|
Denbigh, Ruthin And Corwen Railway
The Denbigh, Ruthin and Corwen Railway was a standard gauge railway line that connected Corwen with Denbigh via Ruthin in North Wales. The line was promoted independently as part of rivalry between the London and North Western Railway and the Great Western Railway for access to Rhyl. It opened in stages from 1862 to 1865, and was worked by the LNWR, and vested in that company in 1879. The line was never busy, serving a rural community, and it was closed to passenger traffic in 1962, and completely in 1965. Conception The Chester and Holyhead Railway completed its main line in 1850, transforming the transport environment in North Wales; however its main focus at opening was the Irish Mail traffic rather than local traffic. It allied itself with routes to London via Crewe, and shortly merged with other lines to form the London and North Western Railway, in 1858.Peter E Baughan, ''A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: 14: North and Mid Wales'', David St John Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vale Of Clwyd Railway
The Vale of Clwyd Railway (VoCR) was a standard-gauge line which connected the towns of Rhyl and Denbigh via St Asaph in North Wales. It opened in 1858, at first without a connection to the main line at Rhyl, but this was provided in 1862. At Denbigh the line later connected to other lines. Although the area became popular with holidaymakers in the 1920s and later, the line never realised its potential, and it closed to passengers in 1955, and completely in 1968. Conception The Chester and Holyhead Railway completed its main line in 1850. There was a considerable area of agricultural land south of the line, towards Denbigh, and a number of schemes were put forward to serve the area. The C&HR found itself short of funds to complete its main line, so it was left to independent promoters to put a scheme forward. This proved to be the Vale of Clwyd Railway, which was authorised by Parliament on 23 June 1856. Contracts for construction were awarded to David Davies and Thomas Sav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ... with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of —later slightly widened to —but, from 1854, a series of Consolidation (business), amalgamations saw it also operate Standard gauge, standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892. The GWR was the only company to keep its identity through the Railways Act 1921, which ama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Cuts
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
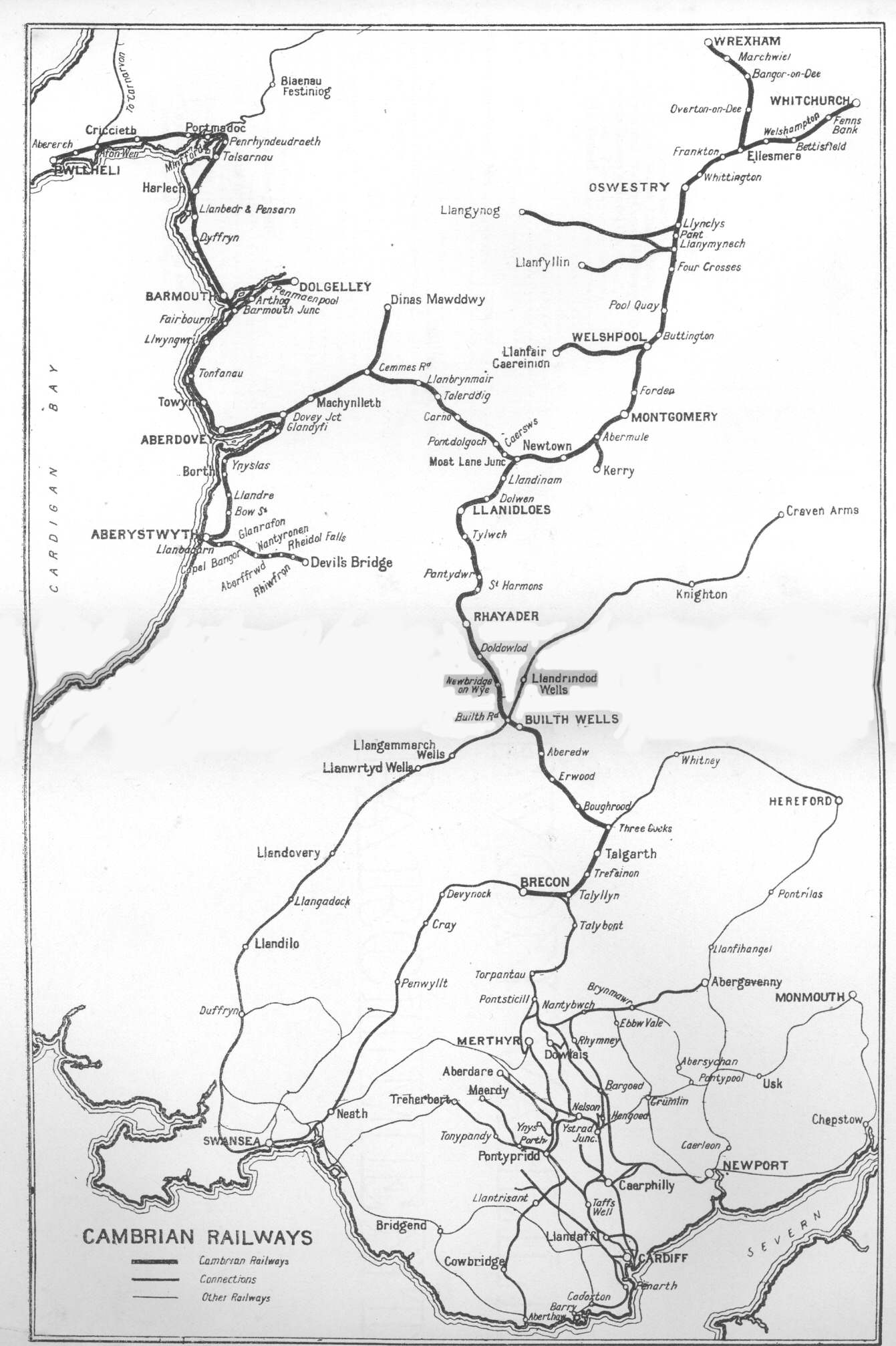
Cambrian Railways
The Cambrian Railways owned of track over a large area of mid Wales. The system was an amalgamation of a number of railways that were incorporated in 1864, 1865 and 1904. The Cambrian connected with two larger railways with connections to the northwest of England via the London and North Western Railway, and the Great Western Railway for connections between London and Wales. The Cambrian Railways amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1922 as a result of the Railways Act 1921. The name is continued today in the route known as the Cambrian Line. History Creation of the Cambrian Railways: 1864 The Cambrian Railways Company was created on 25 July 1864 when the Cambrian Railways Act of Parliament received Royal Assent. The company was formed by amalgamating most of the railway companies in mid Wales: the Oswestry and Newtown Railway, the Llanidloes and Newtown Railway, the Newtown and Machynlleth Railway and the Oswestry, Ellesmere and Whitchurch Railway. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for International Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of all matters relating to Trade and Foreign Plantations, but is commonly known as the Board of Trade, and formerly known as the Lords of Trade and Plantations or Lords of Trade, and it has been a committee of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom. The board has gone through several evolutions, beginning with extensive involvement in colonial matters in the 17th century, to powerful regulatory functions in the Victorian Era and early 20th century. It was virtually dormant in the last third of 20th century. In 2017, it was revitalised as an advisory board headed by the International Trade Secretary who has nominally held the title of President of the Board of Trade, and who at present is the only privy counsellor of the board, the other m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Savin
Thomas Savin (1826 – 23 July 1889) was a British railway engineer who was the contractor who built many railways in Wales and the Welsh borders from 1857 to 1866. He also in some cases was an investor in such schemes. Early life Savin was born in Shropshire at Llwynymaen near Oswestry in 1826. He married in 1852 Eliza Hughes with whom he had two sons who survived him. He initially worked in Oswestry running a mercery business in partnership with Edward Morris, who subsequently purchased then sold the Van lead mines. Railway contractor In 1857 Savin formed a partnership with David Davies to build the Vale of Clwyd Railway. The partnership was the principal contractor for many of the lines that became the Cambrian Railways. The partnership was dissolved in 1860. He also had an interest in or worked on a number of secondary and minor railways, including the Oswestry and Newtown Railway, Brecon and Merthyr Tydfil Junction Railway, the Hereford, Hay and Brecon Railway, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Davies (industrialist)
David Davies (18 December 1818 – 20 July 1890) was a Welsh industrialist and Liberal politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1874 and 1886. Davies was often known as David Davies Llandinam (from the place of his birth, Llandinam in Montgomeryshire). Ivor Bulmer-Thomas: ''Top Sawyer: David Davies of Llandinam'' (Golden Grove, Carmarthen, 1988) He is best remembered today for founding Barry Docks. Early life Davies was the son of David Davies and his wife Elizabeth and the eldest of nine children. He attended the day school at Llandinam but was primarily self-educated. He began work as a sawyer and went into agriculture, working alongside his father, who died when David was aged 20, leaving him to take charge of the family. He was successful from an early age and in 1848 took over a larger farm called Tynymaen, which later became the home farm of the Plasdinam estate. Two years later he took over a further holding, Gwerneirin. Early business career His first en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llangollen And Corwen Railway
The Llangollen and Corwen Railway was formed as a continuation of the Vale of Llangollen Railway to continue the line along the Dee Valley a further to Corwen. This was opened on 1 May 1865 and was worked by the Great Western Railway and subsequently the Western Region of British Railways. It survives today, and is operated as the heritage Llangollen Railway The Llangollen Railway () is a volunteer-run heritage railway in Denbighshire, North Wales, which operates between Llangollen and Corwen. The standard gauge line, which is long, runs on part of the former Ruabon – Barmouth GWR route that .... References See also * Ruabon to Barmouth Line Railway lines in Wales Early Welsh railway companies Railway lines opened in 1865 {{UK-rail-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruabon
Ruabon ( cy, Rhiwabon ) is a village and community in Wrexham County Borough, Wales. The name comes from ''Rhiw Fabon'', ''rhiw'' being the Welsh word for "slope" or "hillside" and ''Fabon'' being a mutation from St Mabon, the original church name, of earlier, Celtic origin. An older English spelling, ''Rhuabon'', can sometimes be seen. In 2001, more than 80% of the population of 2,400 were born in Wales, with 13.6% having some ability in Welsh. Early history There is evidence that a settlement existed in Ruabon in the Bronze Age. In 1898, building works in the centre of Ruabon exposed a cist or stone urn containing cremated human remains dating from 2000 years BC. In 1917, the remains of a Bronze Age round barrow were discovered on the playing fields of Ruabon Grammar School; they contained human remains, a flint arrowhead and a bronze axe. Overlooking Ruabon, the Gardden ( cy, Caer Ddin) is an ancient hillfort surrounded by circular ditches, dating back to the Iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vale Of Llangollen Railway
The Vale of Llangollen Railway was built as a spur from the Shrewsbury and Chester Railway south of Ruabon to the town of Llangollen. The line was built along the northern side of the Dee Valley and authorized by an Act of Parliament on 1 August 1859. It was initially opened for goods only on 1 December 1861 and to passenger traffic on 2 June 1862, and was worked from the outset by the Great Western Railway. The line ran from Llangollen Line Junction (0 miles 54 chains) and served Acrefair, Trevor (and Sun Bank Halt Sun Bank Halt in Wrexham County Borough, Wales, was a minor station on the Ruabon to Barmouth line. It opened as Garth & Sun Bank Halt but was renamed on 1 July 1906. The line was double track and there was never a signal box nor freight facili ... from 1905), before terminating at a temporary station in the east of Llangollen. In 1865 the line was extended by another Great Western Railway-backed line, the Llangollen & Corwen Railway, with the line using a new p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury And Chester Railway
The North Wales Mineral Railway was formed to carry coal and ironstone from the mineral-bearing area around Wrexham to the River Dee wharves. It was extended to run from Shrewsbury and formed part of a main line trunk route, under the title The Shrewsbury and Chester Railway. It opened in 1846 from Chester to Ruabon, and in 1848 from Ruabon to Shrewsbury. It later merged with the Great Western Railway. Much of its main line ran through rural areas, but the important mineral area west of Wrexham, and also near Ruabon, led to considerable development of mineral business. A dense network of branches to access pits and ironworks built up, although the hilly terrain made railway construction difficult. At the end of the nineteenth century passenger services were put on for the mining communities. The main line business developed too, enabling the GWR to access the Mersey, from London and from South Wales, and a heavy long-distance mineral flow built up. That traffic dwindled steep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crewe
Crewe () is a railway town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire East in Cheshire, England. The Crewe built-up area had a total population of 75,556 in 2011, which also covers parts of the adjacent civil parishes of Willaston, Shavington cum Gresty and Wistaston. Crewe is perhaps best known as a large railway junction and home to Crewe Works; for many years, it was a major railway engineering facility for manufacturing and overhauling locomotives, but now much reduced in size. From 1946 until 2002, it was also the home of Rolls-Royce motor car production. The Pyms Lane factory on the west of the town now exclusively produces Bentley motor cars. Crewe is north of London, south of Manchester city centre, and south of Liverpool city centre. History Medieval The name derives from an Old Welsh word ''criu'', meaning 'weir' or 'crossing'. The earliest record is in the Domesday Book, where it is written as ''Creu''. Modern Until the Grand Junction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |