|
Deltics
{{disambig ...
Deltic may refer to: * Napier Deltic, a diesel engine ** British Rail DP1 ("Deltic") a prototype locomotive built by English Electric fitted with the Deltic Engine ** British Rail Class 55, production locomotives powered by Deltic engines ** British Rail Class 23, "Baby Deltic" production locomotives powered by Deltic engines ** Deltic Preservation Society * Deltic acid, a chemical whose molecular backbone resembles the Greek letter delta (Δ) See also * ''Deltics'', a music album by Chris Rea * Deltoid (other) * Deltate (other) * River delta * Delta (letter) Delta (; uppercase Δ, lowercase δ or 𝛿; el, δέλτα, ''délta'', ) is the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 4. It was derived from the Phoenician letter dalet 𐤃. Letters that come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 55
The British Rail Class 55, also known as a Deltic, or English Electric type 5, is a class of diesel locomotive built in 1961 and 1962 by English Electric for British Railways. They were designed for the high-speed express passenger services on the East Coast Main Line (ECML) between Edinburgh and . They gained the name "Deltic" from the prototype locomotive, DP1 ''Deltic'' (the running number DP1 was never carried), which in turn was named after its Napier Deltic power units. At the time of their introduction into service, the Class 55s were the most powerful single-unit diesel locomotives in the world, with a power output of . They had an official maximum speed of , however this was frequently exceeded, especially in their later years of service, with speeds of up to , being recorded on level gradients, and up to whilst descending Stoke Bank. Twenty-two locomotives were built, which were used for express passenger services on the ECML, particularly from London to and Edinburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 23
The British Rail Class 23 were a class of ten Bo-Bo diesel-electric locomotives built by the English Electric Company (EE) in 1959. The power unit used was a Napier Deltic T9-29 9-cylinder engine of driving an EE generator, which powered the four traction motors. They were numbered from D5900 to D5909. The T9-29 diesel engine was a single, half-sized version of those used in the more powerful British Rail Class 55 'Deltic' locomotives, and the overall design and external appearance of the Class 23 was also similar to the Class 55, but much shorter, leading to their nickname of ''Baby Deltics''. Introduction and service history On initial completion, the first locomotives were found to weigh over the specification weight of . A programme of lightening was begun: some of this involved cutting circular lightening holes into the bogie frames, and replacing steel buffer beams or roof panels with aluminium. Much of the over-weight was due to ancillary components, particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Deltic
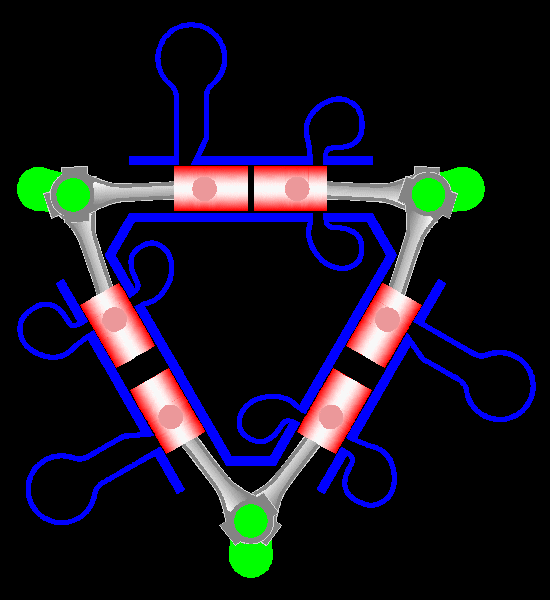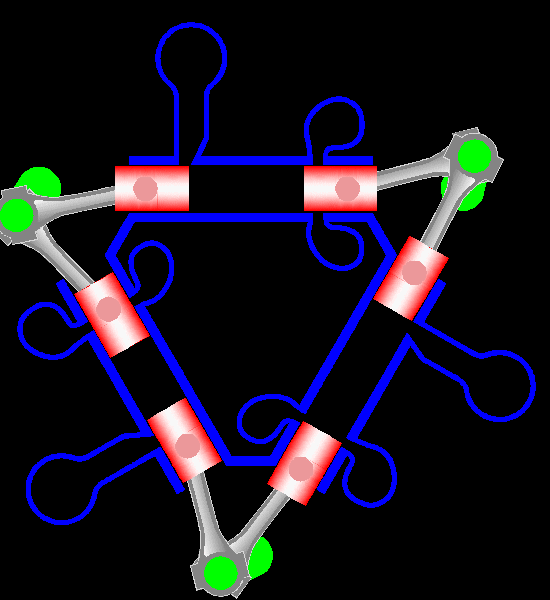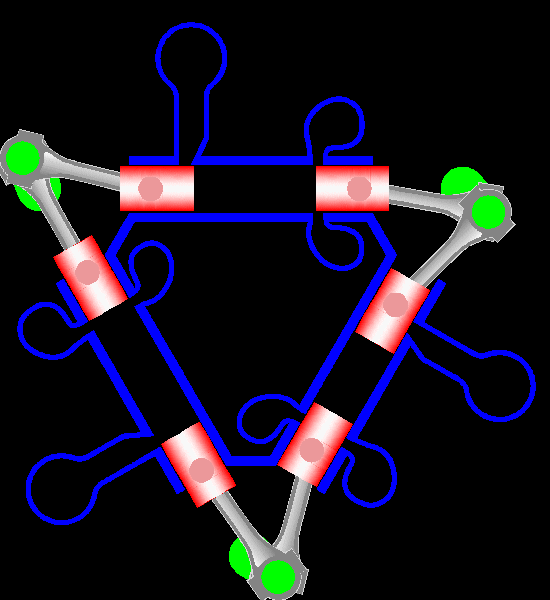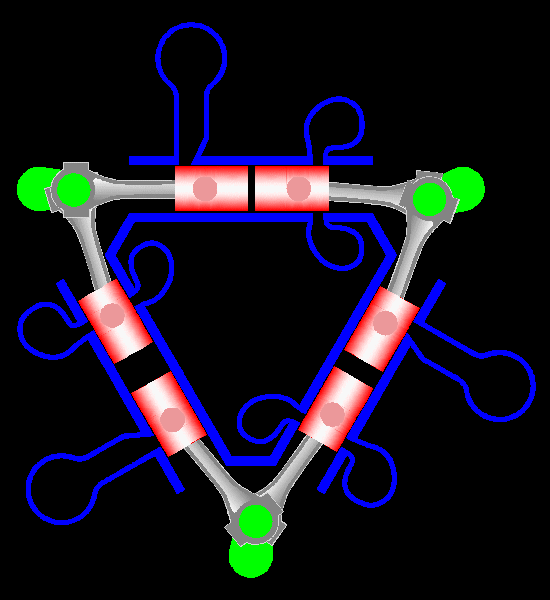
The Napier Deltic engine is a British opposed-piston valveless, supercharged uniflow scavenged, two-stroke diesel engine used in marine and locomotive applications, designed and produced by D. Napier & Son. Unusually, the cylinders were disposed in a three-bank triangle, with a crankshaft at each corner of the triangle. The term Deltic (meaning "in the form of the Greek letter (capital) delta") is used to refer to both the Deltic E.130 opposed-piston, high-speed diesel engine and the locomotives produced by English Electric using these engines, including its demonstrator locomotive named ''DELTIC'' and the production version for British Railways, which designated these as (TOPS) Class 55. A single, half-sized, turbocharged Deltic power unit also featured in the English Electric-built Type 2 locomotive, designated as the Class 23. Both locomotive and engine became better known as the "Baby Deltic". History and design The Deltic story began in 1943 when the British Admiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail DP1
English Electric DP1, commonly known as ''Deltic'', is a prototype demonstrator locomotive employing two Napier Deltic engines, built by English Electric in 1955. The high power of the locomotive at an acceptably low axleload resulted in 22 similar locomotives being ordered by British Railways for use on East Coast Main Line express passenger services, the serial production of which became the British Rail Class 55. Background and design The English Electric company, which had absorbed the engine-maker Napier & Son into its group at the instruction of the Ministry of Aircraft Production in 1942, was a major builder of diesel and electric locomotives. The two George Nelsons (Sir George, and his son, known in the works as "Half") saw the potential of Napier's Deltic engine for rail traction and in 1954–1955 built a demonstrator at its Dick, Kerr works in Preston. Officially numbered DP1, its internal project title was ''Enterprise'', and it was intended that the locomotive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltic Preservation Society
The Deltic Preservation Society is a railway preservation group based in England. The society is dedicated to the preservation and restoration of the remaining Class 55 "Deltic" diesel locomotives operated by British Rail from the 1960s to the 1980s. Formation The Deltic Preservation Society (DPS) was founded in 1977 following the entry into service of the Class 43 High Speed Train. A group of Class 55 enthusiasts made the decision to join together to ensure that a working locomotive was kept running, forming the DPS to raise funds to this end. By 1982, when the Class 55 was withdrawn, the Society numbered over 1,500, with the result that it was able to purchase two locomotives, D9009/55009 (''Alycidon'') and D9019/55019 (''Royal Highland Fusilier''), from British Rail. These two units were moved immediately from Doncaster Works and put into service on the North Yorkshire Moors Railway. A third locomotive, D9015/55015 (''Tulyar'') was added to the inventory in 1986 when it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltics
{{disambig ...
Deltic may refer to: * Napier Deltic, a diesel engine ** British Rail DP1 ("Deltic") a prototype locomotive built by English Electric fitted with the Deltic Engine ** British Rail Class 55, production locomotives powered by Deltic engines ** British Rail Class 23, "Baby Deltic" production locomotives powered by Deltic engines ** Deltic Preservation Society * Deltic acid, a chemical whose molecular backbone resembles the Greek letter delta (Δ) See also * ''Deltics'', a music album by Chris Rea * Deltoid (other) * Deltate (other) * River delta * Delta (letter) Delta (; uppercase Δ, lowercase δ or 𝛿; el, δέλτα, ''délta'', ) is the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 4. It was derived from the Phoenician letter dalet 𐤃. Letters that come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltic Acid
Deltic acid or dihydroxycyclopropenone is a chemical substance with the chemical formula C3O(OH)2. It can be viewed as a ketone and double Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol of cyclopropene. At room temperature, it is a stable white solid, soluble in diethyl ether, that decomposes (sometimes explosively) between 140 °C and 180 °C, and reacts slowly with water. Derivatives Deltate and salts Deltic acid is considered an acid because it is a particularly acidic Enol#Enediols, enediol, with hydroxyl groups relatively easily losing their protons (p''K''a1 = 2.57, p''K''a2 = 6.03), leaving behind the symmetric deltate anion, . The first deltate salt (chemistry), salts (of lithium and potassium) were described in 1976, also by Eggerding and West. Lithium deltate Li2C3O3 is a water-soluble white solid. Like the other cyclic dianions with formula , the deltate anion has a pronounced aromaticity, aromatic character which contributes to its relative stability. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid (other)
Deltoid (delta-shaped) can refer to: * The deltoid muscle, a muscle in the shoulder * Kite (geometry), also known as a deltoid, a type of quadrilateral * A deltoid curve, a three-cusped hypocycloid * A leaf shape * The deltoid tuberosity, a part of the humerus * The deltoid ligament, a ligament in the ankle See also *Delta (other) Delta commonly refers to: * Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet * River delta, at a river mouth * D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta") * Delta Air Lines, US * Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19 Delta may also r ... *'' The Deltoid Pumpkin Seed'' (1973), a book by John McPhee {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltate (other)
The word deltate, in its most common senses, is derived from the Greek delta (letter), specifically the capital form (Δ). It may mean: * In biology, a triangular leaf shape. * In chemistry, a salt of deltic acid, which has three carbon atoms connected in a triangle. See also * Deltoid (other) * River delta A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition (geology), deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, res ... * Deltic (other) {{disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
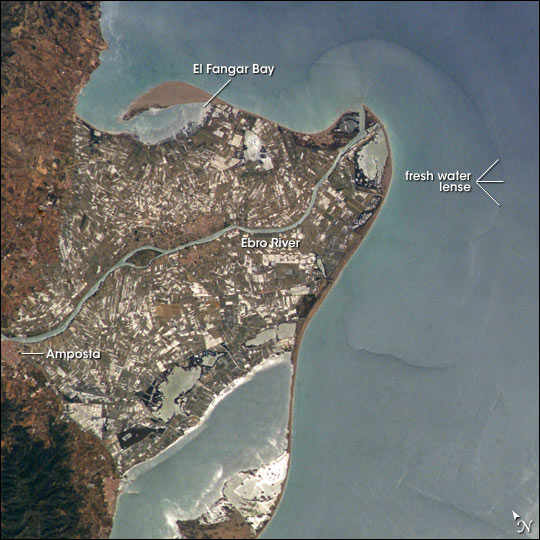
River Delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition (geology), deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or (more rarely) another river that cannot carry away the supplied sediment. It is so named because its triangle shape resembles the Greek letter Delta. The size and shape of a delta is controlled by the balance between watershed processes that supply sediment, and receiving basin processes that redistribute, sequester, and export that sediment. The size, geometry, and location of the receiving basin also plays an important role in delta evolution. River deltas are important in human civilization, as they are major agricultural production centers and population centers. They can provide Coast, coastline defense and can impact drinking water supply. They are also Ecology, ecologically important, with different species' assemblages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_D5907_(8191732824).jpg)
.jpg)
