uneven, is received into the angular interval between the posterior border of the great wing of the sphenoid bone and the basilar part of the occipital bone; it presents the anterior or internal openin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Orbital Fissure
The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives passage to multiple structures, including the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, ophthalmic nerve, abducens nerve, ophthalmic veins, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus. Structure The superior orbital fissure is usually 22 mm wide in adults, and is much larger medially. Its boundaries are formed by the (caudal surface of the) lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, and (medial border of the) greater wing of the sphenoid bone. Contents The superior orbital fissure is traversed by the following structures: * (superior and inferior divisions of the) oculomotor nerve (CN III) * trochlear nerve (CN IV) * lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) * abducens nerve (CN VI) * superior ophthalmic vein and superior division of the inferior ophthalmic vein * sympathetic fibres from the cavernous nerve pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncus
The uncus is an anterior extremity of the parahippocampal gyrus. It is separated from the apex of the temporal lobe by a slight fissure called the incisura temporalis (also called rhinal sulcus). Although superficially continuous with the hippocampal gyrus, the uncus forms morphologically a part of the rhinencephalon. An important landmark that crosses the inferior surface of the uncus is the band of Giacomini. The term comes from the Latin word uncus, meaning ''hook'', and it was coined by Félix Vicq-d'Azyr (1748–1794).JC Tamraz, YG Comair. Atlas of Regional Anatomy of the Brain Using MRI (2006), p 8. Clinical significance The part of the olfactory cortex that is on the temporal lobe covers the area of the uncus, which leads into the two significant clinical aspects of the uncus: uncinate fits and uncal herniations. * Seizures, often preceded by hallucinations of disagreeable odors, often originate in the uncus. * In situations of tumor, hemorrhage, or edema, increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure The temporal lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative (denotative) or explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). Medial temporal lobe structures that are critical for long-term memory include the hippocampus, along with the surrounding hippocampal region consisting of the perirhinal, parahippocampal, and entorhinal neocortical regions. The hippocampus is critical for memory formation, and the surrounding medial temporal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
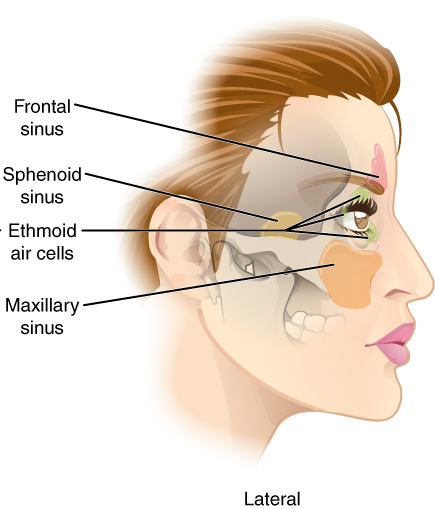
Sphenoidal Air Sinus
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus occurring within the within the body of the sphenoid bone. It represents one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 64 The pair of sphenoid sinuses are separated in the middle by a septum of sphenoid sinuses. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical. Anatomy On average, a sphenoid sinus measures 2.2 cm vertical height, 2 cm in transverse breadth; and 2.2 cm antero-posterior depth. Each spehoid sinus is contained within the body of sphenoid bone, being situated just inferior to the sella turcica. The two sphenoid sinuses are separated medially by the septum of sphenoidal sinuses (which is usually asymmetrical). An opening of sphenoidal sinus forms a passage between each sphenoidal sinus, and the nasal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophysis Cerebri
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity (sella turcica) covered by a dural fold (diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland help to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |