|
Desmodium Triflorum
''Grona triflora'', known as creeping tick trefoil or three-flower beggarweed, is a plant in the family Fabaceae. It is native to tropical regions around the globe and introduced to subtropical regions including the southern United States. File:Desmodium triflorum in Kadavoor.jpg, Foliage File:Desmodium triflorum fruit and seeds.jpg, Fruit and seeds File:Desmodium triflorum at Peradeniya Royal Botanical Garden.jpg, At Peradeniya Royal Botanical Garden Phytochemicals ''Grona triflora'' (''Desmodium triflorum'') contains alkaloids including ''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptophan methyl ester, dimethyltryptamine-''N''-oxide, hypaphorine (structurally related to plakohypaphorine), phenylethylamine, hordenine, tyramine Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood ..., and trigonelline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Thiruvithamkoor. Spread over , Kerala is the 21st largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 census, Kerala is the 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the first prominent kingdom based in Kerala. The Ay kingdom in the deep south and the Ezhimala kingdom in the north formed the other kingdoms in the early years of the Common Era (CE). The region had been a prominent spic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabaceae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. Article 18.5 states: "The following names, of long usage, are treated as validly published: ....Leguminosae (nom. alt.: Fabaceae; type: Faba Mill. Vicia L.; ... When the Papilionaceae are regarded as a family distinct from the remainder of the Leguminosae, the name Papilionaceae is conserved against Leguminosae." English pronunciations are as follows: , and . commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, are a large and agriculturally important of |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. It is essential in humans, meaning that the body cannot synthesize it and it must be obtained from the diet. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3. It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Function Amino acids, including tryptophan, are used as building blocks in protein biosynthesis, and proteins are required to sustain life. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyltryptamine-N-oxide
Dimethyltryptamine-''N''-oxide (DMT-''N''-oxide) is a dimethyltryptamine metabolite In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c .... References Tryptamines Amine oxides {{amine-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plakohypaphorine
Plakohypaphorines are halogenated indolic non-proteinogenic amino acids named for their similarity to hypaphorine (''N,N,N''-trimethyltryptophan). First reported in the Caribbean sponge Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate throug ... ''Plakortis simplex'' in 2003, plakohypaphorines A-C were the first iodine-containing indoles to be discovered in nature. Plakohypaphorines D-F, also found in ''P. simplex'', were reported in 2004 by a group including the researchers who discovered the original plakohypaphorines. References *Taglialatela-Scafati Orazio et al., 2003. ''Plakohypaphorines A-C, Iodine-Containing Alkaloids from the Caribbean Sponge'' Plakortis simplex. European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2003(2), pp. 284–287. *Borrelli, Francesca, et al., 2004. ''Iodinated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation. Phenethylamine is sold as a dietary supplement for purported mood and weight loss-related therapeutic benefits; however, in orally ingested phenethylamine, a significant amount is metabolized in the small intestine by monoamine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hordenine
Hordenine is an alkaloid of the phenethylamine class that occurs naturally in a variety of plants, taking its name from one of the most common, barley (''Hordeum'' species). Chemically, hordenine is the ''N''-methyl derivative (chemistry), derivative of N-Methyltyramine, ''N''-methyltyramine, and the ''N'',''N''-dimethyl derivative of the well-known biogenic amine tyramine, from which it is biosynthetically derived and with which it shares some pharmacological properties (see below). , hordenine is widely sold as an ingredient of nutritional supplements, with the claims that it is a stimulant of the central nervous system, and has the ability to promote weight loss by enhancing metabolism. In experimental animals, given sufficiently large doses parenterally (by injection), hordenine does produce an increase in blood pressure, as well as other disturbances of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous systems. These effects are generally not reproduced by oral administration of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
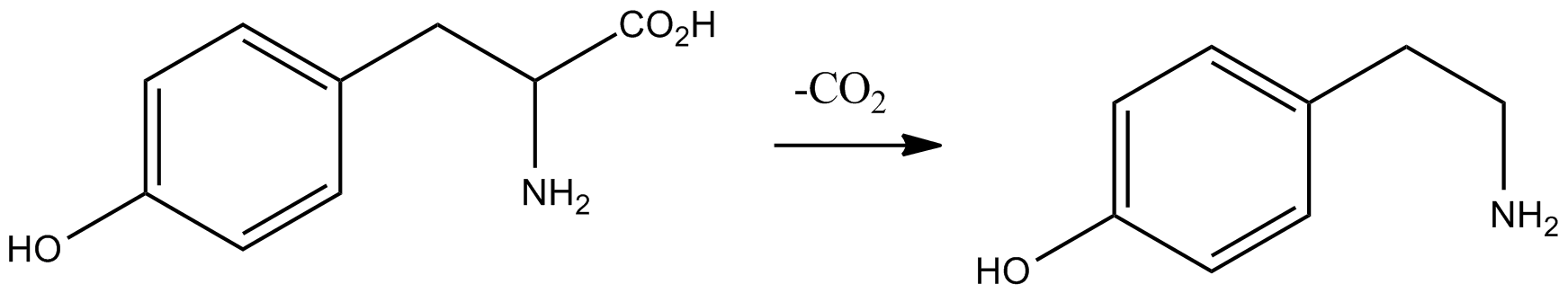
Tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Occurrence Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals, and is metabolized by various enzymes, including monoamine oxidases. In foods, it often is produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay. Foods that are fermented, cured, pickled, aged, or spoiled have high amounts of tyramine. Tyramine levels go up when foods are at room temperature or go past their freshness date. Specific foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include: * strong or ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonelline
Trigonelline is an alkaloid with chemical formula . It is a zwitterion formed by the methylation of the nitrogen atom of niacin (vitamin B3). Trigonelline is a product of niacin metabolism that is excreted in urine of mammals. Trigonelline occurs in many plants. It has been isolated from the Japanese radish (''Raphanus sativus'' cv. Sakurajima Daikon), fenugreek seeds (''Trigonella foenum-graecum'', hence the name), garden peas, hemp seed, oats, potatoes, ''Stachys'' species, dahlia, ''Strophanthus'' species, and ''Dichapetalum cymosum''. Trigonelline is also found in coffee. Higher levels of trigonelline is found in arabica coffee. Holtz, Kutscher, and Theilmann have recorded its presence in a number of animals. Chemistry Trigonelline crystallizes as a monohydrate from alcohol in hygroscopic prisms (m.p. 130 °C or 218 °C 'dry, dec.''. It is readily soluble in water or warm alcohol, less so in cold alcohol, and slightly so in chloroform or ether. The salts c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmodium
''Desmodium'' is a genus of plants in the legume family Fabaceae, sometimes called tick-trefoil, tick clover, hitch hikers or beggar lice. There are dozens of species and the delimitation of the genus has shifted much over time. These are mostly inconspicuous plants; few have bright or large flowers. Though some can become sizeable plants, most are herbs or small shrubs. Their fruit are loments, meaning each seed is dispersed individually enclosed in its segment. This makes them tenacious plants and some species are considered weeds in places. They have a variety of uses. Uses Several ''Desmodium'' species contain potent secondary metabolites that are released into the soil and aerially. Allelopathic compounds are used in agriculture in push-pull technology: ''Desmodium heterocarpon'', ''Desmodium intortum'', and ''Desmodium uncinatum'' are inter-cropped in maize and sorghum fields to repel ''Chilo partellus'', a stem-boring grass moth, and suppress witchweeds, including As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. An internationally important botanical research and education institution, it employs 1,100 staff. Its board of trustees is chaired by Dame Amelia Fawcett. The organisation manages botanic gardens at Kew in Richmond upon Thames in south-west London, and at Wakehurst, a National Trust property in Sussex which is home to the internationally important Millennium Seed Bank, whose scientists work with partner organisations in more than 95 countries. Kew, jointly with the Forestry Commission, founded Bedgebury National Pinetum in Kent in 1923, specialising in growing conifers. In 1994, the Castle Howard Arboretum Trust, which runs the Yorkshire Arboretum, was formed as a partnership between Kew and the Castle Howard Estate. In 2019, the organisation had 2,316,699 public visitors at Kew, and 312,813 at Wakehurst. Its site at Kew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |